Sea floor spreading and the effects it has on the world In partnership
... New seafloor rock is formed by the ridges under the sea because as the plates spread molten material from the earth’s interior (mantle) rises to the surface and the cool sea water hardens this material into rock. The divergent plates constantly produces new rock from Earth’s mantle. The seafloor clo ...
... New seafloor rock is formed by the ridges under the sea because as the plates spread molten material from the earth’s interior (mantle) rises to the surface and the cool sea water hardens this material into rock. The divergent plates constantly produces new rock from Earth’s mantle. The seafloor clo ...
PNW Geology
... We’re interpreting events & conditions in the past using available evidence – • the rock record observable at the surface • subsurface sampling (wells) & geophysics • rocks in other places that are somehow relevant (age, etc.) • models of how the Earth works (especially plate tectonics) • interpre ...
... We’re interpreting events & conditions in the past using available evidence – • the rock record observable at the surface • subsurface sampling (wells) & geophysics • rocks in other places that are somehow relevant (age, etc.) • models of how the Earth works (especially plate tectonics) • interpre ...
Plate tectonics/boundaries
... 23. Classifying Classify each of the plate boundaries shown on the figure and identify the type of boundary not shown. A- divergent boundary, sea floor spreads from this boundary Convergent boundary- where the continental crust and oceanic crust meet and the oceanic plate is subducted or pushed unde ...
... 23. Classifying Classify each of the plate boundaries shown on the figure and identify the type of boundary not shown. A- divergent boundary, sea floor spreads from this boundary Convergent boundary- where the continental crust and oceanic crust meet and the oceanic plate is subducted or pushed unde ...
Rock and Rock Materials
... • Usually results in exposure of different types of rock materials at surface • Indicative of past and/or present forces • Potential for environmental hazard? • Often associated with natural resources (minerals, petroleum, etc.) • Effects on fluid pathways (as preferential pathways or barriers) ...
... • Usually results in exposure of different types of rock materials at surface • Indicative of past and/or present forces • Potential for environmental hazard? • Often associated with natural resources (minerals, petroleum, etc.) • Effects on fluid pathways (as preferential pathways or barriers) ...
Chapter 8 Volcanoes Section 1, Why Volcanoes Form
... • Rock melts when its temperature increases or when the pressure on the rock decreases. • Water can lower the melting temperature of rock and cause the rock to melt. ...
... • Rock melts when its temperature increases or when the pressure on the rock decreases. • Water can lower the melting temperature of rock and cause the rock to melt. ...
Plate Tectonic, Earthquakes, and Volcanoes Test Review
... We know that the __outer core_ layer is liquid because of _seismic____ waves that are produced by _earthquakes___________. ...
... We know that the __outer core_ layer is liquid because of _seismic____ waves that are produced by _earthquakes___________. ...
CHANGING LANDFORMS
... This activity is meant to illustrate how landforms change as Earth’s plates move. Explain to students that during this unit, they will learn that Earth is covered with plates. The wooden board will represent the plates under the ocean, which are heavy and strong. The rug will represent the plates un ...
... This activity is meant to illustrate how landforms change as Earth’s plates move. Explain to students that during this unit, they will learn that Earth is covered with plates. The wooden board will represent the plates under the ocean, which are heavy and strong. The rug will represent the plates un ...
Origin of Planets Our Solar System as Example General Properties
... – How long does the gas last?! • Are there faster ways to make planets?! • What about planet building for binary stars?! ...
... – How long does the gas last?! • Are there faster ways to make planets?! • What about planet building for binary stars?! ...
Plate Tectonics
... What is plate tectonics? In the 1960s geologists used surveys of the ocean floor to explain continental drift with the theory of plate tectonics. The Earth's surface is made up of a number of large plates that are in constant, slow motion. ...
... What is plate tectonics? In the 1960s geologists used surveys of the ocean floor to explain continental drift with the theory of plate tectonics. The Earth's surface is made up of a number of large plates that are in constant, slow motion. ...
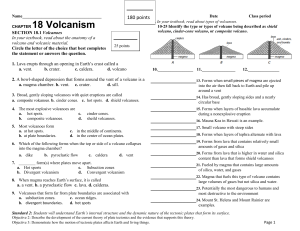
CHAPTER 18 Volcanism
... The greatest challenge for mountain climbers is Mt. Everest, whose peak rises 8,872 meters above sea level. This is the highest mountain in the world, though many mountains around it are almost as high. Mt. Everest is in the Himalayas, a series of massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across ...
... The greatest challenge for mountain climbers is Mt. Everest, whose peak rises 8,872 meters above sea level. This is the highest mountain in the world, though many mountains around it are almost as high. Mt. Everest is in the Himalayas, a series of massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across ...
E8C4_PlateMovement_Final
... Now to come back to the journal question posed in the introduction of this benchmark; If weathering and erosion have been wearing away Earth’s surface for billions of years then why is Earth’s surface not flat? As we have seen, there are both destructive and constructive forces shaping the planet. E ...
... Now to come back to the journal question posed in the introduction of this benchmark; If weathering and erosion have been wearing away Earth’s surface for billions of years then why is Earth’s surface not flat? As we have seen, there are both destructive and constructive forces shaping the planet. E ...
Lesson 4 – A Deeper Look at Plate Movement - Project 3D-VIEW
... continuing to move, riding on the underlying convection cells, and scientists are monitoring their movement. While most plates are only moving a few centimeters a year, some move more quickly than others. ...
... continuing to move, riding on the underlying convection cells, and scientists are monitoring their movement. While most plates are only moving a few centimeters a year, some move more quickly than others. ...
Seafloor Spreading
... In contrast to the youngest or newest seafloor rock found at mid-ocean ridges, the oldest rock is found at or close to trenches. The oldest seafloor rock is “only” about 180 million years old. Many continental rocks are much older than this; the oldest continental rock is over 4 billion years old. T ...
... In contrast to the youngest or newest seafloor rock found at mid-ocean ridges, the oldest rock is found at or close to trenches. The oldest seafloor rock is “only” about 180 million years old. Many continental rocks are much older than this; the oldest continental rock is over 4 billion years old. T ...
here - Crescent School
... similar fit appears across the Pacific. The fit is even more striking when the submerged continental shelves are compared rather than the coastlines. ...
... similar fit appears across the Pacific. The fit is even more striking when the submerged continental shelves are compared rather than the coastlines. ...
semester one review crossword
... Element A pure substance that cannot be broken down Compound A substance made of two or more elements bonded together Cleavage The tendency of some minerals to break along smooth, flat surfaces Deposition The process in which sediment is laid down Rock A naturally occurring solid mixture of one or m ...
... Element A pure substance that cannot be broken down Compound A substance made of two or more elements bonded together Cleavage The tendency of some minerals to break along smooth, flat surfaces Deposition The process in which sediment is laid down Rock A naturally occurring solid mixture of one or m ...
Chapter 2: The Earth`s Mobile Crust Continental Drift
... Formation of elementary particles Gravitational formation of dense regions 12 bya first stars 4.55 bya Rotating cloud of gas from which sun and planets formed, initiated by “supernova” = exploding star – Accretion (Gaining material) – Differentiation (Separating based on density) – Evidence of rocks ...
... Formation of elementary particles Gravitational formation of dense regions 12 bya first stars 4.55 bya Rotating cloud of gas from which sun and planets formed, initiated by “supernova” = exploding star – Accretion (Gaining material) – Differentiation (Separating based on density) – Evidence of rocks ...
Edible Tectonics - KMS 8th Science
... Convergent Plate Boundaries (when one plate is an ocean): • Mega-thrust earthquakes • Violently erupting volcanic mountains (which become islands if they form ...
... Convergent Plate Boundaries (when one plate is an ocean): • Mega-thrust earthquakes • Violently erupting volcanic mountains (which become islands if they form ...
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
... surfaces by friction and impact with other rock materials. This gives the rocks a rounded appearance. This occurs in flowing water, wind actions (i.e. natural sand blasting), and glaciers. 4. Organic Activity – Plant roots can crack rock material by the hydraulic pressures associated with root growt ...
... surfaces by friction and impact with other rock materials. This gives the rocks a rounded appearance. This occurs in flowing water, wind actions (i.e. natural sand blasting), and glaciers. 4. Organic Activity – Plant roots can crack rock material by the hydraulic pressures associated with root growt ...
CV - Blake Dyer
... Research Interests The goal of my research is to better understand how sediments record the Earth-system response to changing boundary conditions. The information stored in the sedimentary rock record offers a broad range of past environmental variability that serves as a powerful baseline to differ ...
... Research Interests The goal of my research is to better understand how sediments record the Earth-system response to changing boundary conditions. The information stored in the sedimentary rock record offers a broad range of past environmental variability that serves as a powerful baseline to differ ...
ch 15 ppt - Walton High School
... Scarring and disruption of land surface Collapse or subsidence of land above underground mines Wind-or water-caused erosion of toxin-laced mining wastes Emission of toxic chemicals into atmosphere Exposure of wildlife to toxic mining wastes stored in holding ponds and leakage of such waste • Contami ...
... Scarring and disruption of land surface Collapse or subsidence of land above underground mines Wind-or water-caused erosion of toxin-laced mining wastes Emission of toxic chemicals into atmosphere Exposure of wildlife to toxic mining wastes stored in holding ponds and leakage of such waste • Contami ...
Salahaddin University College of Science Geology Department
... 50) A specialized form of concordant igneous intrusion that is characterized by a dome in the country rock and a nearly planar floor is called a: A) Lopolith B) Laccolith C) Batholith D) Stock 51)The most common mineral found in igneous rock is: A) Feldspar B) Olivine C) Muscovite D) Fluorite 52) Th ...
... 50) A specialized form of concordant igneous intrusion that is characterized by a dome in the country rock and a nearly planar floor is called a: A) Lopolith B) Laccolith C) Batholith D) Stock 51)The most common mineral found in igneous rock is: A) Feldspar B) Olivine C) Muscovite D) Fluorite 52) Th ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.