Organic Chemistry
... “Organic” Chemistry • Historically, organic compounds are defined as compounds extracted or isolated from plants and animals. – VITALISM: Scientists believed that organic compounds contained a vital force that was only found in living systems • Disproved by Friederich Wohler in 1828 by synthesizing ...
... “Organic” Chemistry • Historically, organic compounds are defined as compounds extracted or isolated from plants and animals. – VITALISM: Scientists believed that organic compounds contained a vital force that was only found in living systems • Disproved by Friederich Wohler in 1828 by synthesizing ...
PowerPoint 簡報 - SALEM-Immanuel Lutheran College
... Limit the total number of reaction steps in a synthesis to not more than four ...
... Limit the total number of reaction steps in a synthesis to not more than four ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... their standard states. • Standard entropies tend to increase with increasing molar mass. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... their standard states. • Standard entropies tend to increase with increasing molar mass. Chemical Thermodynamics © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Slide 1 - Catalysis Eprints database
... Cobalt catalyzed hydroformylation- Mechanism Co2(CO)8 + H2 ⇋ (high pressure) 2[CoH(CO)4] 1. The complex loses CO to produce the coordinatively unsaturated complex catalyst. 2. The complex catalyst coordinates to the alkene (Propene). 3. Undergoes insertion reaction → n-alkyl complex (may be branche ...
... Cobalt catalyzed hydroformylation- Mechanism Co2(CO)8 + H2 ⇋ (high pressure) 2[CoH(CO)4] 1. The complex loses CO to produce the coordinatively unsaturated complex catalyst. 2. The complex catalyst coordinates to the alkene (Propene). 3. Undergoes insertion reaction → n-alkyl complex (may be branche ...
Mole-Mass Conversions
... Unlike mole-particle conversions where the conversion factor is always 1mole = _______________ particles, each mole-mass conversion factor is _________________ to the substance involved. Convert 2.3 moles of sodium (Na) to grams of Na ...
... Unlike mole-particle conversions where the conversion factor is always 1mole = _______________ particles, each mole-mass conversion factor is _________________ to the substance involved. Convert 2.3 moles of sodium (Na) to grams of Na ...
Review on N acylation reaction
... Scheme 27. Pyridine as catalyst in amide synthesis Usually hydrochloride acceptor should be a base which is stronger than the base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number ...
... Scheme 27. Pyridine as catalyst in amide synthesis Usually hydrochloride acceptor should be a base which is stronger than the base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number ...
Hybrization of Orbitals
... Key differences between MO and VB theory: MO theory has electrons distributed over molecule VB theory localizes an electron pair between two atoms MO theory combines AOs on DIFFERENT atoms to make ...
... Key differences between MO and VB theory: MO theory has electrons distributed over molecule VB theory localizes an electron pair between two atoms MO theory combines AOs on DIFFERENT atoms to make ...
EXPERIMENT 4 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif
... solubility behavior. Alcohols with a larger organic radical are more like alkanes and less like water. Alcohols with more than two –OH groups are more water soluble than similar alcohols with only one –OH group. Each –OH function can solubilize 4 to 5 carbons. Melting (Fusion), Boiling points and De ...
... solubility behavior. Alcohols with a larger organic radical are more like alkanes and less like water. Alcohols with more than two –OH groups are more water soluble than similar alcohols with only one –OH group. Each –OH function can solubilize 4 to 5 carbons. Melting (Fusion), Boiling points and De ...
published a paper
... GMP, we generated a 30 -[32P] 6SGMP marker by end labeling an RNA sequence containing a terminal 30 6SGMP with 50 -[32P] pCp, followed by digestion using T2 ribonuclease (see Experimental Procedures). Interestingly, when the pR1-PRPP product was end labeled and digested in the same manner it comigra ...
... GMP, we generated a 30 -[32P] 6SGMP marker by end labeling an RNA sequence containing a terminal 30 6SGMP with 50 -[32P] pCp, followed by digestion using T2 ribonuclease (see Experimental Procedures). Interestingly, when the pR1-PRPP product was end labeled and digested in the same manner it comigra ...
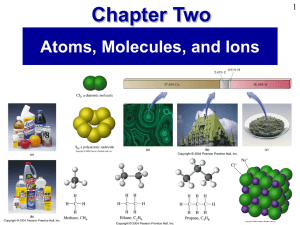
Prentice Hall Ch 02 Atoms Molecules Ions
... We usually write mass ratios in a form such as “the ratio of O to Mg is 0.6583:1.” The first number represents the mass of the first element named—in this case, a mass of oxygen, say 0.6583 g oxygen—and the second number represents the mass of the second element named—here a mass of magnesium. Altho ...
... We usually write mass ratios in a form such as “the ratio of O to Mg is 0.6583:1.” The first number represents the mass of the first element named—in this case, a mass of oxygen, say 0.6583 g oxygen—and the second number represents the mass of the second element named—here a mass of magnesium. Altho ...
Limiting - Faculty Web Pages
... And therefore the yield would be 90.%. Obviously we would also have 10.% of the original amount of H2 and 10.% of the original amount of Cl2 left over. In every day experiments we will have to combine both concepts, that of the limiting reactant and that of percentage yield. As a final example, let’ ...
... And therefore the yield would be 90.%. Obviously we would also have 10.% of the original amount of H2 and 10.% of the original amount of Cl2 left over. In every day experiments we will have to combine both concepts, that of the limiting reactant and that of percentage yield. As a final example, let’ ...
Stoichiometry - HCC Learning Web
... You might also want to look at the Wikipedia article about stoichiometry here. ...
... You might also want to look at the Wikipedia article about stoichiometry here. ...
lecture slides file
... Number with a name - Unit of measure A measurement makes no sense unless units are specified. Say, you are to get to the airport in 3. Three what? Minutes? Hours? Gallons of gas? Remembering names of different units for the same property, and the relationship between them can be cumbersome.... 12 i ...
... Number with a name - Unit of measure A measurement makes no sense unless units are specified. Say, you are to get to the airport in 3. Three what? Minutes? Hours? Gallons of gas? Remembering names of different units for the same property, and the relationship between them can be cumbersome.... 12 i ...
Print this article - Bangladesh Journals Online
... assignable for protons Hd and Ha respectively. The two doublets of doublet at δ 6.5 (JHa-Hb = JHb-Hc = J = 8.0 Hz) and 6.9 (JHb-Hc= JHc-Hd = J = 8.0 Hz) accounts for the Ha and Hd respectively, while the relatively downfield signal at δ 8.5 has been assigned for the imine (=N-H) proton of 2-mercapto ...
... assignable for protons Hd and Ha respectively. The two doublets of doublet at δ 6.5 (JHa-Hb = JHb-Hc = J = 8.0 Hz) and 6.9 (JHb-Hc= JHc-Hd = J = 8.0 Hz) accounts for the Ha and Hd respectively, while the relatively downfield signal at δ 8.5 has been assigned for the imine (=N-H) proton of 2-mercapto ...
Polymerization - Cornell University
... Polymerization - Formation of large polymers Polymers = organic compounds made up of smaller chains covalently bonded together. Each individual unit = monomer Ex of polymers = synthetic plastics, nylon, proteins, starch, cellulose 2 Types of polymerization reactions Addition Polymerization - joining ...
... Polymerization - Formation of large polymers Polymers = organic compounds made up of smaller chains covalently bonded together. Each individual unit = monomer Ex of polymers = synthetic plastics, nylon, proteins, starch, cellulose 2 Types of polymerization reactions Addition Polymerization - joining ...
PDF Full-text
... The Lewis structure [1] is central to a great deal of chemical reasoning and therefore has been the inspiration for chemically intuitive analysis of quantum computations on molecules. Pauling immediately recognized the compatibility of Lewis’s rule of two with Valence Bond theory and wrote this in a ...
... The Lewis structure [1] is central to a great deal of chemical reasoning and therefore has been the inspiration for chemically intuitive analysis of quantum computations on molecules. Pauling immediately recognized the compatibility of Lewis’s rule of two with Valence Bond theory and wrote this in a ...
Carbonyl compounds
... so that the two homologous series are more conveniently considered together. However, the attachment of a hydrogen to the carbonyl group of an aldehyde does give it certain properties which ketones do not share, and which enables the two families of organic compounds to be distinguished from one ano ...
... so that the two homologous series are more conveniently considered together. However, the attachment of a hydrogen to the carbonyl group of an aldehyde does give it certain properties which ketones do not share, and which enables the two families of organic compounds to be distinguished from one ano ...
Organic Reactions in Organised Media
... Insufficient contact between reactants will prevent the reaction from running efficiently. This is almost always the case when immiscible hydrophilic and hydrophobic reagents are involved in the process. Due to the relatively small interfacial area of the two-phase systems that are formed, the rate ...
... Insufficient contact between reactants will prevent the reaction from running efficiently. This is almost always the case when immiscible hydrophilic and hydrophobic reagents are involved in the process. Due to the relatively small interfacial area of the two-phase systems that are formed, the rate ...