Lesson 25 notes – Analysing circular motion - science
... the force (down) due to gravitational attraction can be written F = mg; ...
... the force (down) due to gravitational attraction can be written F = mg; ...
Projectile Motion-ppt
... 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
... 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three forces. 6. Calculate the acceleration on an inclined plane when given the angle of incline. ...
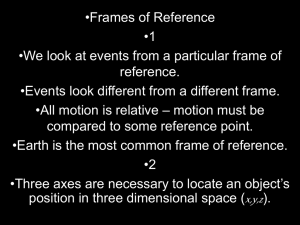
Frames of Reference
... •Fictitious forces explains motion in a rotating (non-inertial) frame of reference. •From fixed frame no unbalanced force is seen. •Objects moving in a circle have an acceleration toward the center called centripetal force. •Centrifugal force is the fictitious force that balances this by being exert ...
... •Fictitious forces explains motion in a rotating (non-inertial) frame of reference. •From fixed frame no unbalanced force is seen. •Objects moving in a circle have an acceleration toward the center called centripetal force. •Centrifugal force is the fictitious force that balances this by being exert ...
Force and Motion
... Lamont wants to move a 4,800 gram box from the floor to a shelf directly above the box. It takes Lamont 8 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 0.4 meters from the ground. It takes 12 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 1.2 meters off the ground. How much more work in joules is required ...
... Lamont wants to move a 4,800 gram box from the floor to a shelf directly above the box. It takes Lamont 8 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 0.4 meters from the ground. It takes 12 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 1.2 meters off the ground. How much more work in joules is required ...
Motion, Forces, and Simple Machines
... 2. instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any instant of time. 3. Velocity is the speed of an object and its direction of motion 4. acceleration describes how velocity changes with time Formula: A = change in speed/time ...
... 2. instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any instant of time. 3. Velocity is the speed of an object and its direction of motion 4. acceleration describes how velocity changes with time Formula: A = change in speed/time ...
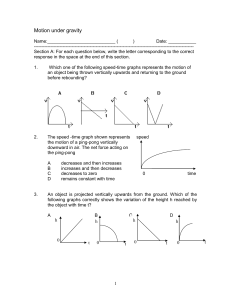
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
motion
... 9.The force constant of a spring is 60N/m.If abullet of 30gm is shot by the gun ,so that its spring is compressed by 12cm. calculate the velocity of the ball?[5.36m/s] 10.A gardner moves a lawn roller through a distance of 100m with a force of 50N .Calculate his wages, if he is to be paid 10 paise f ...
... 9.The force constant of a spring is 60N/m.If abullet of 30gm is shot by the gun ,so that its spring is compressed by 12cm. calculate the velocity of the ball?[5.36m/s] 10.A gardner moves a lawn roller through a distance of 100m with a force of 50N .Calculate his wages, if he is to be paid 10 paise f ...
physics: semester 1 final review
... Write this Law as a mathematical equation: What would happen to the acceleration of the sled if the force pushing it were tripled? 43. An unbalanced force on an object produces a change in its _________________ (more than one answer possible) 44. Two balls collide. What two basic conservation laws o ...
... Write this Law as a mathematical equation: What would happen to the acceleration of the sled if the force pushing it were tripled? 43. An unbalanced force on an object produces a change in its _________________ (more than one answer possible) 44. Two balls collide. What two basic conservation laws o ...
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
... come from? – Gravity acting on the object • Remember the vertical distance that an object falls beneath the ideal straight line is the same as the distance it would travel in a free fall So, we can use the distance equation we had for objects in a freefall Δy = ½(g)t2 Since ‘g’ is constant (10.0m/s2 ...
... come from? – Gravity acting on the object • Remember the vertical distance that an object falls beneath the ideal straight line is the same as the distance it would travel in a free fall So, we can use the distance equation we had for objects in a freefall Δy = ½(g)t2 Since ‘g’ is constant (10.0m/s2 ...
Standard Physics Final Exam Review Guide
... 2) What is the acceleration of a speed boat that goes from 0 to 45 mi/hr in 30 seconds? 3) A car speeds up from a velocity of 8 m/s to a velocity of 12 m/s in 4 seconds. What is the car’s acceleration? ...
... 2) What is the acceleration of a speed boat that goes from 0 to 45 mi/hr in 30 seconds? 3) A car speeds up from a velocity of 8 m/s to a velocity of 12 m/s in 4 seconds. What is the car’s acceleration? ...
Part IV
... • Inertia The tendency of an object to maintain its state of rest or motion. • MASS A measure of the inertia of a mass. – The quantity of matter in an object. – As we already discussed, the SI System quantifies mass by having a standard mass = Standard Kilogram (kg). (Similar to standards for le ...
... • Inertia The tendency of an object to maintain its state of rest or motion. • MASS A measure of the inertia of a mass. – The quantity of matter in an object. – As we already discussed, the SI System quantifies mass by having a standard mass = Standard Kilogram (kg). (Similar to standards for le ...
UNIT-07
... [c] F in eq.[1] is the net force on m, F = F1+ F2+ F3…… , where F1, F2, F3, etc. are the individual forces acting on m. To emphasize this point, sometimes the second law (eq.[1]) is written as: ...
... [c] F in eq.[1] is the net force on m, F = F1+ F2+ F3…… , where F1, F2, F3, etc. are the individual forces acting on m. To emphasize this point, sometimes the second law (eq.[1]) is written as: ...
AP Physics C I.E - Midway ISD / Home Page
... later, its angular velocity is 5.0 rad/s. Calculate the angular displacement during this time interval. ...
... later, its angular velocity is 5.0 rad/s. Calculate the angular displacement during this time interval. ...
File
... What is force is needed to start the sled moving? What force is needed to keep the sled moving at a constant velocity? Once moving, what total force must be applied to cause the sled to accelerate 3.0m/s2? ...
... What is force is needed to start the sled moving? What force is needed to keep the sled moving at a constant velocity? Once moving, what total force must be applied to cause the sled to accelerate 3.0m/s2? ...
Slide 1
... UAB = -W ∆y = -W (yB – yA) = WyA - WyB The work done on the particle does not depend on the path taken between points A and B, it only depends on the heights of A and B above a datum at y=0. This function Wy is called the potential energy of the body with respect to gravity, or Vg. Thus, UAB = VgA - ...
... UAB = -W ∆y = -W (yB – yA) = WyA - WyB The work done on the particle does not depend on the path taken between points A and B, it only depends on the heights of A and B above a datum at y=0. This function Wy is called the potential energy of the body with respect to gravity, or Vg. Thus, UAB = VgA - ...