* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Edible Tectonics - KMS 8th Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
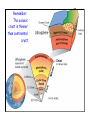
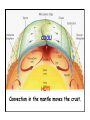
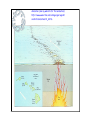
Edible Tectonics: Examining The Theory of Plate Tectonics Earth's Interior What statistics surprise you? Remember: The oceanic crust is thinner than continental crust. COOL! HOT! Convection in the mantle moves the crust. Earth's Plates Move In Three Different Ways: Features & Events Found along Divergent Plate Boundaries: • Rift (on land) or Ridge (underwater) • Small, spewing volcanoes • Small, frequent earthquakes • Small "mountains" • Sea-floor Spreading (how the Atlantic Ocean grew to be the size it is... and it is still getting wider, about 1" per year) • New crust forms • Faults (remember… cracks) Features & Events Found along Convergent Plate Boundaries (when one plate is an ocean): • Mega-thrust earthquakes • Violently erupting volcanic mountains (which become islands if they form underwater) • Subduction (crust is destroyed) • Trenches (underwater) • Faults • Folded mountains (usually volcanic) Features & Events Found along Convergent Plate Boundaries (when both are continental): • Earthquakes • Gigantic, folded mountains • Faults Features & Events Found along Transform Plate Boundaries: • Earthquakes • No igneous rocks • Little or no other geologic features to observe Let's Review the Three Plate Boundaries: Animation (see my website for these animations): http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo2/content/animations/2_1.htm Earth's Plate Boundaries Understanding how plates interact helps to explain why earthquakes and volcanoes happen where they do on Earth with one exception... Sometimes volcanoes are found at the interior of a tectonic plate... Hmmm... Scientists call that a hotspot, which is a weak spot in the middle of a tectonic plate where magma surfaces & a volcano forms; hotspots track the movement of the plate because the "spot" is thought to remain stationary. Challenge: Show a hotspot with the materials you have! Animation (see my website for this animation): http://www.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo2/ content/animations/2_6.htm ` Geological features & events observed at a hotspot: • Small, spewing volcanoes (that can be violent) • Older, extinct volcanoes that have passed over the "hotspot," creating a line leading to the current, active volcano • Small, frequent earthquakes • Small mountains Known Major Worldwide Hotspots It is estimated that there are several in Antarctica not shown.