06 Objectives
... 7. Choose two different objects and compare the sizes of their inertias. How are mass and inertia related? 8. Explain how Newton’s First Law applies to the following demonstrations and situations: a. Hoop and chalk b. Spinning raw and hard boiled eggs c. Penny and eraser on a card (fast and slow mot ...
... 7. Choose two different objects and compare the sizes of their inertias. How are mass and inertia related? 8. Explain how Newton’s First Law applies to the following demonstrations and situations: a. Hoop and chalk b. Spinning raw and hard boiled eggs c. Penny and eraser on a card (fast and slow mot ...
Midterm Examination
... collision the 1 kg body has velocity 3 m/s directed due north and the 2 kg body has velocity 5 m/s directed northeast (i.e. 45o east of due north). The two bodies stick together, forming a body of mass 3 kg. a/ Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the 3 kg body. b/ Is this collision e ...
... collision the 1 kg body has velocity 3 m/s directed due north and the 2 kg body has velocity 5 m/s directed northeast (i.e. 45o east of due north). The two bodies stick together, forming a body of mass 3 kg. a/ Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the 3 kg body. b/ Is this collision e ...
Power point review
... Mass on outside (away from center of rotation) = high rotational inertia (more “laziness”) Ex) Hollow sphere ...
... Mass on outside (away from center of rotation) = high rotational inertia (more “laziness”) Ex) Hollow sphere ...
Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... 1.Draw a free-body diagram, labeling the forces act on it 2. Choose a coordinate system (one axis perpendicular to the circular path followed by the object (radial direction) one axis tangent to the circular path (the tangential, or angular direction) The normal direction, perpendicular to the plane ...
... 1.Draw a free-body diagram, labeling the forces act on it 2. Choose a coordinate system (one axis perpendicular to the circular path followed by the object (radial direction) one axis tangent to the circular path (the tangential, or angular direction) The normal direction, perpendicular to the plane ...
Document
... • Newton’s laws of motion, including an understanding of force, mass and weight, acceleration and inertia applied to sport and physical activities. • The principle of conservation and transfer to momentum, impulse and sequential and/or simultaneous force summation applied to sport and physical activ ...
... • Newton’s laws of motion, including an understanding of force, mass and weight, acceleration and inertia applied to sport and physical activities. • The principle of conservation and transfer to momentum, impulse and sequential and/or simultaneous force summation applied to sport and physical activ ...
Newtons 1st n 2nd law study guide
... 3. State all aspects of Newton’s 1st law. __________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Newton’s 1st law is sometimes called the l ...
... 3. State all aspects of Newton’s 1st law. __________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Newton’s 1st law is sometimes called the l ...
Ch 8
... We wish to locate the point of application of the single force whose magnitude is equal to the weight of the object, and whose effect on the rotation is the same as all the individual particles. ...
... We wish to locate the point of application of the single force whose magnitude is equal to the weight of the object, and whose effect on the rotation is the same as all the individual particles. ...
Vectors and Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... What two forces are acting on him, i.e., what forces does he feel? How are the strengths of the two forces related to each other? Which one of Newton’s laws applies here? forces: ...
... What two forces are acting on him, i.e., what forces does he feel? How are the strengths of the two forces related to each other? Which one of Newton’s laws applies here? forces: ...
Name - Wsfcs
... Velocity has both magnitude and direction, so if an object’s direction changes, it _________________________ even if the speed remains constant. When an object moves in a circular path, it is accelerating because its direction is always changing. This is called ___________________________ __________ ...
... Velocity has both magnitude and direction, so if an object’s direction changes, it _________________________ even if the speed remains constant. When an object moves in a circular path, it is accelerating because its direction is always changing. This is called ___________________________ __________ ...
newton`s laws of motion
... perfect ellipse – hence Kepler’s 1st law.(use calculus) – The fact that force is always directed towards Sun gives Kepler’s 2nd law (conservation of angular momentum) – Newton’s law gives formula for period of orbit ...
... perfect ellipse – hence Kepler’s 1st law.(use calculus) – The fact that force is always directed towards Sun gives Kepler’s 2nd law (conservation of angular momentum) – Newton’s law gives formula for period of orbit ...
L05_projectile
... Free-Fall Trajectories • Only force is gravity (straight down) • Acceleration is straight down with magnitude g • No acceleration in horizontal direction • Vertical and horizontal components of velocity are independent ...
... Free-Fall Trajectories • Only force is gravity (straight down) • Acceleration is straight down with magnitude g • No acceleration in horizontal direction • Vertical and horizontal components of velocity are independent ...
Final Exam Review
... Your final exam grade will be determined by the following criteria: 1. Written examination (70%) 2. Electronic Project (30%) You must take the exam on the specified date scheduled. No make-ups will be allowed unless special circumstances prevail. Question Types Objective (M/C; Fill in the Blanks; TF ...
... Your final exam grade will be determined by the following criteria: 1. Written examination (70%) 2. Electronic Project (30%) You must take the exam on the specified date scheduled. No make-ups will be allowed unless special circumstances prevail. Question Types Objective (M/C; Fill in the Blanks; TF ...
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
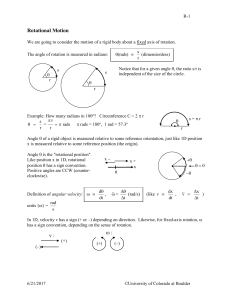
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
Chp+12+Quest REVISED 2012
... 11. Complete the statement; If the mass stays the same, and the force INCREASES then +/acceleration will _____________. So in order to change the motion of a massive object, a ___________ force is needed. 12. Complete the state; If the force stays the same, and the mass INCREASES then acceleration w ...
... 11. Complete the statement; If the mass stays the same, and the force INCREASES then +/acceleration will _____________. So in order to change the motion of a massive object, a ___________ force is needed. 12. Complete the state; If the force stays the same, and the mass INCREASES then acceleration w ...