* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 52 Ecology
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
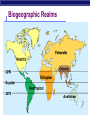
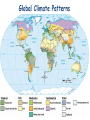
Introduction to Ecology Chapter 52 http://www.geog.uni-heidelberg.de/~ttavk/weltkarten/globen/1997-1998-biosphere-Nasa.jpg Ecology • interactions of organisms with their environment Organisms & the Environment • Abiotic Factors: non-living • temperature, humidity, precipitation, water, climate, wind, sunlight, soil composition, etc… • Biotic Factors: living • predation, herbivory, presence or absence of pollinators, food resources, parasites, pathogens, competing organisms Levels of Organization Biosphere Biome Ecosystem Community Population Organism BBECPO BIOSPHERE portion of planet in which all life exists (includes land, water, atmosphere) Extends from: 8 km above the Earth’s surface to 11 km below the ocean’s surface BIOME • the world’s ecosystems classified according to dominant vegetation & rainfall Biomes Aquatic • Marine • Intertidal zones • Oceanic Pelagic • Coral reefs • Marine benthic zone • Freshwater • Lakes • Wetlands • Streams and rivers • Estuaries Terrestrial Tropical Desert Savanna Chaparral Grassland Coniferous forest (taiga) • Broadleaf forest (deciduous) • Tundra (arctic) • • • • • • ECOSYSTEM All the organisms in a community plus abiotic factors ecosystems are transformers of energy & processors of matter Ecosystems are self-sustaining what is needed? capture energy transfer energy cycle nutrients COMMUNITY • All the organisms that inhabit an area POPULATION individuals of the same species living in an area. capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring) Biogeographic Realms Organism’s Habitat • habitat: place where an organism lives • dispersal: movement of individuals from areas of high population density (or their area of origin) • disruption of existing communities and ecosystems usually occurs Organism’s Tolerance • tolerance: range of conditions an organism can withstand • acclimation: changing in response to environmental factors Climate • Macroclimate: global and regional • Microclimate: community • affected by: • • • • sunlight – warming – longitudinal variations temperature water wind • temperature & moisture: main factors that limit plant & animal species in geographic regions Global Climate Patterns Responses to Change in Biotic & Abiotic Environment • Migration • Hibernation / Dormancy • Conformers: change with the environments • Regulators: maintain homeostasis regardless of external environment Organism’s Niche • Niche: organism’s role in the environment • includes ALL biotic & abiotic factors an organism needs or uses • fundamental niche: range or resources the organism can potentially use • realized niche: resources the organism actually uses • if niches overlap competition for resources • Natural Selection No two species can occupy the same niche! Competitive exclusion principle