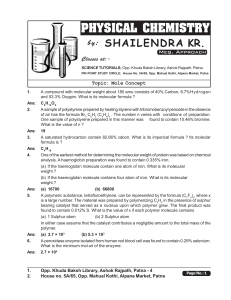
Mole Concept - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... (a) If the haemoglobin molecule contain one atom of iron. What is its molecular weight ? (b) If the haemoglobin molecule contains four atom of iron. What is its molecular weight ? ...
... (a) If the haemoglobin molecule contain one atom of iron. What is its molecular weight ? (b) If the haemoglobin molecule contains four atom of iron. What is its molecular weight ? ...
Aromatic Substitution Reactions
... begin by reaction of an electrophile with the pi electrons of an alkene. This results in the formation of a carbocation called an arenium ion. Removal of a proton from the arenium ion by some weak base that is present restores the aromatic ring and results in the substitution of the electrophile for ...
... begin by reaction of an electrophile with the pi electrons of an alkene. This results in the formation of a carbocation called an arenium ion. Removal of a proton from the arenium ion by some weak base that is present restores the aromatic ring and results in the substitution of the electrophile for ...
Molecular diffusion at surfaces
... bonds and draws the charge from the metal atoms, leading to weakening of the metalmetal bonds. But carbon forms a covalent Fe 3d-C2s,2p interactions with iron there by gets more stabilized. The ionization potential input parameters for the C 2s and 2p orbitals are decreased by 1.5 eV from their atom ...
... bonds and draws the charge from the metal atoms, leading to weakening of the metalmetal bonds. But carbon forms a covalent Fe 3d-C2s,2p interactions with iron there by gets more stabilized. The ionization potential input parameters for the C 2s and 2p orbitals are decreased by 1.5 eV from their atom ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
Notes - Text
... It is used for the preparation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. • The process is carried out at high temperature (500°C) and pressure (200 atm) in the presence of a catalyst. • Ammonia is a good source of fixed nitrogen for plants. • Much of the NH3 produced industrially is used as a fertilize ...
... It is used for the preparation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. • The process is carried out at high temperature (500°C) and pressure (200 atm) in the presence of a catalyst. • Ammonia is a good source of fixed nitrogen for plants. • Much of the NH3 produced industrially is used as a fertilize ...
Paper
... The curves obtained by the approximation using equations (5), (11) and (12) are shown in Fig.4 together with the reference experimental points. The system (5) includes 4 different energy parameters. Since at high values of these parameters, typical for oxide melts, the excess chemical potentials exp ...
... The curves obtained by the approximation using equations (5), (11) and (12) are shown in Fig.4 together with the reference experimental points. The system (5) includes 4 different energy parameters. Since at high values of these parameters, typical for oxide melts, the excess chemical potentials exp ...
msc_pre_chemistry_pap1_bl2
... Fig.4.3 Variation in energies of 5T2g and 1A1g terms with increasing for d6 octahedral complexes. At weak field (high spin complexes) the ground term is 5T2g, while at strong fields (low spin complexes) it is 1A1g Note that in the region immediately on each side of the spin crossover point, the ...
... Fig.4.3 Variation in energies of 5T2g and 1A1g terms with increasing for d6 octahedral complexes. At weak field (high spin complexes) the ground term is 5T2g, while at strong fields (low spin complexes) it is 1A1g Note that in the region immediately on each side of the spin crossover point, the ...
examination paper - University of Calgary
... The examination consists of Parts 1 - 9, each of which should be attempted. Note that some Parts provide you with a choice of questions, i.e. answer 4 out of 5. These will be graded in numerical order until the required number have been completed, regardless of whether they are right or wrong. Parts ...
... The examination consists of Parts 1 - 9, each of which should be attempted. Note that some Parts provide you with a choice of questions, i.e. answer 4 out of 5. These will be graded in numerical order until the required number have been completed, regardless of whether they are right or wrong. Parts ...
Untitled
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without either the prior written permission of the publisher or a licence permitting restricted ...
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without either the prior written permission of the publisher or a licence permitting restricted ...
molecules Palladium and Organocatalysis: An Excellent Recipe for Asymmetric Synthesis
... combined for the improvement of catalytic processes [4–6]. The combination of organocatalysis and transition-metal catalysis allows not only the development of novel transformations, but also the enhancement of the stereochemistry, efficiency and/or scope of well known reactions [7]. One of the main ...
... combined for the improvement of catalytic processes [4–6]. The combination of organocatalysis and transition-metal catalysis allows not only the development of novel transformations, but also the enhancement of the stereochemistry, efficiency and/or scope of well known reactions [7]. One of the main ...
Chapter 12. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... www.ncerthelp.com (Visit for all ncert solutions in text and videos, CBSE syllabus, note and many more) ...
... www.ncerthelp.com (Visit for all ncert solutions in text and videos, CBSE syllabus, note and many more) ...
... 8. The coefficients of a balanced chemical equation tell you the relative number of reactants products moles of ______________________ and ______________________ in a chemical reaction. 9. Why is the relative number of moles of reactants and products the most important information that a balanced ch ...
Hybridisation
... therefore the outer shell electrons (2s2 2p2) have merged to form 4 hybrid sp3 orbitals of equal energy • One electron is in each of the hybrid orbitals and can form a sigma bond with a hydrogen atom ...
... therefore the outer shell electrons (2s2 2p2) have merged to form 4 hybrid sp3 orbitals of equal energy • One electron is in each of the hybrid orbitals and can form a sigma bond with a hydrogen atom ...
J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 1672
... of dimeric products, thus decreasing the overall selectivity of the reduction process. It is difficult to overstate the importance of Lewis acids in various types of organic transformations involving carbonyl groups and their equivalents.1 Reduction of carbonyl compounds with hydrosilanes in the pre ...
... of dimeric products, thus decreasing the overall selectivity of the reduction process. It is difficult to overstate the importance of Lewis acids in various types of organic transformations involving carbonyl groups and their equivalents.1 Reduction of carbonyl compounds with hydrosilanes in the pre ...
industry: applying chemical reactions
... plant in Riverwood. Because of a lack of employment opportunities in Riverwood, many of your friends and neighbors have expressed relief at this news from EKS Nitrogen Products Company and WYE Battery Technology Corporation.
... plant in Riverwood. Because of a lack of employment opportunities in Riverwood, many of your friends and neighbors have expressed relief at this news from EKS Nitrogen Products Company and WYE Battery Technology Corporation.
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... Hydrolysis: Conversion of Nitriles into Carboxylic Acids A nitrile can be hydrolyzed in either basic or acidic aqueous solution to yield a carboxylic acid and ammoniz or an amine O ...
... Hydrolysis: Conversion of Nitriles into Carboxylic Acids A nitrile can be hydrolyzed in either basic or acidic aqueous solution to yield a carboxylic acid and ammoniz or an amine O ...
Stoichiometry: Predicting Amounts in Reactions
... Stoichiometry is the process of determining how much product is made or how much reactant is needed during a chemical reaction. As we know, in chemical reactions atoms are conserved. We show thi ...
... Stoichiometry is the process of determining how much product is made or how much reactant is needed during a chemical reaction. As we know, in chemical reactions atoms are conserved. We show thi ...