Check for Understanding
... nickel; because it is able to deflect seismic waves, it must behave as a solid in some fashion. Avg Temperatures of 4,300c • Outer Core- Outer core surrounds the inner core and is believed to be a liquid composed of iron mixed with nickel and trace amounts of lighter elements; Slightly cooler than i ...
... nickel; because it is able to deflect seismic waves, it must behave as a solid in some fashion. Avg Temperatures of 4,300c • Outer Core- Outer core surrounds the inner core and is believed to be a liquid composed of iron mixed with nickel and trace amounts of lighter elements; Slightly cooler than i ...
Environmental Science Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth The Earth as
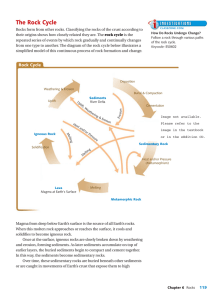
... • Where plates collide, the crust becomes thicker and eventually forms mountain ranges, such as the Himalaya Mountains. Earthquakes • A ___________________________________ is a break in the Earth’s crust along which blocks of the crust slide relative to one another. • When rocks that are under stres ...
... • Where plates collide, the crust becomes thicker and eventually forms mountain ranges, such as the Himalaya Mountains. Earthquakes • A ___________________________________ is a break in the Earth’s crust along which blocks of the crust slide relative to one another. • When rocks that are under stres ...
plate tectonics study guide
... They receive more direct sunlight all year long than the poles do. 3. What causes tides? The gravitational pull of the moon as it revolves around the Earth. 4. What would happen if the gravity between the Sun and Mars increased? The Suns gravity would pull Mars closer and closer to it, eventually co ...
... They receive more direct sunlight all year long than the poles do. 3. What causes tides? The gravitational pull of the moon as it revolves around the Earth. 4. What would happen if the gravity between the Sun and Mars increased? The Suns gravity would pull Mars closer and closer to it, eventually co ...
Pack 15 KS3 Chemistry rock detectives Earth structure
... When geologists talk about plates they mean a large, rigid slab of solid rock. The word tectonics comes from Greek and translates to "to build." If we put these two words together, we get the term plate tectonics and this is the theory geologists use to explain how the Earth's surface is built up. T ...
... When geologists talk about plates they mean a large, rigid slab of solid rock. The word tectonics comes from Greek and translates to "to build." If we put these two words together, we get the term plate tectonics and this is the theory geologists use to explain how the Earth's surface is built up. T ...
Ch. 4 Plate Tectonics This is a satellite image of the San Francisco
... of mostly basalt (A). Basalt is dark, dense, and has a fine texture. Continental crust is mainly made up of granite (B). Granite forms continents, is less dense, large crystals, light colored, and coarsegrained. ...
... of mostly basalt (A). Basalt is dark, dense, and has a fine texture. Continental crust is mainly made up of granite (B). Granite forms continents, is less dense, large crystals, light colored, and coarsegrained. ...
Earth as a Planet
... outer core is less dense than molten iron and probably contains some lighter elements such as sulfur, carbon, or oxygen. The majority of the Earth’s bulk is in the mantle, which is made up of silicate materials like basalt, olivine, and pyroxene. We can sample these materials directly where they are ...
... outer core is less dense than molten iron and probably contains some lighter elements such as sulfur, carbon, or oxygen. The majority of the Earth’s bulk is in the mantle, which is made up of silicate materials like basalt, olivine, and pyroxene. We can sample these materials directly where they are ...
Greek and Latin Roots 1
... Helios – sun god; also called Apollo or Phaethon Heliotrope – (tropos-turn) –plant which turns toward the sun Helium – light gas used in balloons Heliocentric Theory – theory discovered by Nicholas Copernicus, the sun is the center of the universe Aphelion – (apo-away from) – furthest point from the ...
... Helios – sun god; also called Apollo or Phaethon Heliotrope – (tropos-turn) –plant which turns toward the sun Helium – light gas used in balloons Heliocentric Theory – theory discovered by Nicholas Copernicus, the sun is the center of the universe Aphelion – (apo-away from) – furthest point from the ...
General World Cultures Chapter 2- Physical Geography glacier
... months, the sun shines directly on the Northern Hemisphere for more hours of each day. These are the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, these are the winter months, because the South Pole is tilted away from the sun. * During the summer months in the Southern Hemis ...
... months, the sun shines directly on the Northern Hemisphere for more hours of each day. These are the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, these are the winter months, because the South Pole is tilted away from the sun. * During the summer months in the Southern Hemis ...
Earth`s interior - Rochester Community Schools
... seismic waves. Seismic waves are an example of traveling waves, or mechanical waves that travel through a medium. Sound waves are the most familiar example of traveling waves. The speed of sound within a given medium depends on factors such as the density and compressibility of the medium. Seismic w ...
... seismic waves. Seismic waves are an example of traveling waves, or mechanical waves that travel through a medium. Sound waves are the most familiar example of traveling waves. The speed of sound within a given medium depends on factors such as the density and compressibility of the medium. Seismic w ...
Chapter 2: The need for Earth Heritage Conservation
... Much of the early knowledge of the history of the Earth was developed in Britain and many British sites have played a part in the development of now universally-applied principles of geology. These sites have great historical importance. For example, many of the names of periods of geological time a ...
... Much of the early knowledge of the history of the Earth was developed in Britain and many British sites have played a part in the development of now universally-applied principles of geology. These sites have great historical importance. For example, many of the names of periods of geological time a ...
Name: June Proficiency Exam Study Guide 7th Grade Science
... of gases and particles of matter (contains the ozone layer) Geosphere: largest system, solid Earth (Cliff) 7. Give 3 examples of interactions between Earth’s ...
... of gases and particles of matter (contains the ozone layer) Geosphere: largest system, solid Earth (Cliff) 7. Give 3 examples of interactions between Earth’s ...
01 00_Earth_Layers 1
... I CAN… Identify the layers of the earth and explain the different characteristics. ...
... I CAN… Identify the layers of the earth and explain the different characteristics. ...
Plate Tectonic Learning Target Sheet
... thickness of each layer and its composition. Include Asthenosphere and Lithosphere. ...
... thickness of each layer and its composition. Include Asthenosphere and Lithosphere. ...
Core
... • Thinnest layer of the Earth. • Made up of large amounts of silicon and aluminum • Composed of plates on which the continents and oceans rest. These “ride” over molten mantle. • Crust is part of the lithosphere. • Two types of Crust: Oceanic and Continental ...
... • Thinnest layer of the Earth. • Made up of large amounts of silicon and aluminum • Composed of plates on which the continents and oceans rest. These “ride” over molten mantle. • Crust is part of the lithosphere. • Two types of Crust: Oceanic and Continental ...
Deadly quakes help renew the planet
... that plate tectonics rejuvenates the planet." Moreover, geologists say, it demonstrates the Earth's uniqueness. In the decades after the discovery of plate tectonics, space probes among the 70 or so planets and moons that make up the solar system found that the process existed only on Earth — as rev ...
... that plate tectonics rejuvenates the planet." Moreover, geologists say, it demonstrates the Earth's uniqueness. In the decades after the discovery of plate tectonics, space probes among the 70 or so planets and moons that make up the solar system found that the process existed only on Earth — as rev ...
HNRS 228 Astrobiology Chap.4 Geology Bennett et al.
... A a gas is transparent to visible light and opaque to infrared radiation. B a gas is transparent to infrared radiation and opaque to ultraviolet radiation. C ozone is transparent to ultraviolet radiation and opaque to infrared radiation. D methane is transparent to infrared radiation and opaque to v ...
... A a gas is transparent to visible light and opaque to infrared radiation. B a gas is transparent to infrared radiation and opaque to ultraviolet radiation. C ozone is transparent to ultraviolet radiation and opaque to infrared radiation. D methane is transparent to infrared radiation and opaque to v ...
GeomorphReview1 - University of Colorado Denver
... Minerals crystallize from melt, derived from deep within Earth’s crust or mantle – High temperatures, 700° C & more – Crystal size depends on cooling rate • Small = rapid; large = slow (millions of years) ...
... Minerals crystallize from melt, derived from deep within Earth’s crust or mantle – High temperatures, 700° C & more – Crystal size depends on cooling rate • Small = rapid; large = slow (millions of years) ...
Inner Structure of the Earth 3. Mantle
... • When melted, leave behind piles of rock/debris called moraines ...
... • When melted, leave behind piles of rock/debris called moraines ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.