* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rock and Rock Materials
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Geoprofessions wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
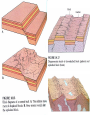
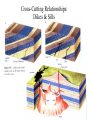
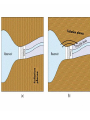
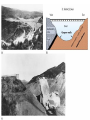
Ch. 2, Part-IIb Geologic Structures Geologic Structures • Generally planar features within, cross-cutting, or disrupting the rock materials/strata (layers) • Important in environmental geology as: – – – – – – – Discontinuities Topography/landforms Indicators of tectonics Implications for natural hazards Structural integrity Planes/zones of weakness Preferrential“pathways” for fluid/contaminants Types of Geologic Structures • • • • Stratification (Layers & Layering) Folding/Tilting Faulting Other Structures – fractures – joints – crosscutting from forceful injections (dikes/sills) Layering/Strata Tilted Layers Indicative of forces causing horizontal layers to be disrupted (tilted) Significance of Layering/Tilting • Basic geologic structure • Planar reference boundaries that define strata (boundaries between/within rock materials) • Implications for landforms/topography? • Potential pathways Folds FOLDS Topography similar to Appalachians Indicative of directed (compressional) forces (past or present) Expressions of directed forces as broken/displaced strata Strike Slip Faulting Dip Slip Faulting Significance of Fault & Folds • Areas of “broken and/or disrupted” crust • Usually associated with topographic features • Usually results in exposure of different types of rock materials at surface • Indicative of past and/or present forces • Potential for environmental hazard? • Often associated with natural resources (minerals, petroleum, etc.) • Effects on fluid pathways (as preferential pathways or barriers) Other Structures • Fractures • Joints • Crosscutting material from forceful injections – Dikes (cross-cuts layering) – Sills (parallel to layering) Cross-Cutting Relationships: Dikes & Sills Jointing Some Environmental Implications of Geologic Structures Layering or Foliation Summary / Review • Building blocks of rock materials: atoms, molecules, minerals, rocks/rock materials • Most abundant minerals are silicates • Basic building block is the silica tetrahedra • Rock properties determined by properties of component materials (minerals) • Three main classes of rocks – Igneous: Formed from molten material – Sedimentary: Clastic, chemical, organic, combinations – Metamorphic: foliated, non-foliated Summary / Review • Rock type provides various types of information – – – – – Environment/setting in which they were formed Tectonic implications Implications for natural hazards Physical, chemical properties Etc. • Geologic Structures: – – – – Layering, tilting Folding Faulting Other types (fractures, jointing, cross-cutting features) • Implications/significance of geologic structures Chapter (Section) Objectives • Review of some of the important mineral and rock types and their environmental significance – Relationships between atoms, minerals, rocks, rock materials – Basic silicate building block(s) – Properties of rocks & minerals – Basic rock types, basis for classification, types of information they tell us • Appreciation/significance of geologic structures – Layering – Folds – Faults – Other structures (joints, dikes/sills, etc.)