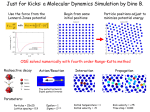
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORKSHEET – Dynamics 2 - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
Survey
Document related concepts
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
WORKSHEET – Dynamics 2 1. A physics book sits at rest on a table. You give it a brief push, so that the book starts to slide. It slides a short distance and then stops again. a) Why was it motionless before being pushed? b) Why did it move when it was pushed? c) Why did it come to a stop? d) Under what conditions would have kept moving? (List several possibilities) 2. The force of gravity is a mutual attraction between objects. A falling rock, for example, is attracted to earth, and so accelerates towards it. Does the earth attract to the falling rock? 3. A cat has a mass of 4 kg. What would be its mass on the moon? 4. When you are riding in a car, most people claim that they have the sensation of being pushed backwards when the car speeds up, and being pushed forwards when the car slows down. What is really going on? 5. Complete this sentence: If there is no net force acting on an object, then its’ velocity must be __. 6. If there is a net force acting on an object, then Newton’s second law says that it must be accelerating. Why is it that my desk is not accelerating? There is a force of gravity acting on it. 7. While jumping on a trampoline, each time you make contact with the surface of the trampoline there are forces acting between you and it. Describe the force that each (you and the trampoline surface) experience, and the effect of these forces. 8. A 10 kg briefcase is placed on a scale (which indicates forces in newtons). The briefcase and scale are inside an elevator. What does the scale read while the elevator is a) at rest b) accelerating upwards at 2 m/s2 c) accelerating downwards at 2 m/s2 d) moving upwards with constant velocity of 2 m/s 9. An airplane has a mass of 3.1 × 104 kg, and the engine on takeoff provides an applied force of 3.7 × 104 N [U]. Draw a free body diagram for the airplane, and find its acceleration. 10. Which of the four “fundamental” forces is responsible for the following: a) makes paint stick to the wall b) makes the moon go around the earth c) enables a car’s brakes to stop a car d) holds the nucleus together e) is linked to radioactivity 11. A book has a mass of 2 kg on earth. a) What is the weight of the book on the earth? b) What is the mass of the book on the moon? c) What is the weight of the book on the moon knowing that ‘g’ on the moon is equal to 1.6 m/s2? 12. Whiplash is a serious injury that can occur if you are in a car accident - especially if you are hit from behind. Most people claim that your head is snapped backwards in such an injury - what is the physics of what is really happening? 13. Describe how Newton’s 3rd Law can be applied to the shooting of a gun. 14. A car has a mass of 1200 kg. It accelerates at 3 m/s2 [E]. What is the net force acting on the car? 15. A bicycle is moving at 10 m/s. The rider locks up the tires and skids to a stop. How long does it take to stop, if the coefficient of friction acting between the tires and road is 0.3? 16. While investigating a vehicle accident involving a truck hitting a parked car, the forensics department of the police determine that the truck was moving at 10 m/s on impact. There are also skid marks from the truck 30 m long leading to the point of the collision. The coefficient of friction between the tires and the road is determined to be 0.75. How fast was the truck going when the brakes were slammed on? If the speed limit is 60 km/h ... was the truck speeding? 17. A 75 kg person stands on a bathroom scale which measures forces in newtons. The person and scale are inside of an elevator. What value does the scale read if the elevator is a) not moving b) accelerating upwards at 3 m/s2 c) accelerating downwards at 3 m/s2 d) moving upwards with constant velocity of 3 m/s 18. A 150 kg log has a rope tied to. The log is dragged at constant velocity of 1.5 m/s by the rope which is horizontal. What is the tension in the rope? 19. A 2.3 kg model rocket sits on its launch pad. What is the acceleration of the rocket, if the rocket engine applies a force of 15 N upwards? 20. How much force would the engine of the above problem need to supply in order to accelerate the rocket upwards at 15 m/s2? 21. A 65 kg swimmer steps off of a platform 10 m above the water. She drops down to the water, and when she hits the water, she reaches 2 m below the surface before coming to a stop. a) Find her velocity when she reaches the water surface b) Sketch a v-t graph for this motion c) How much force did the water exert on her while it brought her to a stop? (assume it was constant)