* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s Laws of Motion
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
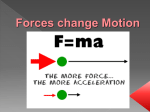
Newton’s Laws of Motion Miss Barnes Sir Isaac Newton http://www.biography.com/articles/SirIsaac-Newton-194903 st 1 Law of Motion An object in motion will stay in motion unless a force acts on it. An object at rest will stay at rest unless a force acts on it. Define it! Science journals out! Write the word: Inertia Write the definition: The tendency of an object to resist any change in motion. st 1 Law of Motion Objects with more mass will have more inertia than objects with less mass. Have you ever been forced against the side of a car as it turns? When the car is changing direction, your body tends to keep moving straight. The car is pushing on you during a turn. st 1 Law of Motion Think of a crash test The car crashes and stops. The dummy has inertia and wants to keep going forward. The seatbelt is what keeps the dummy from continuing to move forward. WEAR YOUR SEATBELT!!! Keyword: AccelerationThe rate at which the speed of an object changes over time. nd 2 Law of Motion Mass, acceleration, and force are related. The law indicates the stronger the force acting on an object, the more the object will accelerate. A force will cause an object with small mass to accelerate more than an object with a large mass. (same force) Acceleration due to a small force on a small object can be the same as the acceleration of a big force on a big object. 2nd Law of Motion The greater the force pushing on the box, the greater the acceleration of the box The greater the mass of the box, the less the acceleration will be. 3rd Law of Motion When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force on the first object. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. 3rd Law of Motion When a person leans on a wall they exert force on the wall. The wall exerts an equal force on the person in the opposite direction. When two bumper cars collide, both drivers feel the impact. Each car gave off an equal and opposite force. Balanced Force Balanced forces do not cause a change in motion. They are equal in size and opposite in direction. Push both of your hand together with the same force. The force is equal in size and opposite in direction, therefore there is no motion. Balanced Forces In a balanced force the two forces cancel each other out and therefore there is no motion. Think about arm wrestling or tug-o-war. Unbalanced Forces Unbalanced forces always cause a change in motion. They are not equal and opposite. Unbalanced Forces Think again about the arm wrestling match. Only this time imagine that you are competing against a world famous body builder. Chances are that his force will be much greater than yours. Your arms will move in the direction he is pushing with a force that is equal to his force minus your force. It will look like this. Unbalanced Forces Unbalanced forces can also be exerted in the same direction. For example, imagine that your family's car breaks down on the road and you have to push it into a parking lot. If you and your brother or sister both push on the car, the resulting force on the car will be the sum of your forces and of course be in the direction that you are applying the force. The figure below shows how this would work.