Uniform Circular Motion
... direction.1 For the body to constantly change direction, rotate around an axis, and keep a constant speed the force must also be perpendicular to the direction of the velocity at all times.1 The forces direction must be towards the axis, essentially pulling the body inwards. As the velocity is alway ...
... direction.1 For the body to constantly change direction, rotate around an axis, and keep a constant speed the force must also be perpendicular to the direction of the velocity at all times.1 The forces direction must be towards the axis, essentially pulling the body inwards. As the velocity is alway ...
Balanced Forces
... – Weight can ____________________with a change in ____________________. – Mass: A measure of how much ____________________ an object has – You know an object has mass because it has ____________________ – SI Unit = ____________________ Centripetal Force Centripetal Force: The ___________________ ...
... – Weight can ____________________with a change in ____________________. – Mass: A measure of how much ____________________ an object has – You know an object has mass because it has ____________________ – SI Unit = ____________________ Centripetal Force Centripetal Force: The ___________________ ...
m/s
... 1. If a car travels west 75 kilometers takes a uturn and travels back east 25 kilometers what is the car’s final displacement? 50 km west ...
... 1. If a car travels west 75 kilometers takes a uturn and travels back east 25 kilometers what is the car’s final displacement? 50 km west ...
DYNAMICS
... • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some dumb guy who got hit on the head with an apple. ...
... • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some dumb guy who got hit on the head with an apple. ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
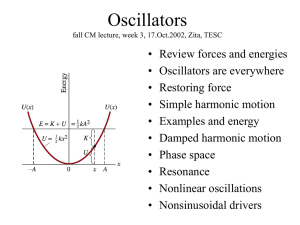
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic eq ...
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic eq ...
Chapter5ReviewProblem
... 1. A person is twirling a ball in a vertical circle with the center of rotation at his side, 2 meters above the ground. If the length of the string holding the ball is 1meter and the time for one revolution is 0.67s and the mass of the ball is 100 g… What is the maximum force on the string? Where do ...
... 1. A person is twirling a ball in a vertical circle with the center of rotation at his side, 2 meters above the ground. If the length of the string holding the ball is 1meter and the time for one revolution is 0.67s and the mass of the ball is 100 g… What is the maximum force on the string? Where do ...
Name
... b. A soccer ball accelerates more than a bowling ball when thrown with the same force. c. A magician pulls a tablecloth out from under dishes and glasses on a table without disturbing them. d. A student leaves a pencil on a desk and the pencil stays in the same spot until another student picks it up ...
... b. A soccer ball accelerates more than a bowling ball when thrown with the same force. c. A magician pulls a tablecloth out from under dishes and glasses on a table without disturbing them. d. A student leaves a pencil on a desk and the pencil stays in the same spot until another student picks it up ...
July
... .Determine the minimum value of P , for which both halves of the cylinder will be in equilibrium on a horizontal plane. ...
... .Determine the minimum value of P , for which both halves of the cylinder will be in equilibrium on a horizontal plane. ...
Document
... will stay in motion and an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. In the car your body was in motion, traveling at the same speed as the car. When the car stopped, your body stayed in motion. If you were not wearing a seatbelt and you were traveling very fast, your ...
... will stay in motion and an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. In the car your body was in motion, traveling at the same speed as the car. When the car stopped, your body stayed in motion. If you were not wearing a seatbelt and you were traveling very fast, your ...
Newtons 2nd law
... • If you are constantly accelerating, there must be a force acting on you the entire time. • The force exerted is the centripetal force and always points toward the center of the circle. • In circular motion the centripetal force is always perpendicular to the motion. ...
... • If you are constantly accelerating, there must be a force acting on you the entire time. • The force exerted is the centripetal force and always points toward the center of the circle. • In circular motion the centripetal force is always perpendicular to the motion. ...
Force
... 1. Describe what a force is in your own words or give an example and explain your answer. 2. Calculate Net Force: Two students push a box in the same direction, and one pushes in the opposite direction. What is the net force on the box if each pushes with a force of 50N? Draw a sketch and solve the ...
... 1. Describe what a force is in your own words or give an example and explain your answer. 2. Calculate Net Force: Two students push a box in the same direction, and one pushes in the opposite direction. What is the net force on the box if each pushes with a force of 50N? Draw a sketch and solve the ...
Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 1 – Due Oct 6,... v. 2: updated Oct 1, 2006
... A of the notes useful. This problem answers the question asked in the lecture notes, “Do there exist position-dependent forces for which the work is not path-independent?” You can construct them mathematically, but it’s hard to think of physical examples. 6. (106a/196a) Calculate the gravitational p ...
... A of the notes useful. This problem answers the question asked in the lecture notes, “Do there exist position-dependent forces for which the work is not path-independent?” You can construct them mathematically, but it’s hard to think of physical examples. 6. (106a/196a) Calculate the gravitational p ...
p250t2f03
... ___ 6. A baseball bat strikes a pitched baseball and sends it flying. Which has the greater magnitude of momentum change during the impact? (A) the ball. (B) the bat. (C) they both have the same magnitude momentum change. (D) it depends upon the speed of the ball. (E) it depends upon the team, the f ...
... ___ 6. A baseball bat strikes a pitched baseball and sends it flying. Which has the greater magnitude of momentum change during the impact? (A) the ball. (B) the bat. (C) they both have the same magnitude momentum change. (D) it depends upon the speed of the ball. (E) it depends upon the team, the f ...
Chapter 8 Practice Test Name 1. A 30 kg object is set into orbit 7.5 x
... D. As a safety margin, the designer plans to make the rollercoaster go at twice the critical speed (twice as fast as you just calculated). At that speed, calculate the centripetal force on the rollercoaster. E. At that safer speed, calculate the normal force the track needs to provide at the highest ...
... D. As a safety margin, the designer plans to make the rollercoaster go at twice the critical speed (twice as fast as you just calculated). At that speed, calculate the centripetal force on the rollercoaster. E. At that safer speed, calculate the normal force the track needs to provide at the highest ...
Pretest Forces
... b. a car turning a corner c. the space shuttle when it is being launched d. a bike moving in a straight line at a constant speed 3. If you triple the net force acting on a moving object, how will its acceleration be affected? ...
... b. a car turning a corner c. the space shuttle when it is being launched d. a bike moving in a straight line at a constant speed 3. If you triple the net force acting on a moving object, how will its acceleration be affected? ...
Are you ready for the Motion #2 Unit Test
... The towbar provides the means by which the trailer is pulled forward. Unless the trailer is accelerating towards the car, this will equal the force that the trailer is exerting on it and, consequently, on the car. This force must overcome the friction presented by the trailer and cause the trailer t ...
... The towbar provides the means by which the trailer is pulled forward. Unless the trailer is accelerating towards the car, this will equal the force that the trailer is exerting on it and, consequently, on the car. This force must overcome the friction presented by the trailer and cause the trailer t ...
Force Practice Problems Name: Per: ______ Answer the following
... a. Which exerts the larger force; the bug on the car or the car on the bug? How come? b. Which experiences a larger acceleration; the bug or the car? How come? 2. A 450.kg mass is accelerated at 2.50m/s2. a. What is the net force causing this acceleration? b. If the mass of the car is doubled, what ...
... a. Which exerts the larger force; the bug on the car or the car on the bug? How come? b. Which experiences a larger acceleration; the bug or the car? How come? 2. A 450.kg mass is accelerated at 2.50m/s2. a. What is the net force causing this acceleration? b. If the mass of the car is doubled, what ...
Math 21a Supplement on Planetary Motion Suppose that an object
... course, this assumes that L ≠ 0. If L = 0, then this means that r´ is proportional to r at each point. That is, r´ = α(t)·r, where α(t) is some function of t. This means that the whole trajectory lies upon a line. Indeed, this last equation implies that the unit vector r/r is constant (when r ≠ 0), ...
... course, this assumes that L ≠ 0. If L = 0, then this means that r´ is proportional to r at each point. That is, r´ = α(t)·r, where α(t) is some function of t. This means that the whole trajectory lies upon a line. Indeed, this last equation implies that the unit vector r/r is constant (when r ≠ 0), ...