Name: Date: Class: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date
... 3. Sedimentary rocks often contain horizontal layers because they are formed by the – a. Deposition of sediment b. Movement of tectonic plates c. Heating of organism. d. Cooling of melted rock. ...
... 3. Sedimentary rocks often contain horizontal layers because they are formed by the – a. Deposition of sediment b. Movement of tectonic plates c. Heating of organism. d. Cooling of melted rock. ...
Internal Structure of the Earth
... Crust – the outer, hardest layer of the lithosphere; continental crust (mostly granite, 2.7 g/cm³, 0-40 km) and oceanic crust (basalt 3.0 g/cm³, 010km) Lithosphere – crust and upper most, solid, rigid portion of the mantle – broken into pieces (0-100 km) ...
... Crust – the outer, hardest layer of the lithosphere; continental crust (mostly granite, 2.7 g/cm³, 0-40 km) and oceanic crust (basalt 3.0 g/cm³, 010km) Lithosphere – crust and upper most, solid, rigid portion of the mantle – broken into pieces (0-100 km) ...
fossil
... EON – largest segment of geologic time ERA PERIOD EPOCH – smallest segment of geologic time ...
... EON – largest segment of geologic time ERA PERIOD EPOCH – smallest segment of geologic time ...
Slide 1
... inner core is a solid section of the Earth and is unattached to the mantle, being suspended by the molten outer core. The inner core is predominantly iron metal with significant amounts of the element nickel. This inner layer in mutual combination with the rotational motion of the Earth creates a dy ...
... inner core is a solid section of the Earth and is unattached to the mantle, being suspended by the molten outer core. The inner core is predominantly iron metal with significant amounts of the element nickel. This inner layer in mutual combination with the rotational motion of the Earth creates a dy ...
Earth`s Layers Notes Printable
... COMPOSITIONAL LAYERS CRUST Outermost, Solid Layer 2: continental and oceanic Composed of; oxygen, silicon and aluminum Oceanic must denser (due to 2x the iron, calcium and magnesium) 30 km MANTLE Hot, slow-flowing rock Convection takes place here Cooler rock sinks, warmer rock rises ...
... COMPOSITIONAL LAYERS CRUST Outermost, Solid Layer 2: continental and oceanic Composed of; oxygen, silicon and aluminum Oceanic must denser (due to 2x the iron, calcium and magnesium) 30 km MANTLE Hot, slow-flowing rock Convection takes place here Cooler rock sinks, warmer rock rises ...
Plate Tectonics
... 3. Rock Clues- Similar rock types of same age found in mountains of England and Eastern U.S. 4. Glacial Clues- Evidence of glaciers exist in areas that are too warm for them now Wegener died in 1930, scientific community made a joke of his work. ...
... 3. Rock Clues- Similar rock types of same age found in mountains of England and Eastern U.S. 4. Glacial Clues- Evidence of glaciers exist in areas that are too warm for them now Wegener died in 1930, scientific community made a joke of his work. ...
earth as a planet
... the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average temperature would be below freezing and Earth would be in a constant global ice age. ...
... the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average temperature would be below freezing and Earth would be in a constant global ice age. ...
Chapter 4 Plate tectonics Review Game
... contain the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field at the time they hardened. The bands move in ...
... contain the direction of the Earth’s magnetic field at the time they hardened. The bands move in ...
Plate Tectonics
... Developed by Alfred Wegner (1900’s) Believed continents were once all combined into one landmass he called Pangaea meaning “All Earth” Continents seemed to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Explained why fossils of the same plants and animals are found on the coast of Africa and South Americ ...
... Developed by Alfred Wegner (1900’s) Believed continents were once all combined into one landmass he called Pangaea meaning “All Earth” Continents seemed to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Explained why fossils of the same plants and animals are found on the coast of Africa and South Americ ...
Sample Questions for Mrs. Igo`s Earth Science Final
... b. where ocean sediments are thickest c. near ocean ridges d. where Earth’s magnetic field changes polarity 50. Many early mapmakers thought Earth’s continents had moved based on ____. a. plate boundary locations c. climatic data b. fossil evidence d. matching coastlines 51. Continental drift was no ...
... b. where ocean sediments are thickest c. near ocean ridges d. where Earth’s magnetic field changes polarity 50. Many early mapmakers thought Earth’s continents had moved based on ____. a. plate boundary locations c. climatic data b. fossil evidence d. matching coastlines 51. Continental drift was no ...
Geology Test
... 19. Base your answer to the question below on the geologic cross section below, which shows a view of rock layers at Earth’s surface. The dashed lines connect points of the same age. Major fossils contained within each rock layer are shown. The valleys are labeled X, Y, and Z. In this region, valle ...
... 19. Base your answer to the question below on the geologic cross section below, which shows a view of rock layers at Earth’s surface. The dashed lines connect points of the same age. Major fossils contained within each rock layer are shown. The valleys are labeled X, Y, and Z. In this region, valle ...
Solar System - MrsAllisonMagee
... • Orbital Period: 365 days • One rotation on its axis every day. • Earth is unique with water being in a liquid state. • Moderate Temperatures due to atmosphere. • Oxygen in atmosphere because of plants. ...
... • Orbital Period: 365 days • One rotation on its axis every day. • Earth is unique with water being in a liquid state. • Moderate Temperatures due to atmosphere. • Oxygen in atmosphere because of plants. ...
The Earth Guiding Questions Minerals Telling Rocks Apart • How
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere • Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones • As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere • Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones • As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... good resource http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html#anchor15039288 ...
... good resource http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html#anchor15039288 ...
EARTH LAYERS PROJECT DUE: Monday September 29, 2014 To
... Pretend that you are about to embark on a journey to the center of the earth. Discuss in detail the type of clothing you will need to wear, the equipment to help you dig your way to the center of the earth. The 8 layers you will go through in their correct order, a brief description and important in ...
... Pretend that you are about to embark on a journey to the center of the earth. Discuss in detail the type of clothing you will need to wear, the equipment to help you dig your way to the center of the earth. The 8 layers you will go through in their correct order, a brief description and important in ...
The Earths interior structure - Lecture 1
... • seismic velocities in the Earth generally increase with depth due to effects of pressure ...
... • seismic velocities in the Earth generally increase with depth due to effects of pressure ...
James Day Assistant Professor Email address:
... Laboratory (SIGL) focusses on better understanding mantle convection by using elements and their isotopes as tracers and employing field observations and direct studies of rocks to understand the history of mantle convection. Mantle convection is also ultimately responsible for creating some economi ...
... Laboratory (SIGL) focusses on better understanding mantle convection by using elements and their isotopes as tracers and employing field observations and direct studies of rocks to understand the history of mantle convection. Mantle convection is also ultimately responsible for creating some economi ...
Introduction to Rocks
... Complete the Ch. 5 Worksheet Write a poem or song about the 3 types of rocks. (Must tell what the three types of rock are and how they are formed. Poem or song must be appropriate and make sense.) Illustrate one of each of the types of rock and write a short paragraph describing what they are ...
... Complete the Ch. 5 Worksheet Write a poem or song about the 3 types of rocks. (Must tell what the three types of rock are and how they are formed. Poem or song must be appropriate and make sense.) Illustrate one of each of the types of rock and write a short paragraph describing what they are ...
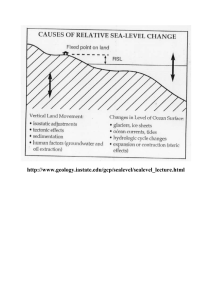
Eustatic Sea Level Change Mechanisms
... Even in these large-scale cases, however, mean sea level can vary from place to place due to local tectonic and hydrographic effects. Several processes that can cause worldwide changes in sea level are listed below. ...
... Even in these large-scale cases, however, mean sea level can vary from place to place due to local tectonic and hydrographic effects. Several processes that can cause worldwide changes in sea level are listed below. ...
Chapter 3.1 - CMenvironmental
... interior to the surface, and can occur on land or in the sea • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean ...
... interior to the surface, and can occur on land or in the sea • Volcanoes are often located near tectonic plate boundaries • The majority of the world’s active volcanoes on land are located along tectonic plate boundaries that surround the Pacific Ocean ...
Physical Properties of Earth`s Layers
... differences in the physical structure of Earth’s interior. In fact, studies of earthquake waves helped scientists discover that Earth’s outer core is liquid. Earthquakes release two types of waves: P waves and S waves. P waves can travel through solids and liquids, but S waves cannot travel through ...
... differences in the physical structure of Earth’s interior. In fact, studies of earthquake waves helped scientists discover that Earth’s outer core is liquid. Earthquakes release two types of waves: P waves and S waves. P waves can travel through solids and liquids, but S waves cannot travel through ...
Earthquakes - TeacherWeb
... Warm up What is an earthquake? What causes them? Where do they occur? ...
... Warm up What is an earthquake? What causes them? Where do they occur? ...
Geology Unit Study Guide - Mr. Ruggiero`s Science 8-2
... Name __________________________________________ ...
... Name __________________________________________ ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.