Homework Chapter 3
... In order for the second ball to reach the same vertical height as the first, the second must have the same initial vertical velocity as the first. Thus, we find ...
... In order for the second ball to reach the same vertical height as the first, the second must have the same initial vertical velocity as the first. Thus, we find ...
Chapter 6 HW 2
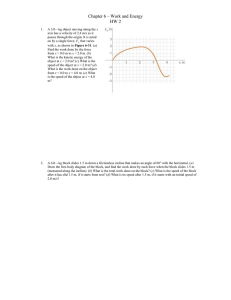
... A 3.0—kg object moving along the x axis has a velocity of 2.4 m/s as it passes through the origin. It is acted on by a single force, Fx, that varies with x, as shown in Figure 6-31. (a) Find the work done by the force from x = 0.0 m to x = 2.0 m. (b) What is the kinetic energy of the object at x = 2 ...
... A 3.0—kg object moving along the x axis has a velocity of 2.4 m/s as it passes through the origin. It is acted on by a single force, Fx, that varies with x, as shown in Figure 6-31. (a) Find the work done by the force from x = 0.0 m to x = 2.0 m. (b) What is the kinetic energy of the object at x = 2 ...
Rotational Motion
... in magnitude to Fhc ,the force on the hanging mass by the cylinder sandwich (via the string) by Newton’s third law. Fhc can be computed by using Newton’s second law on the falling mass. ...
... in magnitude to Fhc ,the force on the hanging mass by the cylinder sandwich (via the string) by Newton’s third law. Fhc can be computed by using Newton’s second law on the falling mass. ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... Linear Speed (V) : The distance travelled by the object during the period (T) is S=2r then; V= S/T V=2r/T V= 2fr Angular Speed (w) : The angle swept by the radius line in unit time is called the angular speed (w). If the angle swept is in time t, then ; w=/t We know that the radius swe ...
... Linear Speed (V) : The distance travelled by the object during the period (T) is S=2r then; V= S/T V=2r/T V= 2fr Angular Speed (w) : The angle swept by the radius line in unit time is called the angular speed (w). If the angle swept is in time t, then ; w=/t We know that the radius swe ...
laws of motion - science8wamogo
... Newton’s 1st Law is also called THE LAW OF INERTIA Inertia is a physical property of matter. It describes an object’s resistance to changes in its motion. Newton’s 1st Law states that all objects have inertia. The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has (and the harder it is to change its ...
... Newton’s 1st Law is also called THE LAW OF INERTIA Inertia is a physical property of matter. It describes an object’s resistance to changes in its motion. Newton’s 1st Law states that all objects have inertia. The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has (and the harder it is to change its ...
Newton`s Laws & Momentum
... and takes place in the direction which the force acts, giving the equation: F = ma • THIRD LAW: The statement used to describe this law is: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... and takes place in the direction which the force acts, giving the equation: F = ma • THIRD LAW: The statement used to describe this law is: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
FINAL EXAM REVIEW GUIDE
... and the conveyor belt’s velocity is 0.55 m/s to the east, what will the can’s velocity be relative to the counter? (ANS: 0.6 m/s @ 24° S of E) ...
... and the conveyor belt’s velocity is 0.55 m/s to the east, what will the can’s velocity be relative to the counter? (ANS: 0.6 m/s @ 24° S of E) ...
Chapter 7: Using Vectors: Motion and Force
... 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
... 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
Practice Problems Semester 1 Exam 1. Express the measurements
... 24. A 1150 kg car is applying a 2,500 N force to accelerate it forward. The force of friction the wheels apply to the road is 500. N. A. Draw the free body diagram, identifying the forces. B. Determine the size of all the forces and label them on the drawing. C. Determine the net force on the object ...
... 24. A 1150 kg car is applying a 2,500 N force to accelerate it forward. The force of friction the wheels apply to the road is 500. N. A. Draw the free body diagram, identifying the forces. B. Determine the size of all the forces and label them on the drawing. C. Determine the net force on the object ...
and y - Cloudfront.net
... 4. Calculate the range of a projectile given the initial velocity vector. 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
... 4. Calculate the range of a projectile given the initial velocity vector. 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
Ph211_CH6_worksheet
... d) What is the magnitude of the normal force at the angle determined in part c? ...
... d) What is the magnitude of the normal force at the angle determined in part c? ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... According to Newton’s first law of motion, what will a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced force do? Which of Newton’s laws explain inertia? What explains the tendency of all objects to resist any change in motion? What is a measure of inertia? What causes a person to fall backward a ...
... According to Newton’s first law of motion, what will a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced force do? Which of Newton’s laws explain inertia? What explains the tendency of all objects to resist any change in motion? What is a measure of inertia? What causes a person to fall backward a ...
NJASK Review – Answer Key
... 9. terminal velocity 10. gravity Fill-In: 11. friction 12. Bernoulli’s Principle 13. Terminal velocity 14. gravity 15. gravity 16. friction Ch. 13 Challenge Matching: 1. velocity 2. acceleration 3. momentum 4. Newton 5. motion 6. inertia 7. speed Fill-In: 8. speed 9. inertia 10. action force 11. ine ...
... 9. terminal velocity 10. gravity Fill-In: 11. friction 12. Bernoulli’s Principle 13. Terminal velocity 14. gravity 15. gravity 16. friction Ch. 13 Challenge Matching: 1. velocity 2. acceleration 3. momentum 4. Newton 5. motion 6. inertia 7. speed Fill-In: 8. speed 9. inertia 10. action force 11. ine ...
File
... 1. An object near the surface of the earth with a weight of 100 newtons is accelerated horizontally at 4 m/s2. What is the net force on the object? (A) 25 N (B) 40 N (C) 250 N (D) 400 N (E) 2500 N 2. A 50-kg student stands on a scale in an elevator. At the instant the elevator has a downward acceler ...
... 1. An object near the surface of the earth with a weight of 100 newtons is accelerated horizontally at 4 m/s2. What is the net force on the object? (A) 25 N (B) 40 N (C) 250 N (D) 400 N (E) 2500 N 2. A 50-kg student stands on a scale in an elevator. At the instant the elevator has a downward acceler ...
SHM Dynamics WS (honors)
... mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
... mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
Forces and The Laws of Motion Newton`s Second and Third Laws
... Action-Reaction Forces • The action and reaction forces occur at exactly the same time and because they coexist, either force can be called the action or the reaction • Action and reaction forces each act on different objects – Although the action-reaction forces are equal and opposite, either obje ...
... Action-Reaction Forces • The action and reaction forces occur at exactly the same time and because they coexist, either force can be called the action or the reaction • Action and reaction forces each act on different objects – Although the action-reaction forces are equal and opposite, either obje ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Unbalanced forces can also be exerted in the same direction. For example, imagine that your family's car breaks down on the road and you have to push it into a parking lot. If you and your brother or sister both push on the car, the resulting force on the car will be the sum of your forces and of co ...
... Unbalanced forces can also be exerted in the same direction. For example, imagine that your family's car breaks down on the road and you have to push it into a parking lot. If you and your brother or sister both push on the car, the resulting force on the car will be the sum of your forces and of co ...
Sample Paper Class IX SECTION A
... Let t be the time taken by the ball to reach the height 122.5 m, then according to the equation of motion: V= u+at We get, 0= 49+t × (9.8) ...
... Let t be the time taken by the ball to reach the height 122.5 m, then according to the equation of motion: V= u+at We get, 0= 49+t × (9.8) ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... These pumpkins will not move unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...
... These pumpkins will not move unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...