* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Program prospectus .
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
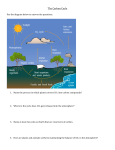
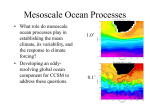
CIDER 2015: Solid Earth Dynamics and Climate --Mantle Interactions with the Hydrosphere & Carbosphere Interactions between the mantle and the major surface reservoirs of water and carbon influence sea level, icesheet dynamics, the volume of the ocean, magma production, the volcanic flux of CO2 to the atmosphere, the loss of carbon via subduction into the mantle. The carbon content and distribution on Earth are important controls on climate, which in turn controls the balance of water and loading processes at Earth’s surface. These loads deform the Earth, sometimes throughout the thickness of the mantle. Mantle-climate interactions over Earth history have led to a planetary surface with a unique H/C ratio. What can we learn about paleoclimate from a better understanding of these climate-solid Earth interactions? What can we learn about the structure and dynamics of the mantle? What can we learn about carbon cycling? CIDER 2015 will involve cross-disciplinary discussions among geophysicists, geochemists, geodynamicists and paleoclimate scientists. Mantle Interactions with the Hydrosphere/Cryosphere -what is "sea level"? -climate and sea level (inference of paleoconditions; prediction of sea-level response to climate variations) . how does the distribution of C on Earth control/influence surface loading? (e.g., whether H2O is in ice or oceans, what the surface water distribution is, etc.) -solid Earth deformation: . measuring solid Earth deformation in response to loads ..glacial isostatic adjustment observations, etc. . elastic and viscous strength of crust and mantle ..how do we know elastic structure, and how well ..how do we know viscosity structure, and how well . load -> deformation kernels ..what is the sensitivity of surface deformation to Earth structure ..(and load position) . mantle flow ..is there such a thing as dynamic topography? . loading history (ice history, water redistribution, tectonics) ..how is ice history reconstructed? what are the limitations? ..coupling between mass distribution in ice, ocean, mantle ..how much does tectonics matter? spreading rates, etc.? -amount of water in the ocean . what controls how much / how fast water moves ice -> ocean? ..climate forcing of temperature: Milankovitch, CO2 amplification ..ice dynamics (incl. geothermal heat flux) . is subduction cycling of water 100% efficient, or is the ocean disappearing into subduction zones? . what are constraints on ocean volume from paleo data? . what are constraints on (changes in) ocean volume from modern observations? Mantle Interactions with the Carbosphere (Continents, Ocean, Atmosphere) -what is the flux of carbon from the atmosphere/continents to the ocean thru time? . weathering flux, river flux, alkalinity, flux from atmosphere . biogenic preservation, inorganic and organic, on the seafloor . how has the CCD changed? . deep biosphere in the oceanic lithosphere . total standing reservoir on ocean floor and spatial distribution . distribution in different oceans, Atlantic v. Pacific v. Tethys v. Iapetus . carbon exchange between the ocean and atmosphere -what is the flux of carbon to the mantle at subduction zones? . subducted flux of carbon (org and inorg) at different margins . how does carbon leave the subducting plate? decarbonation, dehydration, melting . what is the fate of surface carbon in the mantle? diamonds, deep carbon . how has this changed over earth history? -how does carbon in the mantle rise to the surface? . mantle melting with carbon, pervasive carbonated silicate melts in the upper mantle? . what is the flux of CO2 from volcanoes? . how much magmatic CO2 is degassed in the lower crust, stored, released? . what is the diffuse flux of magmatic CO2? . is CO2 petrologically invisible? . is the CO2/Nb ratio constant? . how have MOR spreading rates affected CO2 flux? . LIPS and other major CO2 events in earth history . interactions of magmas and C stored on the seafloor as methane hydrates -what is atmospheric CO2 over time? . paleo records of carbon - ice cores, ocean seds, terrestrial stores, isotopic records . tectonic drivers of climate - orogenesis, continent configuation and effects on atmospheric and ocean circulation . what controls how much CO2 is in the atmosphere over earth history? . how were the early Earth carbon reservoirs different? . why does the Earth's atmosphere and hydrosphere have the H/C ratio it does? -- Connections to the Deep Carbon Observatory (url) . Reservoirs and Fluxes of Carbon . Extreme Chemistry and Physics of Carbon . Deep Life . Deep Energy