Aldehydes and Ketones
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...
Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... disadvantage of this model. - Valence bond theory is based on the hybridization of atomic orbitals. - Hybridization: the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom (generally the central atom) to form a set of hybrid orbitals responsible for forming single, double, & triple bonds. - Hybridization is made ...
... disadvantage of this model. - Valence bond theory is based on the hybridization of atomic orbitals. - Hybridization: the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom (generally the central atom) to form a set of hybrid orbitals responsible for forming single, double, & triple bonds. - Hybridization is made ...
REACTING MASSES – ACTIVITY SHEET
... b) In the reaction, only 280 g of hydrazine was produced. Calculate the percentage yield. c) Calculate the atom economy for this way of making hydrazine. 2) Ibuprofen is a common pain killer used for symptoms such as head aches, tooth ache and period pains. It was invented in the 1960’s by Boots and ...
... b) In the reaction, only 280 g of hydrazine was produced. Calculate the percentage yield. c) Calculate the atom economy for this way of making hydrazine. 2) Ibuprofen is a common pain killer used for symptoms such as head aches, tooth ache and period pains. It was invented in the 1960’s by Boots and ...
NCERT/CBSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 12 textbook
... In C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3 the N is directly attached to the benzene ring therefore the lone pair of electrons of the N atom is the delocalized over the bezene ring.There is a +I effect on C6H5CH2NH2 due to the presence of CH3 group of C6H5NHCH3 , Therefore C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3 are weaker bases than C6H5NH ...
... In C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3 the N is directly attached to the benzene ring therefore the lone pair of electrons of the N atom is the delocalized over the bezene ring.There is a +I effect on C6H5CH2NH2 due to the presence of CH3 group of C6H5NHCH3 , Therefore C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3 are weaker bases than C6H5NH ...
Preparation and Physical Properties of Chitosan Benzoic Acid
... Chitin, the second abundant natural polymer in Nature, and chitosan, a partially deacetylated form of chitin, have recently received much of attention owing to their applicability in wide range of fields such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, agriculture, foods, and material sciences [1–5]. Their film ...
... Chitin, the second abundant natural polymer in Nature, and chitosan, a partially deacetylated form of chitin, have recently received much of attention owing to their applicability in wide range of fields such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, agriculture, foods, and material sciences [1–5]. Their film ...
PDF aldehydes and ketones
... Addition of S nucleophiles (addition of NaHSO3) Addition of NaHSO3 to carbonyl/ aldehydic carbon gives solid adduct; these are sulfonates that are water soluble. Only RCHO, methyl ketones, and cyclic ketones react. Carbonyl compounds can be regenerated on treating the adduct with acid or base. R C ...
... Addition of S nucleophiles (addition of NaHSO3) Addition of NaHSO3 to carbonyl/ aldehydic carbon gives solid adduct; these are sulfonates that are water soluble. Only RCHO, methyl ketones, and cyclic ketones react. Carbonyl compounds can be regenerated on treating the adduct with acid or base. R C ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... In volumetric analysis, a given amount (weight or volume) of an unknown substance is allowed to react with a known volume of a standard solution slowly. A chemical reaction takes place between the solute of an unknown substance and the solute of the standard solution. The completion of the reaction ...
... In volumetric analysis, a given amount (weight or volume) of an unknown substance is allowed to react with a known volume of a standard solution slowly. A chemical reaction takes place between the solute of an unknown substance and the solute of the standard solution. The completion of the reaction ...
Chapter 7- Alcohols
... (i) Boiling points of alcohols are higher than would be predicted based on molecular weight - Extra energy required to break the intermolecular hydrogen bonds (ii) Lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water ...
... (i) Boiling points of alcohols are higher than would be predicted based on molecular weight - Extra energy required to break the intermolecular hydrogen bonds (ii) Lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water ...
Isoindolone Formation via Intramolecular Diels
... A number of different approaches were attempted, but only one realistic alternative was found, utilising an intramolecular Diels−Alder approach1 to build the isoindolone ring (Scheme 4). The initial Vilsmeier reaction,2 whilst operationally straightforward, did present significant challenges due to th ...
... A number of different approaches were attempted, but only one realistic alternative was found, utilising an intramolecular Diels−Alder approach1 to build the isoindolone ring (Scheme 4). The initial Vilsmeier reaction,2 whilst operationally straightforward, did present significant challenges due to th ...
Chemistry Tests Questions
... 19. Write a balanced equation for the reaction of sodium with water. 20. What colour is the potassium flame? 21. How many atoms of fluorine combine with one atom of silicon? 22. How many atoms of fluorine combine with one atom of chlorine? 23. What happens to aluminium powder when tipped into a buns ...
... 19. Write a balanced equation for the reaction of sodium with water. 20. What colour is the potassium flame? 21. How many atoms of fluorine combine with one atom of silicon? 22. How many atoms of fluorine combine with one atom of chlorine? 23. What happens to aluminium powder when tipped into a buns ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... • Identify the product isolated when cyclopentanone reacts with dimethyl amine. ...
... • Identify the product isolated when cyclopentanone reacts with dimethyl amine. ...
Pincer Complexes. Applications in Catalysis
... metallic derivatives represent in many cases the ideal examples to carry out catalytic processes otherwise difficult or impossible to be carried out with conventional diphosphine ligands. The versatility of these species to be modified and modulated both steric and electronically, makes these compou ...
... metallic derivatives represent in many cases the ideal examples to carry out catalytic processes otherwise difficult or impossible to be carried out with conventional diphosphine ligands. The versatility of these species to be modified and modulated both steric and electronically, makes these compou ...
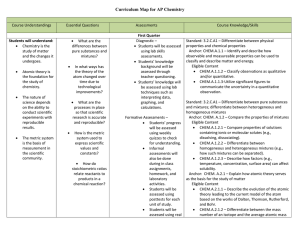
2015 International Practice Exam: Chemistry
... Note: Tables of equations and constants are provided in the exam booklets for both sections of the exam . Students are not allowed to use calculators in Section I of the AP Chemistry Exam . However, students are permitted to use four-function, scientific, or graphing calculators to answer questions ...
... Note: Tables of equations and constants are provided in the exam booklets for both sections of the exam . Students are not allowed to use calculators in Section I of the AP Chemistry Exam . However, students are permitted to use four-function, scientific, or graphing calculators to answer questions ...
Gas/particle partitioning of water-soluble organic aerosol in Atlanta
... for secondary organic gases and particles in Atlanta, but the relatively modest enhancement (∼20%) over pre-sunrise concentrations indicates a substantial regional WSOC background and a relatively long lifetime of both classes of material. This is consistent with the findings of Weber et al. (2007), ...
... for secondary organic gases and particles in Atlanta, but the relatively modest enhancement (∼20%) over pre-sunrise concentrations indicates a substantial regional WSOC background and a relatively long lifetime of both classes of material. This is consistent with the findings of Weber et al. (2007), ...
Amino acids week 7(mine new)
... • Amphoteric means can react with both acid and base . • pH below isoelectric point: • The amino acid is a base and accepts a proton from the the acid. • The amino acid is a positively charged ion. • pH above isoelectric point: • The amino acid is an acid and donates a proton to the base. • The amin ...
... • Amphoteric means can react with both acid and base . • pH below isoelectric point: • The amino acid is a base and accepts a proton from the the acid. • The amino acid is a positively charged ion. • pH above isoelectric point: • The amino acid is an acid and donates a proton to the base. • The amin ...
Determination of Cystein and Methionine by Oscillating Chemical
... complex mechanisms including autocatalytic step [1], such systems are usually referred to as “oscillating reactions”. Oscillating reactions can take place both in the liquid phase [2-4] and in the gaseous phase from heterogeneous catalytic systems [5]. Oscillating chemical reactions are always compl ...
... complex mechanisms including autocatalytic step [1], such systems are usually referred to as “oscillating reactions”. Oscillating reactions can take place both in the liquid phase [2-4] and in the gaseous phase from heterogeneous catalytic systems [5]. Oscillating chemical reactions are always compl ...
Chapter 13: Water and the Lithosphere Preview
... • Effects of acidification on water and land 13.1 The Earth as Acid-Base Reactor The earth is believed to have formed some 4.5 billion years ago from the coalescence of meteorites that circled the early sun. Heating from gravitational forces and nuclear decay melted the interior of the evolving pla ...
... • Effects of acidification on water and land 13.1 The Earth as Acid-Base Reactor The earth is believed to have formed some 4.5 billion years ago from the coalescence of meteorites that circled the early sun. Heating from gravitational forces and nuclear decay melted the interior of the evolving pla ...