Non-Holonomic Motion Planning
... Open and closed loop controls Integration of ordinary differential equations Dynamics of a particle under force field Rigid body dynamics ...
... Open and closed loop controls Integration of ordinary differential equations Dynamics of a particle under force field Rigid body dynamics ...
slides
... – The diagonal elements are called the principal moments of inertia and are a representation of the mass distribution of a body with respect to an axis of rotation: Iii r 2dm r 2 x, y, z dV r 2 x, y, z dxdydz ...
... – The diagonal elements are called the principal moments of inertia and are a representation of the mass distribution of a body with respect to an axis of rotation: Iii r 2dm r 2 x, y, z dV r 2 x, y, z dxdydz ...
Lecture powerpoint
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
Topics covered in PH111 - Rose
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
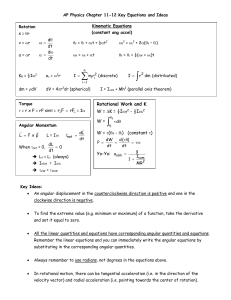
AP Physics Chapter 11-12 Key Equations and Ideas Rotation s = qr
... A body will freely rotate about an axis that always passes through the center of mass of the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
... A body will freely rotate about an axis that always passes through the center of mass of the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
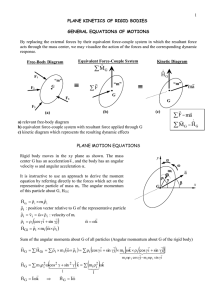
Kinetics: Work, Energy and Power 193 8.6 Spatial (3D) Mechanical
... where q and w are the 3D angular displacement and angular velocities of the rigid body, respectively. Note, even though angular displacement is not a vector, q, represents the angular displacement of the body about each axis. In other words, qx, represents the amount of rotation about the X axis. Th ...
... where q and w are the 3D angular displacement and angular velocities of the rigid body, respectively. Note, even though angular displacement is not a vector, q, represents the angular displacement of the body about each axis. In other words, qx, represents the amount of rotation about the X axis. Th ...
Problem set 13
... of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above formula for α? (c) h3i It can be shown that to take the limit of a rigid rotator (starting from a symmetric top), cos θ must tend to zero faster than I3 . Using this, find the limiting value of α for ...
... of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above formula for α? (c) h3i It can be shown that to take the limit of a rigid rotator (starting from a symmetric top), cos θ must tend to zero faster than I3 . Using this, find the limiting value of α for ...
Problem set 11
... (b) h3i Suppose I1 → I3 so that the symmetric top becomes a spherical top. Based on our study of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above formula for α? 2. h6i Consider force free rotational motion of a symmetric top ( I1 = I2 , I3 ) described ...
... (b) h3i Suppose I1 → I3 so that the symmetric top becomes a spherical top. Based on our study of the spherical top, what do you expect to happen to α? Is this expectation fulfilled by the above formula for α? 2. h6i Consider force free rotational motion of a symmetric top ( I1 = I2 , I3 ) described ...
23. Statics - Galileo and Einstein
... light rigid rod) is mounted on a fixed axle through its center, at an angleθ. It is set in steady rotation. The direction of the angular momentum of the system is: A. Along the axle B. Along the dumbbell rod C. Neither of the above. ...
... light rigid rod) is mounted on a fixed axle through its center, at an angleθ. It is set in steady rotation. The direction of the angular momentum of the system is: A. Along the axle B. Along the dumbbell rod C. Neither of the above. ...
ppt
... per second) points along the axis of rotation (which in this case passes through the point X) Convince yourself this makes sense with the properties of the crossproduct ...
... per second) points along the axis of rotation (which in this case passes through the point X) Convince yourself this makes sense with the properties of the crossproduct ...
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics
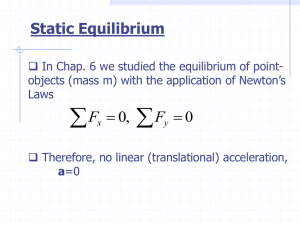
... Static Equilibrium In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...
... Static Equilibrium In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...
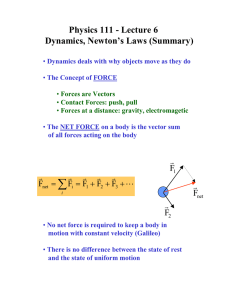
Physics 111 - Lecture 6 Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary)
... • Forces are Vectors • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the body ...
... • Forces are Vectors • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the body ...
PDF
... α21 , are the acceleration of Q2, the angular velocity and acceleration vectors respectively, all of them measured by an observer located at 1. This equation was got by Euler by using a fixed system of principal axes with origin at C2. In that case we have Q = C, and therefore MC = IC α21 + ω 21 × ( ...
... α21 , are the acceleration of Q2, the angular velocity and acceleration vectors respectively, all of them measured by an observer located at 1. This equation was got by Euler by using a fixed system of principal axes with origin at C2. In that case we have Q = C, and therefore MC = IC α21 + ω 21 × ( ...