Chapter 6 - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... The static frictional force keeps an object from starting to move when a force is applied. The static frictional force has a maximum value, but may take on any value from zero to the maximum, depending on what is needed to keep the sum of forces ...
... The static frictional force keeps an object from starting to move when a force is applied. The static frictional force has a maximum value, but may take on any value from zero to the maximum, depending on what is needed to keep the sum of forces ...
ANGULAR POSITION
... axis of rotation by a light rod of length r If a tangential force of magnitude F is applied to the mass, it will move with an acceleration according to Newton’s 2nd law, a = F/m Linear and angular accelerations related by α = a/r Combining: α = a/r = F/mr Multiplying by r/r gives α = rF/mr2 Since to ...
... axis of rotation by a light rod of length r If a tangential force of magnitude F is applied to the mass, it will move with an acceleration according to Newton’s 2nd law, a = F/m Linear and angular accelerations related by α = a/r Combining: α = a/r = F/mr Multiplying by r/r gives α = rF/mr2 Since to ...
17.4 Inertia and Newton`s 1st law of motion
... slow it down, or speed it up, or make it change direction. Sir Isaac Newton was one of the first and greatest physicists (Module 1.9). Newton’s first law of motion states that an object at rest will stay at rest, and a moving object will continue to move with uniform velocity, unless an external for ...
... slow it down, or speed it up, or make it change direction. Sir Isaac Newton was one of the first and greatest physicists (Module 1.9). Newton’s first law of motion states that an object at rest will stay at rest, and a moving object will continue to move with uniform velocity, unless an external for ...
Forces and COM - K
... – In crossing a river, what direction is best? • Velocity of water and swimmer ...
... – In crossing a river, what direction is best? • Velocity of water and swimmer ...
Exam 1A
... Short Answer (4 points each) More than 300 years ago, Isaac Newton claimed that the moon is accelerating toward the planet Earth. Explain how we know that the moon is accelerating toward the earth and why it hasn’t hit the earth over the past 300 years. ...
... Short Answer (4 points each) More than 300 years ago, Isaac Newton claimed that the moon is accelerating toward the planet Earth. Explain how we know that the moon is accelerating toward the earth and why it hasn’t hit the earth over the past 300 years. ...
Motion Unit Class Notes
... - depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them Inertia – an object’s tendency to keep doing what it is doing (rest or motion) - resistance to change - the greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia ...
... - depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them Inertia – an object’s tendency to keep doing what it is doing (rest or motion) - resistance to change - the greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia ...
Final Exam
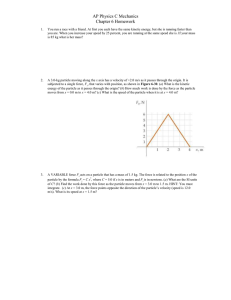
... 10. A block m1=2.0 kg is placed on a frictionless 30o incline and connected to another block m2 = 6 kg by a light string as shown in the figures. The pulley has a moment of inertia 0.40 kg m2 and radius 0.2 m It rotates as the block m2 falls down. Find the acceleration of m1. ( in m/s2) T1 − m1 g si ...
... 10. A block m1=2.0 kg is placed on a frictionless 30o incline and connected to another block m2 = 6 kg by a light string as shown in the figures. The pulley has a moment of inertia 0.40 kg m2 and radius 0.2 m It rotates as the block m2 falls down. Find the acceleration of m1. ( in m/s2) T1 − m1 g si ...
David Walter
... 1. Observe the Position vs. Time graph. Describe how the position of the object changes over time. 2. Observe the Velocity vs. Time graph. Describe how the velocity of the object changes over time. ...
... 1. Observe the Position vs. Time graph. Describe how the position of the object changes over time. 2. Observe the Velocity vs. Time graph. Describe how the velocity of the object changes over time. ...
Newton`s Second Law Spring/Mass Systems: Free Undamped
... pounds stretches a spring ½ foot, then 14 = k(1/2) and k = 28 lbs/ft. Before proceed to Newton’s Second Law, we define the weight, W = mg where mass is measured in slugs, grams, or kilograms. For example, g = 32 ft. /s2 or 9.8 m / s2 or 980 cm / s2. ...
... pounds stretches a spring ½ foot, then 14 = k(1/2) and k = 28 lbs/ft. Before proceed to Newton’s Second Law, we define the weight, W = mg where mass is measured in slugs, grams, or kilograms. For example, g = 32 ft. /s2 or 9.8 m / s2 or 980 cm / s2. ...
Chapter 4
... Equal to the weight of the object plus the net force acting on it See Problem 2 on page 99 Weightlessness is a factor of apparent weight. This does not mean that the object has no weight, rather there are no upward contact forces acting on it. Fscale = mg + ma (going up) Fscale = mg – ma (going down ...
... Equal to the weight of the object plus the net force acting on it See Problem 2 on page 99 Weightlessness is a factor of apparent weight. This does not mean that the object has no weight, rather there are no upward contact forces acting on it. Fscale = mg + ma (going up) Fscale = mg – ma (going down ...
slide show
... through displacement (change of position motion) – Kinetic energy is force by distance – t/s2 * s = t/s – If mass is displaced (moves), work is performed and the potential energy of force (energy per unit space) is transformed into the kinetic energy of force (energy per unit space times displacemen ...
... through displacement (change of position motion) – Kinetic energy is force by distance – t/s2 * s = t/s – If mass is displaced (moves), work is performed and the potential energy of force (energy per unit space) is transformed into the kinetic energy of force (energy per unit space times displacemen ...
File - Phy 2048-0002
... kinematics and dynamics of translational motion – that is, motion without rotation. Now we will widen our view of the natural world to include objects that both rotate and translate. ...
... kinematics and dynamics of translational motion – that is, motion without rotation. Now we will widen our view of the natural world to include objects that both rotate and translate. ...
Practice test Midterm 2-1_Chapter 7
... The rigid body shown rotates about an axis through its center of mass and perpendicular to the paper. If M = 2.0 kg and L = 80 cm, what is the kinetic energy of this object when its angular speed about this axis is equal to 5.0 rad/s? Neglect the mass of the connecting rod and treat the masses as pa ...
... The rigid body shown rotates about an axis through its center of mass and perpendicular to the paper. If M = 2.0 kg and L = 80 cm, what is the kinetic energy of this object when its angular speed about this axis is equal to 5.0 rad/s? Neglect the mass of the connecting rod and treat the masses as pa ...
Knight_ch04
... 3) The force of the kick, acting in the direction of motion. 4) Friction, acting opposite the direction of motion. 5) 1, 2 and 4 but not 3. ...
... 3) The force of the kick, acting in the direction of motion. 4) Friction, acting opposite the direction of motion. 5) 1, 2 and 4 but not 3. ...
KINEMATICS PROBLEMS: NEWTON`S LAWS
... Does it follow that block B has twice the acceleration of block A? Justify your answer using Newton's second law. ...
... Does it follow that block B has twice the acceleration of block A? Justify your answer using Newton's second law. ...
香港考試局
... A student performing a centripetal force experiment whirls a rubber bung attached to one end of a string which passes through a glass tube with smooth openings, and has a weight W hanging at its other end. The weight of the rubber bung is much smaller than W. The rubber bung is set into a horizontal ...
... A student performing a centripetal force experiment whirls a rubber bung attached to one end of a string which passes through a glass tube with smooth openings, and has a weight W hanging at its other end. The weight of the rubber bung is much smaller than W. The rubber bung is set into a horizontal ...