Newton intro with hover pucks
... – Applied (push or pull exerted by an outside object) • Remember we need an unbalanced forced to cause a change in motion. • The motion will not change if the forces acting on it are ZERO! • Tendency of an object to maintain its present motion or no motion is INERTIA ...
... – Applied (push or pull exerted by an outside object) • Remember we need an unbalanced forced to cause a change in motion. • The motion will not change if the forces acting on it are ZERO! • Tendency of an object to maintain its present motion or no motion is INERTIA ...
2 - ScienceScene
... of- war. Realcontexts: Changing the direction--changing the direction of a billiard ball, bus turning a corner; changing the speed--car speeding up, a rolling ball slowing down, magnets changing the motion of objects, walking, swimming, jumping, rocket motion, objects resting on a table, tug- of- wa ...
... of- war. Realcontexts: Changing the direction--changing the direction of a billiard ball, bus turning a corner; changing the speed--car speeding up, a rolling ball slowing down, magnets changing the motion of objects, walking, swimming, jumping, rocket motion, objects resting on a table, tug- of- wa ...
Summary of Chapters 1-3 Equations of motion for a uniformly acclerating object
... or a big spaceship (air-track unnecessary) These springs can be taken anywhere in the universe and used to measure the mass of any cart. Also, the stretching of these springs can be used to define the unit of force. ...
... or a big spaceship (air-track unnecessary) These springs can be taken anywhere in the universe and used to measure the mass of any cart. Also, the stretching of these springs can be used to define the unit of force. ...
m/s
... that act between any two masses. “Every object in the universe attracts every other object.” – Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation. ...
... that act between any two masses. “Every object in the universe attracts every other object.” – Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation. ...
Chapter 8
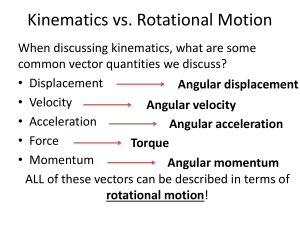
... Moment of Inertia • Remember back to Newton’s 1st Law of Motion, Objects tend to stay in motion, or at rest, unless acted upon by a net force. • Notice it says Motion, but does not specify whether the motion is linear or rotational. • We also said that Newton’s 1st Law describes the term inertia, o ...
... Moment of Inertia • Remember back to Newton’s 1st Law of Motion, Objects tend to stay in motion, or at rest, unless acted upon by a net force. • Notice it says Motion, but does not specify whether the motion is linear or rotational. • We also said that Newton’s 1st Law describes the term inertia, o ...
Newton`s Second Law Pre E-‐lab Lesson Plan (45
... them to think about the force being applied to them by the slinky, and how the different masses of the cars will affect the distance they are pulled. Let go of the cars and allow the slinky ...
... them to think about the force being applied to them by the slinky, and how the different masses of the cars will affect the distance they are pulled. Let go of the cars and allow the slinky ...
Components of vectors
... It is often necessary to find the components of a vector, usually in two perpendicular directions. This process is called the resolution of a vector. What you are really doing is finding the effectiveness of the vector along a specified direction. The component of a vector along any direction is the ...
... It is often necessary to find the components of a vector, usually in two perpendicular directions. This process is called the resolution of a vector. What you are really doing is finding the effectiveness of the vector along a specified direction. The component of a vector along any direction is the ...
Newton`s Laws - Dr. Robert MacKay
... • Newton’s Universal Law of Gravity Newton came up with these laws in about 1670 to describe the motion of the planets around the sun. These fairly simple rules explained planetary motion extremely well. This was a problem scientists had struggled with for thousands of years with no success. These s ...
... • Newton’s Universal Law of Gravity Newton came up with these laws in about 1670 to describe the motion of the planets around the sun. These fairly simple rules explained planetary motion extremely well. This was a problem scientists had struggled with for thousands of years with no success. These s ...
Name - North Salem Schools Teachers Module
... If additional objects are involved, draw separate free body diagrams for each object ...
... If additional objects are involved, draw separate free body diagrams for each object ...
7. On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is only about 1/6 of
... and not in another? If so, give a specific example. You are riding in an elevator. Describe two situations in which your apparent weight is greater than your true weight. For each case, identify all forces acting on the object and draw a free body diagram. Then, identify the forces that cause the ac ...
... and not in another? If so, give a specific example. You are riding in an elevator. Describe two situations in which your apparent weight is greater than your true weight. For each case, identify all forces acting on the object and draw a free body diagram. Then, identify the forces that cause the ac ...
Some Facts about the Motion?
... It is the total force or net force ftable 2 N (to the left) that determines an object’s acceleration. Fnet 10 N 2 N If there is more than one 8 N (to the right) vector acting on an object, the forces are added together as F 8N vectors, taking into account a net m 5 kg their directions. ...
... It is the total force or net force ftable 2 N (to the left) that determines an object’s acceleration. Fnet 10 N 2 N If there is more than one 8 N (to the right) vector acting on an object, the forces are added together as F 8N vectors, taking into account a net m 5 kg their directions. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motionpowerpoint
... kg car to accelerate at 2 m/s2? F=m a = 1000 kg x 2 m/s2 = 2000 kg-m/s2 = 2N ...
... kg car to accelerate at 2 m/s2? F=m a = 1000 kg x 2 m/s2 = 2000 kg-m/s2 = 2N ...
Name
... 24. According to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, force depends on a. mass and direction c. friction and gravity b. inertia d. mass and acceleration ...
... 24. According to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, force depends on a. mass and direction c. friction and gravity b. inertia d. mass and acceleration ...
I. Motion - Peach County Schools
... gravity, weight, friction 1. Net force- the force that results from combining all the forces exerted on an object. ...
... gravity, weight, friction 1. Net force- the force that results from combining all the forces exerted on an object. ...























