sci-10-17-1 - St John Brebeuf
... There are 3 layers within the mantle. 1) beneath the crust is the solid outer mantle. Together with the crust, this layer forms the rigid lithosphere 2) Asthenosphere: It is so hot and has so much pressure on it from the lithosphere above that it behaves like a viscous fluid, or soft plastic, even t ...
... There are 3 layers within the mantle. 1) beneath the crust is the solid outer mantle. Together with the crust, this layer forms the rigid lithosphere 2) Asthenosphere: It is so hot and has so much pressure on it from the lithosphere above that it behaves like a viscous fluid, or soft plastic, even t ...
Earthquakes and volcanoes theory - racce
... Earth’s interior consists of several layers: the crust (divided in continental and oceanic), the mantle and the core (internal and external) ...
... Earth’s interior consists of several layers: the crust (divided in continental and oceanic), the mantle and the core (internal and external) ...
Earth*s Structure
... •All continents originally one land mass: Pangea 245 million years ago •Wegener’s Hypothesis: continental driftsingle land mass broke up many times over the years and moved to where they are now ...
... •All continents originally one land mass: Pangea 245 million years ago •Wegener’s Hypothesis: continental driftsingle land mass broke up many times over the years and moved to where they are now ...
Plate Tectonics - Earth and Environmental Sciences
... Plates are constructed by volcanism at divergent margins Plates slide past each other along transform margins Oceanic plates cool, becoming heavier, and sink at convergent margins. Important Question: Are continents new or old? ...
... Plates are constructed by volcanism at divergent margins Plates slide past each other along transform margins Oceanic plates cool, becoming heavier, and sink at convergent margins. Important Question: Are continents new or old? ...
Description Crust Mantle Liquid Outer Core Solid
... elements (K/Rb) as well as lithophile elements, but a few elements predominate, especially in silicate minerals, while some ore metals are rare (Cu/Sn). Because the crust was formed from material extruded from the mantle, it is to be expected that the mantle ...
... elements (K/Rb) as well as lithophile elements, but a few elements predominate, especially in silicate minerals, while some ore metals are rare (Cu/Sn). Because the crust was formed from material extruded from the mantle, it is to be expected that the mantle ...
Introducción a la Geofísica
... c) What is isostacy? What is the primary evidence for it? Why are some areas in North America and Finland not in isostatic equilibrium? What kind of geophysical (gravity) signals do you expect? 3) Briefly describe the mechanical and compositional characteristics of a) Crust ...
... c) What is isostacy? What is the primary evidence for it? Why are some areas in North America and Finland not in isostatic equilibrium? What kind of geophysical (gravity) signals do you expect? 3) Briefly describe the mechanical and compositional characteristics of a) Crust ...
Journey to the Center of Earth
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
Symposium in celebration of the work of Tony Watts University
... Symposium in celebration of the work of Tony Watts University Museum of Natural History, Oxford. September 19 2016 9:00- 9:15Welcome ...
... Symposium in celebration of the work of Tony Watts University Museum of Natural History, Oxford. September 19 2016 9:00- 9:15Welcome ...
20130926123994
... • 220 million years ago… • Pangaea – one large land mass • Africa & South America moved apart • India & Asia collided forming…. ...
... • 220 million years ago… • Pangaea – one large land mass • Africa & South America moved apart • India & Asia collided forming…. ...
Our dynamic earth
... Structure of the earth • At the very centre of the earth is the inner core ,the next layer is the outer core, then the mantle and finally the crust of which has two types ; the oceanic crust and the continental crust. • Both types of crust is 60 miles deep. • The inner core can reach to the level o ...
... Structure of the earth • At the very centre of the earth is the inner core ,the next layer is the outer core, then the mantle and finally the crust of which has two types ; the oceanic crust and the continental crust. • Both types of crust is 60 miles deep. • The inner core can reach to the level o ...
The Solid Earth
... Deepest (and largest) earthquakes associated with subduction zones EQ >100 km can only occur on subducting slab Magnitude 8.5+ only occur at convergent boundaries ...
... Deepest (and largest) earthquakes associated with subduction zones EQ >100 km can only occur on subducting slab Magnitude 8.5+ only occur at convergent boundaries ...
EQ I - Facts, Rebound, & Seismograph
... is derived from the earth’s interior The motions of the earth’s plates are frequently the cause of this rapid energy release ...
... is derived from the earth’s interior The motions of the earth’s plates are frequently the cause of this rapid energy release ...
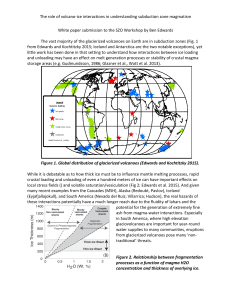
The role of volcano-ice interactions in understanding
... The vast majority of the glacierized volcanoes on Earth are in subduction zones (Fig. 1 from Edwards and Kochtitzky 2015; Iceland and Antarctica are the two notable exceptions), yet little work has been done in that setting to understand how interactions between ice loading and unloading may have ...
... The vast majority of the glacierized volcanoes on Earth are in subduction zones (Fig. 1 from Edwards and Kochtitzky 2015; Iceland and Antarctica are the two notable exceptions), yet little work has been done in that setting to understand how interactions between ice loading and unloading may have ...
Slide 1
... Resistance to flow. • How can viscosity be changed. • 1. Adding Heat • 2. Adding Water • This will become extremely important when studying volcanoes. ...
... Resistance to flow. • How can viscosity be changed. • 1. Adding Heat • 2. Adding Water • This will become extremely important when studying volcanoes. ...
CSCOPE Unit 7 Forces That Change the Earth
... Lithosphere—the solid part of earth that includes the crust and the outer mantle Magma—liquid, molten rock beneath Earth’s surface ...
... Lithosphere—the solid part of earth that includes the crust and the outer mantle Magma—liquid, molten rock beneath Earth’s surface ...
B6 Isostacy B6.1 Airy and Pratt hypotheses
... Total uplift since the ice sheet melted is in excess of 100 m in the centre of Hudson’s Bay. Modern uplift rates are much slower than immediately after the ice sheets melted. These values have been confirmed by gravity measurements made by the GRACE satellite (Tamisiea et al., 2007). Gravity changes ...
... Total uplift since the ice sheet melted is in excess of 100 m in the centre of Hudson’s Bay. Modern uplift rates are much slower than immediately after the ice sheets melted. These values have been confirmed by gravity measurements made by the GRACE satellite (Tamisiea et al., 2007). Gravity changes ...
Section 10.3
... Scientists conclude that Earth formed from the gas and dust that surrounded our young sun. At first, Earth’s surface was made of the same materials as its center. Later, the materials melted and became fluid. More dense materials settle toward the center. Less dense materials rose toward the surface ...
... Scientists conclude that Earth formed from the gas and dust that surrounded our young sun. At first, Earth’s surface was made of the same materials as its center. Later, the materials melted and became fluid. More dense materials settle toward the center. Less dense materials rose toward the surface ...
Earth Science Exam Review 7
... A the total number of organisms alive at the same time in an ecosystem B the minimum number of individuals needed to have balance in an ecosystem C the total number of individuals, living and dead, that have been supported by an ecosystem D the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can sup ...
... A the total number of organisms alive at the same time in an ecosystem B the minimum number of individuals needed to have balance in an ecosystem C the total number of individuals, living and dead, that have been supported by an ecosystem D the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can sup ...
The Theory of Continental Drift (Now Plate Tectonics)
... - It is believed that about 250 million years ago there was one large continent called _____________. - Gradually due to tectonic forces, Pangea broke into northern _____________ and southern _____________________. - It is believed that as the plates continue to move, in about 50 million years, ____ ...
... - It is believed that about 250 million years ago there was one large continent called _____________. - Gradually due to tectonic forces, Pangea broke into northern _____________ and southern _____________________. - It is believed that as the plates continue to move, in about 50 million years, ____ ...
Program prospectus .
... . how does the distribution of C on Earth control/influence surface loading? (e.g., whether H2O is in ice or oceans, what the surface water distribution is, etc.) -solid Earth deformation: . measuring solid Earth deformation in response to loads ..glacial isostatic adjustment observations, etc. . el ...
... . how does the distribution of C on Earth control/influence surface loading? (e.g., whether H2O is in ice or oceans, what the surface water distribution is, etc.) -solid Earth deformation: . measuring solid Earth deformation in response to loads ..glacial isostatic adjustment observations, etc. . el ...
Name: Date: Science 6 Study Guide Vocabulary to know: Climate
... toward the sun get more solar radiation than other areas tilted away from the sun. What is an ice age? A time when large sheets of ice covered Earth’s surface. This happened about 2 million years ago. Ice ages are followed by warm periods called interglacial periods. What is an interglacial period? ...
... toward the sun get more solar radiation than other areas tilted away from the sun. What is an ice age? A time when large sheets of ice covered Earth’s surface. This happened about 2 million years ago. Ice ages are followed by warm periods called interglacial periods. What is an interglacial period? ...
Convection in the mantle is commonly related to plate tectonic
... Mantle Convection & Plate Tectonics: Basic Intro Convection in the mantle is commonly related to plate tectonic processes, but the primary cause is still under debate. Two forces acting on the plates include convective heat rising from deep in the Earth & the strong gravitational pull on the cold su ...
... Mantle Convection & Plate Tectonics: Basic Intro Convection in the mantle is commonly related to plate tectonic processes, but the primary cause is still under debate. Two forces acting on the plates include convective heat rising from deep in the Earth & the strong gravitational pull on the cold su ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.