Free Body Diagram
... A diagram of all the external forces on an object. The object is drawn as is floating in space (“free”). •Only include forces on the diagram, not other vectors such as acceleration or velocity. ...
... A diagram of all the external forces on an object. The object is drawn as is floating in space (“free”). •Only include forces on the diagram, not other vectors such as acceleration or velocity. ...
Physics
... Q.12. Two equal forces have their resultant equal to either . What is the inclination between them? Q.13. State and prove the theorem of parallel axis for moment of inertia. Q.14. State and prove Work – Energy Theorem for variable force . Q.15 A man weighs 70 kg.He stands on a weighing machine in a ...
... Q.12. Two equal forces have their resultant equal to either . What is the inclination between them? Q.13. State and prove the theorem of parallel axis for moment of inertia. Q.14. State and prove Work – Energy Theorem for variable force . Q.15 A man weighs 70 kg.He stands on a weighing machine in a ...
Name - forehandspace
... b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of Motion states a. That people should do unto others as they would have people do unto them. b. That objects in motion will stay in motion until acted upon by ...
... b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of Motion states a. That people should do unto others as they would have people do unto them. b. That objects in motion will stay in motion until acted upon by ...
AP Physics Chapter 5-8 Key Equations and Ideas Forces (pulleys
... position (x = 0) than it was initially. It is negative if the block ends up farther away from x = 0. It is zero if the block ends up in the same initial position. ...
... position (x = 0) than it was initially. It is negative if the block ends up farther away from x = 0. It is zero if the block ends up in the same initial position. ...
Cornell Notes 3.3 Newton`s Laws November 29, 2011 Pages 91
... If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. Forces can be used to increase or decrease the speed of an object, or to change the direction an object is moving. ...
... If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. Forces can be used to increase or decrease the speed of an object, or to change the direction an object is moving. ...
Air Pressure, Forces, and Motion
... of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. acceleration = 0.0 unless the objected is acted on by an unbalanced force ...
... of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. acceleration = 0.0 unless the objected is acted on by an unbalanced force ...
Chap. 2 Force Vectors
... When a rigid body rotates about a fixed axis perpendicular to the plane of the body at point O, the body’s center of gravity G moves in a circular path of radius rG. Thus, the acceleration of point G can be represented by a tangential component (aG)t = rG α and a normal component (aG)n = rG ω2. Sinc ...
... When a rigid body rotates about a fixed axis perpendicular to the plane of the body at point O, the body’s center of gravity G moves in a circular path of radius rG. Thus, the acceleration of point G can be represented by a tangential component (aG)t = rG α and a normal component (aG)n = rG ω2. Sinc ...
Slide 1
... and angular acceleration - they are very different quantities. α is derived in a similar way as translational acceleration – take the time derivative of angular velocity. ...
... and angular acceleration - they are very different quantities. α is derived in a similar way as translational acceleration – take the time derivative of angular velocity. ...
Ch. 9 Rotational Kinematics
... MOI is a property of physics that indicates the relative difference in how easy or difficult it will be to set any object in motion about a defined axis of rotation. MOI is always measured relative to a point of reference. MOI depends on an object’s mass and on its shape. MOI depends on the d ...
... MOI is a property of physics that indicates the relative difference in how easy or difficult it will be to set any object in motion about a defined axis of rotation. MOI is always measured relative to a point of reference. MOI depends on an object’s mass and on its shape. MOI depends on the d ...
Gravitation Force
... All corps maintain their state of motion (rest or constant velocity) if no force is applied Center of Mass /Gravity Average of every position of a body weighted by their mass Point whose motion describes the object motion if all mass was concentrated in a single point Different from geometric center ...
... All corps maintain their state of motion (rest or constant velocity) if no force is applied Center of Mass /Gravity Average of every position of a body weighted by their mass Point whose motion describes the object motion if all mass was concentrated in a single point Different from geometric center ...
review – midterm 2017
... 28. The unit Newton (N) is made up of the three base units. What are they? ...
... 28. The unit Newton (N) is made up of the three base units. What are they? ...
Equilibrium of Concurrent, Coplanar Force Systems Powerpoint
... Where is a body’s mass center? We’ll study that in Module 4. But in this class, the entire body is at rest, so we know that the mass center, wherever it is, has zero acceleration. ...
... Where is a body’s mass center? We’ll study that in Module 4. But in this class, the entire body is at rest, so we know that the mass center, wherever it is, has zero acceleration. ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
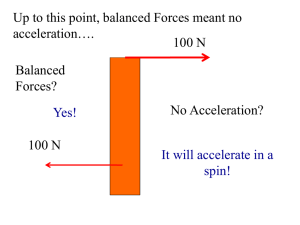
... A net force will cause and object to accelerate in one dimension, but what about rotational acceleration? Would a Force exerted at .5r from the center produce the same rotational acceleration around the center as……. ….. the same force exerted at r from the center? ...
... A net force will cause and object to accelerate in one dimension, but what about rotational acceleration? Would a Force exerted at .5r from the center produce the same rotational acceleration around the center as……. ….. the same force exerted at r from the center? ...