avogadro exam 1994 - University of Waterloo
... This exam is being written by several thousand students. Please be sure that you follow the instructions below. We'll send you a report on your performance. Top performers are eligible for a prize. ...
... This exam is being written by several thousand students. Please be sure that you follow the instructions below. We'll send you a report on your performance. Top performers are eligible for a prize. ...
No Slide Title
... Increases with molecular size due to increased van der Waals’ forces. Alcohols have higher boiling points than similar molecular mass alkanes This is due to the added presence of inter-molecular hydrogen bonding. More energy is required to separate the molecules. ...
... Increases with molecular size due to increased van der Waals’ forces. Alcohols have higher boiling points than similar molecular mass alkanes This is due to the added presence of inter-molecular hydrogen bonding. More energy is required to separate the molecules. ...
The alcohols
... Increases with molecular size due to increased van der Waals’ forces. Alcohols have higher boiling points than similar molecular mass alkanes This is due to the added presence of inter-molecular hydrogen bonding. More energy is required to separate the molecules. ...
... Increases with molecular size due to increased van der Waals’ forces. Alcohols have higher boiling points than similar molecular mass alkanes This is due to the added presence of inter-molecular hydrogen bonding. More energy is required to separate the molecules. ...
Light color and different dyestuff
... wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation (light) differently from other wavelengths. Normal daylight, or white light, is a mixture of all the wavelengths to which we can respond and some to which we cannot, in particular the infra‐red and ultra‐violet rays. We respond to wavelengths between about ...
... wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation (light) differently from other wavelengths. Normal daylight, or white light, is a mixture of all the wavelengths to which we can respond and some to which we cannot, in particular the infra‐red and ultra‐violet rays. We respond to wavelengths between about ...
polymer
... • Amino acids condense to create an amide linkage. • The amide group that contains the two amino acids is called a peptide linkage. • Protein synthesis occurs by sequential condensation at the carboxylic end of the growing chain leading to a polypeptide. Chemistry, 2nd Canadian Edition ©2013 John Wi ...
... • Amino acids condense to create an amide linkage. • The amide group that contains the two amino acids is called a peptide linkage. • Protein synthesis occurs by sequential condensation at the carboxylic end of the growing chain leading to a polypeptide. Chemistry, 2nd Canadian Edition ©2013 John Wi ...
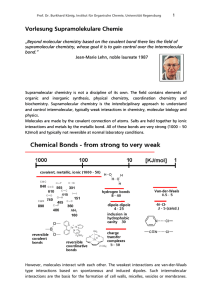
Vorlesung Supramolekulare Chemie
... Receptor molecule or guest binding site for intermolecular molecular recognition must be preorganized. The conformation and orientation of functional groups in the non-bound state should already be close to the one in the host-guest complex to minimize entropic loss. Simple non-covalent aggregates u ...
... Receptor molecule or guest binding site for intermolecular molecular recognition must be preorganized. The conformation and orientation of functional groups in the non-bound state should already be close to the one in the host-guest complex to minimize entropic loss. Simple non-covalent aggregates u ...
Chemical Reactions
... 1. Begin with atoms that appear in only one compound on the left and only one compound on the right. In the equation for the reaction of propane and oxygen, begin with either carbon or hydrogen 2. If an atom occurs as a free element—as for example, as Mg, Na, O2, or H2—balance this element last. 3. ...
... 1. Begin with atoms that appear in only one compound on the left and only one compound on the right. In the equation for the reaction of propane and oxygen, begin with either carbon or hydrogen 2. If an atom occurs as a free element—as for example, as Mg, Na, O2, or H2—balance this element last. 3. ...
Kinetics of the fading of phenolphthalein in alkaline solution
... One drop of diluted phenolphthalein solution is added to about half a cuvette of NaOH solution, the cuvette is inverted several times tomix, and the ahsarhanee is measured in the spectraphotometer at regular intervals of time. The exact volumes of NaOH and phenolphthalein solutions are not critical, ...
... One drop of diluted phenolphthalein solution is added to about half a cuvette of NaOH solution, the cuvette is inverted several times tomix, and the ahsarhanee is measured in the spectraphotometer at regular intervals of time. The exact volumes of NaOH and phenolphthalein solutions are not critical, ...
chm 205 - National Open University of Nigeria
... Many elements exist in more than one form. These forms are called allotropes, and the phenomenon is called allotropy. The two common allotropic forms of carbon, viz., diamond and graphite are well-known. These are, in fact, giant macromolecules consisting of C atoms linked by a network of covalent b ...
... Many elements exist in more than one form. These forms are called allotropes, and the phenomenon is called allotropy. The two common allotropic forms of carbon, viz., diamond and graphite are well-known. These are, in fact, giant macromolecules consisting of C atoms linked by a network of covalent b ...
CHAPTER 16
... Enthalpy of Reaction in Exothermic Reactions If a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is ignited, water will form and energy will be released explosively. The energy that is released comes from the reactants as they form products. Because energy is released, the reaction is exothermic, and the energy of ...
... Enthalpy of Reaction in Exothermic Reactions If a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen is ignited, water will form and energy will be released explosively. The energy that is released comes from the reactants as they form products. Because energy is released, the reaction is exothermic, and the energy of ...
Magic of Chemical Reactions 2. - mt
... 3. This is achieved by bringing reactants in contact with each other and then by supplying energy in the form of either heat, light or electricity. 4. This results in breaking of bonds in the reactants and rearrangement of atoms of reactants and formation of new bonds in the product. 5. Thus, a chem ...
... 3. This is achieved by bringing reactants in contact with each other and then by supplying energy in the form of either heat, light or electricity. 4. This results in breaking of bonds in the reactants and rearrangement of atoms of reactants and formation of new bonds in the product. 5. Thus, a chem ...
Equilibrium - Clayton State University
... - Many reactions do not go to completion - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
... - Many reactions do not go to completion - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry: The Hydrosphere
... a. __________________________ and __________________________ b. __________________________ and __________________________ c. __________________________ and __________________________ Note: H2O is amphoteric since it can behave as an acid or a base. CHEM 161: Chapter 4 v0916 ...
... a. __________________________ and __________________________ b. __________________________ and __________________________ c. __________________________ and __________________________ Note: H2O is amphoteric since it can behave as an acid or a base. CHEM 161: Chapter 4 v0916 ...
Chem 110 2014 - University of KwaZulu
... Brown, LeMay, Bursten, Murphy, Langford, Sagatys: Chemistry 2e © 2010 Pearson Australia ...
... Brown, LeMay, Bursten, Murphy, Langford, Sagatys: Chemistry 2e © 2010 Pearson Australia ...
Derivatization of polar compounds for GC - Sigma
... •Reaction mechanism: nucleophilic attack on the silicon atom in the silylating reagent •For completion of the reaction, the basicity of the leaving group on the silyating reagent (X), must be greater than the group to be replaced on the sample •Ease of silylation generally follows this trend: ...
... •Reaction mechanism: nucleophilic attack on the silicon atom in the silylating reagent •For completion of the reaction, the basicity of the leaving group on the silyating reagent (X), must be greater than the group to be replaced on the sample •Ease of silylation generally follows this trend: ...
Sample Midterm 1B
... 2. a. (1 Mark) Butanol, C4H9OH, Diethyl Ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3 and Pentane C5H12 all have similar molecular weights but Butanol has a much higher boiling point. What property of butanol would explain this boiling point difference? ...
... 2. a. (1 Mark) Butanol, C4H9OH, Diethyl Ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3 and Pentane C5H12 all have similar molecular weights but Butanol has a much higher boiling point. What property of butanol would explain this boiling point difference? ...
CBSE Living Science Chemistry Class X
... The above chemical equation is a skeletal chemical equation for the chemical reaction involved in the Activity 1 and is an unbalanced equation. By unbalanced equation, we mean that the number of atoms of each element on the left and right hand side of the arrow is not equal. There are two atoms of o ...
... The above chemical equation is a skeletal chemical equation for the chemical reaction involved in the Activity 1 and is an unbalanced equation. By unbalanced equation, we mean that the number of atoms of each element on the left and right hand side of the arrow is not equal. There are two atoms of o ...
Chem101, 2nd Major Exam, term061
... The hydrogen atom has only one orbital. The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical model, the ...
... The hydrogen atom has only one orbital. The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical model, the ...