Sect. 2.5 - TTU Physics
... Work & Energy • Definition: A particle is acted on by a total force F. The Work done on the particle in moving it from (arbitrary) position 1 to (arbitrary) position 2 in space is defined as line integral (limits from 1 to 2): W12 ∫ Fdr • By Newton’s 2nd Law (using chain rule of differentiation) ...
... Work & Energy • Definition: A particle is acted on by a total force F. The Work done on the particle in moving it from (arbitrary) position 1 to (arbitrary) position 2 in space is defined as line integral (limits from 1 to 2): W12 ∫ Fdr • By Newton’s 2nd Law (using chain rule of differentiation) ...
Exam 1
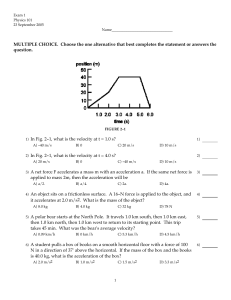
... A polar bear starts at the North Pole. It travels 1.0 km south, then 1.0 km east, then 1.0 km north, then 1.0 km west to return to its starting point. This trip takes 45 min. What was the bear's average velocity? A) 0.09 km/h ...
... A polar bear starts at the North Pole. It travels 1.0 km south, then 1.0 km east, then 1.0 km north, then 1.0 km west to return to its starting point. This trip takes 45 min. What was the bear's average velocity? A) 0.09 km/h ...
Forces in Motion
... • All forces act in pairs. • If a force is exerted, another force is exerted that is equal in size, but opposite in direction to the first force. ...
... • All forces act in pairs. • If a force is exerted, another force is exerted that is equal in size, but opposite in direction to the first force. ...
Widely separated binary systems of very low mass stars Phan Bao
... The total energy E of a system can change only by amounts of energy that are transferred to or from the system. ...
... The total energy E of a system can change only by amounts of energy that are transferred to or from the system. ...
2016 sample exam
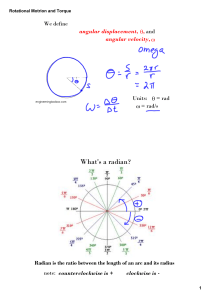
... the centre of the central spindle, along the spindle axis with acceleration a; we assume the spaceship’s axis is also aligned along the spindle axis, and that it is already spinning about this axis with angular velocity ω. Describe quantitatively the path that a spot of paint on the outer cylindrica ...
... the centre of the central spindle, along the spindle axis with acceleration a; we assume the spaceship’s axis is also aligned along the spindle axis, and that it is already spinning about this axis with angular velocity ω. Describe quantitatively the path that a spot of paint on the outer cylindrica ...
Unit 2 Objectives: Forces and Laws of Motion
... 7. The gravitational attractive force on the moon is 1/6 that of earth giving objects an acceleration of 1.67 m/s2 (in other words, on the moon g= 1.67 m/s2). What would be the mass of a 150-kg TV set on the moon? 150 kg 8. Using the concept of combining vectors, determine the net force when a 6 N a ...
... 7. The gravitational attractive force on the moon is 1/6 that of earth giving objects an acceleration of 1.67 m/s2 (in other words, on the moon g= 1.67 m/s2). What would be the mass of a 150-kg TV set on the moon? 150 kg 8. Using the concept of combining vectors, determine the net force when a 6 N a ...
Name - westlake-science
... 21. What force is responsible for your socks sticking together after they have been in a clothes dryer? ...
... 21. What force is responsible for your socks sticking together after they have been in a clothes dryer? ...
Living Things - Christian Heritage School
... to accelerate at 2.0 m/s2. Calculate the net force that causes this acceleration. Read and Understand What information have you been given? Mass of the water-skier (m) = 55 kg Acceleration of the water-skier (a) = 2.0 m/s2 ...
... to accelerate at 2.0 m/s2. Calculate the net force that causes this acceleration. Read and Understand What information have you been given? Mass of the water-skier (m) = 55 kg Acceleration of the water-skier (a) = 2.0 m/s2 ...
Chapter 2: Motion
... D. is divided by mass. 10. Which of the following statements are true of both weight and mass? A. Weight is a force, mass is a measure of inertia. B. Mass depends on gravity, weight does not. C. Heavier objects weigh more than light objects. D. Gravity is necessary to measure both weight and mass. 1 ...
... D. is divided by mass. 10. Which of the following statements are true of both weight and mass? A. Weight is a force, mass is a measure of inertia. B. Mass depends on gravity, weight does not. C. Heavier objects weigh more than light objects. D. Gravity is necessary to measure both weight and mass. 1 ...
Newton`s Laws
... Isaac Newton (1642-1727) Issac Newton’s monumental work, Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, was published in 1687. It proposed scientific laws that are still used today to describe the motion of objects. (credit: Service commun de la documentation de l'Université de Strasbourg) ...
... Isaac Newton (1642-1727) Issac Newton’s monumental work, Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, was published in 1687. It proposed scientific laws that are still used today to describe the motion of objects. (credit: Service commun de la documentation de l'Université de Strasbourg) ...
Now
... The greater the mass of an object the greater its gravitational pull on another object. • Small mass = small pull • Large mass = large pull ...
... The greater the mass of an object the greater its gravitational pull on another object. • Small mass = small pull • Large mass = large pull ...
Force Applied at an Angle Force Applied at an Angle
... Force Applied at an Angle ex. A desk of mass 30.0 kg is pushed forward at an angle of 30° to the floor at a constant speed by a force of 50 N. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction of the surface. ...
... Force Applied at an Angle ex. A desk of mass 30.0 kg is pushed forward at an angle of 30° to the floor at a constant speed by a force of 50 N. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction of the surface. ...