File
... A partly enclosed coastal body of water containing a mixture of salt and fresh water (brackish water). It has one or more rivers or streams flowing into it and a free connection to the open sea. ...
... A partly enclosed coastal body of water containing a mixture of salt and fresh water (brackish water). It has one or more rivers or streams flowing into it and a free connection to the open sea. ...
Ecology Unit Vocabulary List
... Ecology Unit Vocabulary List Ecology = the study of how organisms interact with their environment. Ecologist = scientist who studies relationships between organisms and environments Ecosystem = a community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings Habitat = ...
... Ecology Unit Vocabulary List Ecology = the study of how organisms interact with their environment. Ecologist = scientist who studies relationships between organisms and environments Ecosystem = a community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings Habitat = ...
28 Ecosystems - answers
... 5 (a) The abiotic factors which might affect an animal living at the bottom of the sea might be; water pressure, light, salinity. (any two) (b) The abiotic factors which might affect a plant growing on mountains might be; temperature, wind speed, drainage of water, light intensity. (any two) 6 The b ...
... 5 (a) The abiotic factors which might affect an animal living at the bottom of the sea might be; water pressure, light, salinity. (any two) (b) The abiotic factors which might affect a plant growing on mountains might be; temperature, wind speed, drainage of water, light intensity. (any two) 6 The b ...
Unit 11 Learning Packet
... 4. An animal that relies on interaction with the environment to help it control body temperature is known as a(n) a. endotherm b. ectotherm c. mesoderm d. endoderm 5. The single most important characteristic that separates birds from other living animals is the presence of a. two legs b. feathers c. ...
... 4. An animal that relies on interaction with the environment to help it control body temperature is known as a(n) a. endotherm b. ectotherm c. mesoderm d. endoderm 5. The single most important characteristic that separates birds from other living animals is the presence of a. two legs b. feathers c. ...
Paris Mountain State Park Forest Ecology Vocabulary List Abiotic
... Forest floor – bottom layer, made of soil, decomposing leaves and other organisms. Herb layer – layer near the ground, made of soft-stemmed small plants. Shrub layer – middle layer made of low woody plants with branching trunks. Understory layer – fourth layer up made of smaller, shade tolerant tree ...
... Forest floor – bottom layer, made of soil, decomposing leaves and other organisms. Herb layer – layer near the ground, made of soft-stemmed small plants. Shrub layer – middle layer made of low woody plants with branching trunks. Understory layer – fourth layer up made of smaller, shade tolerant tree ...
ecology - Algonac Community Schools
... enter barrel Barrel has certain amount it can hold (carrying capacity) Many factors keep the population from reaching carrying capacity ...
... enter barrel Barrel has certain amount it can hold (carrying capacity) Many factors keep the population from reaching carrying capacity ...
Glossary - Queensland Museum
... back into the ecosystem. For example: bacteria and fungi. The organic debris produced during the decomposition of plants and animals. An integrated unit made up of the community of living organisms and the physical environment in a specific area. It is the system through which matter cycles and ener ...
... back into the ecosystem. For example: bacteria and fungi. The organic debris produced during the decomposition of plants and animals. An integrated unit made up of the community of living organisms and the physical environment in a specific area. It is the system through which matter cycles and ener ...
5a - homeostasis and feedback
... • Maintaining a stable internal environment within a narrow range • Necessary for proper function of enzymes that carry out all metabolic processes • Involves all organ systems ...
... • Maintaining a stable internal environment within a narrow range • Necessary for proper function of enzymes that carry out all metabolic processes • Involves all organ systems ...
Zoology - Images
... •We will spend a brief time looking at Kingdom Protista-a refresher from Biology •Will include because protists are “animal like” ...
... •We will spend a brief time looking at Kingdom Protista-a refresher from Biology •Will include because protists are “animal like” ...
Aquatic Communities: Habitats
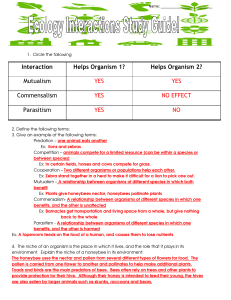
... Competition (-,-) is when organisms compete for a resource such as food, light or space. Predation (+,-) is when one organism benefits by eating something else. Mutualism (+,+) is when both organisms benefit. Commensalism (+, 0) is when one organism benefits and the other is not affected. Parasitism ...
... Competition (-,-) is when organisms compete for a resource such as food, light or space. Predation (+,-) is when one organism benefits by eating something else. Mutualism (+,+) is when both organisms benefit. Commensalism (+, 0) is when one organism benefits and the other is not affected. Parasitism ...
ECOLOGY VOCABULARY • habitat-‐ The specific environment
... ECOLOGY VOCABULARY habitat-‐ The specific environment where an organism lives based on what the organisms requires to survive. Defined by how much water, oxygen, and food is required by an organism. ...
... ECOLOGY VOCABULARY habitat-‐ The specific environment where an organism lives based on what the organisms requires to survive. Defined by how much water, oxygen, and food is required by an organism. ...
Middle School Science Room 212 – Miss Lida Lesson 1 – Explore
... While cell walls support plant cells, a protein called collagen holds animal cells together. Animals are the only living things that have nerve cells. Most animals also have muscle cells that help them move. All animals get energy from the food they take into their bodies. All animals begin as a fer ...
... While cell walls support plant cells, a protein called collagen holds animal cells together. Animals are the only living things that have nerve cells. Most animals also have muscle cells that help them move. All animals get energy from the food they take into their bodies. All animals begin as a fer ...
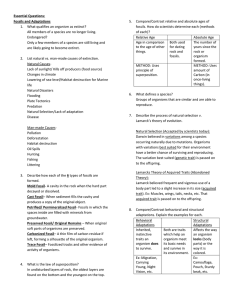
Interaction Helps Organism 1? Helps Organism 2? Mutualism YES
... The honeybee uses the nectar and pollen from several different types of flowers for food. The pollen is carried from one flower to another and pollinates to help make additional plants. Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection fo ...
... The honeybee uses the nectar and pollen from several different types of flowers for food. The pollen is carried from one flower to another and pollinates to help make additional plants. Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection fo ...
The Evolution of Animals
... Many cnidarians have two stages of life The immature polyp stage of life is sessile, remaining fixed to a solid surface The adult, medusa stage of life is motile, capable of swimming freely in the water Have true tissues Nervous tissue, muscle-like tissue, digestive tissue Lack true organs Mollusca ...
... Many cnidarians have two stages of life The immature polyp stage of life is sessile, remaining fixed to a solid surface The adult, medusa stage of life is motile, capable of swimming freely in the water Have true tissues Nervous tissue, muscle-like tissue, digestive tissue Lack true organs Mollusca ...
Name
... 26. An eagle eats rabbits and a rabbit eats grass. What would happen if the rabbits died in a particular area? The eagles would have no food so their population would decrease and grass would grow back. 27. In food chains what organisms do there need to be more of? plants – producers 28. What is the ...
... 26. An eagle eats rabbits and a rabbit eats grass. What would happen if the rabbits died in a particular area? The eagles would have no food so their population would decrease and grass would grow back. 27. In food chains what organisms do there need to be more of? plants – producers 28. What is the ...
Required information: 1. Common and Scientific Name of Species 2
... Ecology Project Rubric Assignment: Find all the information about the organism as shown below. ...
... Ecology Project Rubric Assignment: Find all the information about the organism as shown below. ...
Slide 1
... C. to defend the body against illness and infection D. to coordinate movement of the body ...
... C. to defend the body against illness and infection D. to coordinate movement of the body ...