* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PP4 8th Grade - Plates Change Position over time
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
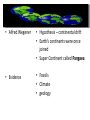
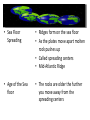
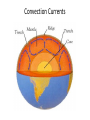
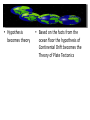
Continents change position over time • Alfred Wegener • Hypothesis – continental drift • Earth’s continents were once joined • Super Continent called Pangaea • Evidence • Fossils • Climate • geology • Fossils • Mesosaurus – found on the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America • Climate • Ice scratches on South America • Tropical plant fossil in Greenland • Geology • Rocks that make up the continents • North America lines up with Scotland • Theory • Evidence and explanations lead to the Theory of Plate Tectonics • Sea Floor Evidence • Sea Floor Spreading • Age of the Sea Floor • Trenches • Sea Floor Spreading • Ridges form on the sea floor • As the plates move apart molten rock pushes up • Called spreading centers • Mid-Atlantic Ridge • Age of the Sea floor • The rocks are older the further you move away from the spreading centers • Ocean Trenches • Deep canyons on the ocean floor • Dense crust is sinking into the asthenosphere • Size of earth • Earth isn’t changing size because at the same rate that new crust is forming (at spreading centers), old crust is being destroyed (at trenches) • How does it happen? • Convection Currents – Hot molten rock rises – Cooled rock sinks – Moves the tectonic plates like a conveyer belt Convection Currents • Hypothesis becomes theory • Based on the facts from the ocean floor the hypothesis of Continental Drift becomes the Theory of Plate Tectonics