* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanisms of Plate Motion
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
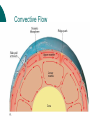
Warm Up 11/26 The Hawaiian Islands were formed when the Pacific Plate moved over ____. a. a hot spot c. the Aleutian Plate b. a subduction zone d. an ocean ridge 2. Strips of alternating magnetic polarities found in rocks in the ocean basins ____. a. conflict with the theory of plate tectonics b. provide evidence that Earth’s magnetic field has never reversed polarity c. indicate changes in Earth’s gravitation field d. provide evidence for seafloor spreading 3. The formation of the Hawaiian Islands is associated with ____. a. a convergent plate boundary c. a transform fault boundary b. a divergent plate boundary d. no plate boundary of any kind Answers: 1) a. 2) d. 3) d. 1. Mechanisms of Plate Motion Chapter 9, Section 5 Causes of Plate Motion Scientists generally agree that convection occurring in the mantle is the basic driving force for plate tectonics Convective Flow – the motion of matter resulting from convection The slow movements of the plates and mantle are driven by the unequal distribution of Earth’s heat from the radioactive decay elements Convective Flow Slab-Pull and Ridge-Push Slab-Pull – old oceanic crust, which is relatively cool and dense, sinks into the asthenosphere and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along Slab-pull is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle Ridge-Push – causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the sides of the oceanic ridge as a result of gravity Mantle Convection Mantle Plumes – hot plumes of rock that are attributed to the upward flowing arms of mantle convection Mantle plumes sometimes show themselves on the surface as hot spots and volcanoes Whole-mantle convection is when slabs of cold oceanic lithosphere descend into the lower mantle, at the same time, hot mantle plumes originating near the mantle-core boundary move heat toward the surface Another model is called the deep-layer model , and can be likened to a lava lamp, heat from Earth’s interior causes the layers to mix and combine in swirling patterns The unequal distribution of heat within Earth causes the thermal convection in the mantle that ultimately drives plate motion Whole-Mantle Convection Deep-Layer Model Assignment Read Chapter 9, Section 5 (pg. 269270) Do 9.5 Assessment #1-5 (pg. 270) Study for the Chapter 9 Quiz!