Interactions Among Organisms
... It is where the organism finds food, shelter and mates. Several species can live in the same habitat but will use the resources in different ways. ...
... It is where the organism finds food, shelter and mates. Several species can live in the same habitat but will use the resources in different ways. ...
Linking body-size distributions and food-web structure (PDF
... log2 maximum body mass Figure 1: Relationships between the δ15N of white muscle tissue (mean ± 95% CL) and maximum weight of North Sea fishes. Since δ15N (trophic level) increases with body size within species, fish from different species were compared at an equivalent stage of their life history. T ...
... log2 maximum body mass Figure 1: Relationships between the δ15N of white muscle tissue (mean ± 95% CL) and maximum weight of North Sea fishes. Since δ15N (trophic level) increases with body size within species, fish from different species were compared at an equivalent stage of their life history. T ...
Soil types determine what plants and animals can live in an area
... • Commensalism is a form of symbiosis that helps one species but has no effect on the other. Ex: flatworms and horseshoe crabs • When one species is harmed and the other benefits, it is parasitism. Ex: some mistletoe and trees ...
... • Commensalism is a form of symbiosis that helps one species but has no effect on the other. Ex: flatworms and horseshoe crabs • When one species is harmed and the other benefits, it is parasitism. Ex: some mistletoe and trees ...
The Human Body – Study Guide Part 1
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________ 3. Where and how does digestion begin? ________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________ 4. In which part of the bo ...
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________ 3. Where and how does digestion begin? ________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________ 4. In which part of the bo ...
Ecology ppt notes
... Abiotic Factors The __________________ components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. Examples of Abiotic Factors: ...
... Abiotic Factors The __________________ components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. Examples of Abiotic Factors: ...
What is Animal Science - Riverside High School
... Nostrils, nasal cavity pharynx, larynx, trachea and lungs. 5. Nervous systemCentral Nervous System – Spinal cord and brain – Coordinates movement and allows the sense of hearing, sight, smell, touch and taste Peripheral nervous System – controls body tissues including the organs transmits messages f ...
... Nostrils, nasal cavity pharynx, larynx, trachea and lungs. 5. Nervous systemCentral Nervous System – Spinal cord and brain – Coordinates movement and allows the sense of hearing, sight, smell, touch and taste Peripheral nervous System – controls body tissues including the organs transmits messages f ...
Body Systems Quiz
... 4. What protects the body from injury and infection? SKIN 5. The process by which an organism's internal environment is kept stable in spite of changes in the external environment is called HOMEOSTASIS. ...
... 4. What protects the body from injury and infection? SKIN 5. The process by which an organism's internal environment is kept stable in spite of changes in the external environment is called HOMEOSTASIS. ...
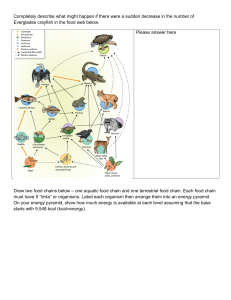
Completely describe what might happen if there were a sudden
... a. Communities make up species, which make up populations. b. Populations make up species, which make up communities. c. Species make up communities, which make up populations. d. Species make up populations, which make up communities. ...
... a. Communities make up species, which make up populations. b. Populations make up species, which make up communities. c. Species make up communities, which make up populations. d. Species make up populations, which make up communities. ...
Ecology
... • Symbiosis: where 2 species live together closely. • Mutualism: where both species benefit from the relationship. • Commensalism: when one member benefits and the other is ...
... • Symbiosis: where 2 species live together closely. • Mutualism: where both species benefit from the relationship. • Commensalism: when one member benefits and the other is ...
How Living things interact
... • A result of natural selection • Adaptations- the behaviors and physical characteristics that allow organisms to live successfully in their environments. • If they do not well suited to survive in their environment they will not reproduce as much. What will happen to ...
... • A result of natural selection • Adaptations- the behaviors and physical characteristics that allow organisms to live successfully in their environments. • If they do not well suited to survive in their environment they will not reproduce as much. What will happen to ...
Cells
... contract to pull ribs up and out. The DIAPHRAGM muscle contracts to pull down the lungs. Tissue expands to suck in air. BREATH OUT -- you get rid of other gases that your body does not need. Rib muscles relax. The Diaphragm muscle relaxes. Tissue returns to resting position and forces air out. ...
... contract to pull ribs up and out. The DIAPHRAGM muscle contracts to pull down the lungs. Tissue expands to suck in air. BREATH OUT -- you get rid of other gases that your body does not need. Rib muscles relax. The Diaphragm muscle relaxes. Tissue returns to resting position and forces air out. ...
Species Interactions in Biological Communities
... The Viceroy butterfly uses mimicry to look like the Monarch butterfly. Can you tell them apart? ...
... The Viceroy butterfly uses mimicry to look like the Monarch butterfly. Can you tell them apart? ...
Relationships in Ecosystems
... Within An Ecosystem… • Habitat- provides shelter and resources so that animals can survive • Niche- the role of an organism in its ecosystem- how does it survive? ...
... Within An Ecosystem… • Habitat- provides shelter and resources so that animals can survive • Niche- the role of an organism in its ecosystem- how does it survive? ...
The postCambrian era was characterized by animal
... Changes in the environment often create new niches (living spaces) that contribute to rapid speciation and increased diversity. On the other hand, cataclysmic events, such as volcanic eruptions and meteor strikes that obliterate life, can result in devastating losses of diversity. Such periods of ma ...
... Changes in the environment often create new niches (living spaces) that contribute to rapid speciation and increased diversity. On the other hand, cataclysmic events, such as volcanic eruptions and meteor strikes that obliterate life, can result in devastating losses of diversity. Such periods of ma ...
Animal Body Systems Vocabulary Handout
... bones which make up the vertebral column and skull Appendicular Skeleton part of the skeleton which includes the pectoral girdle, the pelvic girdle and the upper and lower limbs ...
... bones which make up the vertebral column and skull Appendicular Skeleton part of the skeleton which includes the pectoral girdle, the pelvic girdle and the upper and lower limbs ...
Name
... impacted using the terms “Benefits,” “Harmed,” or “No impact.” For each situation, assume that Organism A initiates the relationship. ...
... impacted using the terms “Benefits,” “Harmed,” or “No impact.” For each situation, assume that Organism A initiates the relationship. ...
Characteristic of living things
... things are sensitive to their environment. They have the ability to detect change and to respond to this. Producing Or Consuming ‘Food’: Food or nutrients are either ingested or absorbed by living things such as fungi and animals, or produced by the organism itself e.g. plants Respiration: all o ...
... things are sensitive to their environment. They have the ability to detect change and to respond to this. Producing Or Consuming ‘Food’: Food or nutrients are either ingested or absorbed by living things such as fungi and animals, or produced by the organism itself e.g. plants Respiration: all o ...
Chapter 1 Vocabulary Review
... A group of organisms that are physically similar and can mate with each other and produce offspring that can also mate and ...
... A group of organisms that are physically similar and can mate with each other and produce offspring that can also mate and ...
Environmental Science
... • Organisms in any community can be divided into three groups based on how they obtain energy. • Let’s examine to see how energy passes through these groups in an ecosystem. ...
... • Organisms in any community can be divided into three groups based on how they obtain energy. • Let’s examine to see how energy passes through these groups in an ecosystem. ...
Goal 1 - Wsfcs
... To grow or cause to grow gradually less or smaller, as in number, amount, or intensity. ...
... To grow or cause to grow gradually less or smaller, as in number, amount, or intensity. ...
Population Dynamics
... Q. Give an example of predation by naming a predator and its prey. A. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Q. Where one organism lives in or on a second species, feeding on it and causing it harm is called … A. _____________________________________ ...
... Q. Give an example of predation by naming a predator and its prey. A. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Q. Where one organism lives in or on a second species, feeding on it and causing it harm is called … A. _____________________________________ ...
Study Guide for Science Unit 4
... an organism no longer exists in an ecosystem. *Animals have to adapt to or leave the ecosystem in order to survive. *Endangered plants and animals have very few of their kind left. These plants and animals must be protected from humans, use there adaptations to survive, and reproduce for the species ...
... an organism no longer exists in an ecosystem. *Animals have to adapt to or leave the ecosystem in order to survive. *Endangered plants and animals have very few of their kind left. These plants and animals must be protected from humans, use there adaptations to survive, and reproduce for the species ...