Plate tectonics vocab
... 7.Tectonic plate- a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle. 8.Continental drift- the hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations. 9.Sea-floor spreading- the process by ...
... 7.Tectonic plate- a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle. 8.Continental drift- the hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations. 9.Sea-floor spreading- the process by ...
Origin and Structure of the Ocean Basins - GMCbiology
... • Plates sliding past each other • Occur at regions between ...
... • Plates sliding past each other • Occur at regions between ...
Timeline for Core Geology
... French Academy of Sciences. 1760 - John Michell suggests earthquakes are caused by one layer of rocks rubbing against another 1776 - James Keir suggests that some rocks might have been formed by the crystallisation of molten lava 1779 - Comte de Buffon speculates that the Earth is older than the 6,0 ...
... French Academy of Sciences. 1760 - John Michell suggests earthquakes are caused by one layer of rocks rubbing against another 1776 - James Keir suggests that some rocks might have been formed by the crystallisation of molten lava 1779 - Comte de Buffon speculates that the Earth is older than the 6,0 ...
Mechanisms of Plate Motion
... basic driving force for plate tectonics Convective Flow – the motion of matter resulting from convection The slow movements of the plates and mantle are driven by the unequal distribution of Earth’s heat from the radioactive decay elements ...
... basic driving force for plate tectonics Convective Flow – the motion of matter resulting from convection The slow movements of the plates and mantle are driven by the unequal distribution of Earth’s heat from the radioactive decay elements ...
The Interior of the Earth
... (The lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates.) The asthenosphere is the semi-liquid layer of upper mantle. (The plates are believed to flow slowly on top of the asthenosphere.) ...
... (The lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates.) The asthenosphere is the semi-liquid layer of upper mantle. (The plates are believed to flow slowly on top of the asthenosphere.) ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #10
... heat). (2) Water is unusual in that it expands when it changes from its liquid state to its solid state, i.e., when it freezes, therefore its solid state (ice) is less dense than its liquid state, so ice floats on water. With most any other common substance the solid state is denser than and sinks i ...
... heat). (2) Water is unusual in that it expands when it changes from its liquid state to its solid state, i.e., when it freezes, therefore its solid state (ice) is less dense than its liquid state, so ice floats on water. With most any other common substance the solid state is denser than and sinks i ...
rocks
... Four major glacier ice advances have occurred in the last 40,000 years. All of Minnesota was covered by ice three times but southeastern Minnesota was not covered during the last ice age – the Wisconsin- 10,000 years ago. Each time glaciers moved south, they pushed sediment like a snowplow pushes sn ...
... Four major glacier ice advances have occurred in the last 40,000 years. All of Minnesota was covered by ice three times but southeastern Minnesota was not covered during the last ice age – the Wisconsin- 10,000 years ago. Each time glaciers moved south, they pushed sediment like a snowplow pushes sn ...
- Catalyst - University of Washington
... of the Isthmus of Panama and development of the Gulf Stream and north Atlantic thermo-haline circulation ,as well as major mountain building in the northern hemisphere. How do you think these events are related? Cenozoic surface water temperature reconstruction (using planktonic foraminifera) of the ...
... of the Isthmus of Panama and development of the Gulf Stream and north Atlantic thermo-haline circulation ,as well as major mountain building in the northern hemisphere. How do you think these events are related? Cenozoic surface water temperature reconstruction (using planktonic foraminifera) of the ...
ScienceChapter6Study..
... How can wind cause erosion? Wind can move loose soil or sand, but it can also act like sandpaper or a sandblaster as it blows these loose particles against rock. What forces coastline changes? Waves beating against the coast. How can gravity and water change Earth’s surface? Causes landslides and mu ...
... How can wind cause erosion? Wind can move loose soil or sand, but it can also act like sandpaper or a sandblaster as it blows these loose particles against rock. What forces coastline changes? Waves beating against the coast. How can gravity and water change Earth’s surface? Causes landslides and mu ...
NAME - Quia
... 3. Which statement best describes the relationship between the total amount of water vapor the atmosphere can hold and the temperature of the atmosphere? A. The amount of water vapor is not related to atmospheric temperature. B. The amount of water vapor increases as the atmospheric temperature incr ...
... 3. Which statement best describes the relationship between the total amount of water vapor the atmosphere can hold and the temperature of the atmosphere? A. The amount of water vapor is not related to atmospheric temperature. B. The amount of water vapor increases as the atmospheric temperature incr ...
Earthquakes
... crustal surface from below with great force & thus is caused severe earth tremor of high magnitude. 2. Faulting- The horizontal & vertical movements caused by endogenetic forces result in the formation of faults & folds which in turn cause iso static disequilibrium in the crustal rocks which ultimat ...
... crustal surface from below with great force & thus is caused severe earth tremor of high magnitude. 2. Faulting- The horizontal & vertical movements caused by endogenetic forces result in the formation of faults & folds which in turn cause iso static disequilibrium in the crustal rocks which ultimat ...
A1,A2 and A3 : Introduction to Geophysics
... ● The outer core has a radius of 3480 km. Composition is believed to be liquid Fe-O or Fe-S alloy. Rapid convection generates the Earth's magnetic field. Outer surface of the core is termed the core-mantle boundary (CMB). ● The inner core has a radius of 1221 km and is composed of solid iron (roughl ...
... ● The outer core has a radius of 3480 km. Composition is believed to be liquid Fe-O or Fe-S alloy. Rapid convection generates the Earth's magnetic field. Outer surface of the core is termed the core-mantle boundary (CMB). ● The inner core has a radius of 1221 km and is composed of solid iron (roughl ...
Final Exam Topics
... accumulation and wastage, Snowline, Flow of a glacier, Glacial erosion: Abrasion, formation of U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys, fjords, fjord lakes, rock-basin lakes, Glacial deposition: Till, end, medial and lateral moraines, outwash material, erratics, Pluvial and glacial lakes, Varve, Signs of ...
... accumulation and wastage, Snowline, Flow of a glacier, Glacial erosion: Abrasion, formation of U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys, fjords, fjord lakes, rock-basin lakes, Glacial deposition: Till, end, medial and lateral moraines, outwash material, erratics, Pluvial and glacial lakes, Varve, Signs of ...
Earth`s layers
... combine with another plate. Sometimes plates slide under another plate to become mantle rock again. The boundaries where plates meet are usually the sites of earthquakes and volcanoes. ...
... combine with another plate. Sometimes plates slide under another plate to become mantle rock again. The boundaries where plates meet are usually the sites of earthquakes and volcanoes. ...
Earthquake Locations/Terminology Elastic Rebound Theory Seismic
... Deformation: A change in the shape ...
... Deformation: A change in the shape ...
Unit 3 study Guide
... 21.) What are the different types of seismic waves? Give information about each type. Body Waves: P-waves – bend slightly when they travel from one layer to another ------ S-waves – cannot travel through liquid material Surface Waves: travel along the surface * They all travel outwards in all direc ...
... 21.) What are the different types of seismic waves? Give information about each type. Body Waves: P-waves – bend slightly when they travel from one layer to another ------ S-waves – cannot travel through liquid material Surface Waves: travel along the surface * They all travel outwards in all direc ...
PP4 8th Grade - Plates Change Position over time
... continents • North America lines up with Scotland ...
... continents • North America lines up with Scotland ...
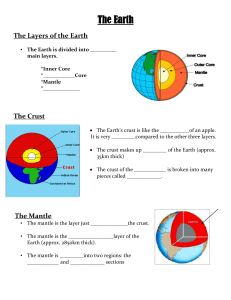
The Earth The Layers of the Earth • The Earth is divided into ______
... puzzle, especially South America and Africa. ...
... puzzle, especially South America and Africa. ...
Lecture #1
... causes the most property damage. • Earthquakes - sudden movements of the Earth’s crust that occur along faults where one rock mass slides past another – Gradual movement - called creep or seismic slip • When friction prevents creep, stress builds up until eventually released with a sudden jerk. • Po ...
... causes the most property damage. • Earthquakes - sudden movements of the Earth’s crust that occur along faults where one rock mass slides past another – Gradual movement - called creep or seismic slip • When friction prevents creep, stress builds up until eventually released with a sudden jerk. • Po ...
Plate Tectonics
... “Plate Tectonics” after mapping the ocean floor. He discovered that the Atlantic gets larger each year. ...
... “Plate Tectonics” after mapping the ocean floor. He discovered that the Atlantic gets larger each year. ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.