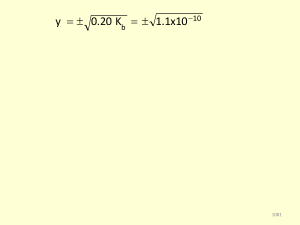Chapter 1 Chirality in clinical analysis 1.1. Introduction
... biochemical and biomedical research and in rational drug design and disease discovery [3]. The chemistry of tetravalent carbon, the central atom of organic molecules, allows it to have a planar or a three-dimensional structure, and can thereby generate stereoisomers. Chiral molecules are molecules w ...
... biochemical and biomedical research and in rational drug design and disease discovery [3]. The chemistry of tetravalent carbon, the central atom of organic molecules, allows it to have a planar or a three-dimensional structure, and can thereby generate stereoisomers. Chiral molecules are molecules w ...
09_Lecture
... • The equilibrium constant, K, defines the extent of a chemical reaction as a ratio of the concentration of the products to the concentration of the reactants. • If a chemical reaction at equilibrium is disturbed, the reaction can regain its equilibrium according to Le Châtelier’s principle by shift ...
... • The equilibrium constant, K, defines the extent of a chemical reaction as a ratio of the concentration of the products to the concentration of the reactants. • If a chemical reaction at equilibrium is disturbed, the reaction can regain its equilibrium according to Le Châtelier’s principle by shift ...
(C 2 H 5 ) 2 NH diethylamine, 2° amine
... The LONE PAIR on the nitrogen atom in 1°, 2° and 3° amines makes them ... LEWIS BASES - they can be lone pair donors ...
... The LONE PAIR on the nitrogen atom in 1°, 2° and 3° amines makes them ... LEWIS BASES - they can be lone pair donors ...
No Slide Title
... The LONE PAIR on the nitrogen atom in 1°, 2° and 3° amines makes them ... LEWIS BASES - they can be lone pair donors ...
... The LONE PAIR on the nitrogen atom in 1°, 2° and 3° amines makes them ... LEWIS BASES - they can be lone pair donors ...
FREE Sample Here
... Saturated fats _______ than unsaturated fats. contain more water have more glycerol have more single carbon-carbon bonds have fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms ...
... Saturated fats _______ than unsaturated fats. contain more water have more glycerol have more single carbon-carbon bonds have fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms ...
advanced placement chemistry workbook and note set
... calculate solution concentration, and determine volumes of solutions required based upon concentration data ...
... calculate solution concentration, and determine volumes of solutions required based upon concentration data ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylations of N,O- and
... enantioselective alkylation of N,O- and N, N-acetals. Stable, readily available acetals la-i can be alkylated with a variety of nucleophiles in up to 96% ee with as little as 1 mol % of catalyst 2. This research has many practical applications including the large scale synthesis of ~,-oxo-t~-amino a ...
... enantioselective alkylation of N,O- and N, N-acetals. Stable, readily available acetals la-i can be alkylated with a variety of nucleophiles in up to 96% ee with as little as 1 mol % of catalyst 2. This research has many practical applications including the large scale synthesis of ~,-oxo-t~-amino a ...
Chapter 8 and 9 – Energy Balances
... ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) is the change in enthalpy that results from dissolving one mole of solute in r moles of liquid solvent at constant T. In the limit when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in an infinitely large amount of solvent, ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) approaches a limiting value known as the heat of solution at ...
... ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) is the change in enthalpy that results from dissolving one mole of solute in r moles of liquid solvent at constant T. In the limit when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in an infinitely large amount of solvent, ∆ Hˆ s (T , r ) approaches a limiting value known as the heat of solution at ...
The O 1s and V 2p X-ray Absorption Spectra of Vanadium Oxides
... O 1s and V 2p XAS spectra of several vanadium oxides with diffxent formal valences and chemical environments. Tliese materials were selected among many others transition-metal oxides because they present particularly interesting electric and magnetic properties. Most of the experimental studies done ...
... O 1s and V 2p XAS spectra of several vanadium oxides with diffxent formal valences and chemical environments. Tliese materials were selected among many others transition-metal oxides because they present particularly interesting electric and magnetic properties. Most of the experimental studies done ...
Question Bank - Edudel.nic.in
... The well known mineral fluorite is chemically calcium fluoride. It is known that in one unit cell of this mineral there are 4 Ca2+ ions and 8F– ions and that Ca2+ ions are arranged in a fcc lattice. The F– ions fill all the tetrahedral holes in the fcc lattice of Ca2+ ions. The edge of the unit cell ...
... The well known mineral fluorite is chemically calcium fluoride. It is known that in one unit cell of this mineral there are 4 Ca2+ ions and 8F– ions and that Ca2+ ions are arranged in a fcc lattice. The F– ions fill all the tetrahedral holes in the fcc lattice of Ca2+ ions. The edge of the unit cell ...
Activation of Alcohols Toward Nucleophilic Substitution: Conversion
... alcohols are converted to saturated alkyl halides.6 Because the use of HCl shows poor results for the conversion of an alcohol to an alkyl chloride, a catalyst such as the zinc used in the Lucas reagent is required. This reaction was improved by adding zinc chloride and had the advantage of milder c ...
... alcohols are converted to saturated alkyl halides.6 Because the use of HCl shows poor results for the conversion of an alcohol to an alkyl chloride, a catalyst such as the zinc used in the Lucas reagent is required. This reaction was improved by adding zinc chloride and had the advantage of milder c ...
PDF of this page - UIS Catalog
... acid-base concepts, periodicity and solution chemistry. The chemical principles will be demonstrated with laboratory exercises that involve the use of materials and methods common to the ordinary kitchen. Course Information: This course cannot be counted toward any science major or minor. The course ...
... acid-base concepts, periodicity and solution chemistry. The chemical principles will be demonstrated with laboratory exercises that involve the use of materials and methods common to the ordinary kitchen. Course Information: This course cannot be counted toward any science major or minor. The course ...
Fundamentals Diagnostic Quiz
... a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. *c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. d) A compound is a specific combination of atoms of more than one element. e) In a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created ...
... a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. *c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. d) A compound is a specific combination of atoms of more than one element. e) In a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created ...
Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... disadvantage of this model. - Valence bond theory is based on the hybridization of atomic orbitals. - Hybridization: the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom (generally the central atom) to form a set of hybrid orbitals responsible for forming single, double, & triple bonds. - Hybridization is made ...
... disadvantage of this model. - Valence bond theory is based on the hybridization of atomic orbitals. - Hybridization: the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom (generally the central atom) to form a set of hybrid orbitals responsible for forming single, double, & triple bonds. - Hybridization is made ...
A study on the nickel(II)
... square-planar. Simultaneously, two protons were released to form [NiH 22 L]. The involvement of other fam nitrogens in complex formation seemed to be obvious but no detailed analysis of the binding sites for either of the two Ni(II) complexes was presented [1]. In this work, a continuation of our ea ...
... square-planar. Simultaneously, two protons were released to form [NiH 22 L]. The involvement of other fam nitrogens in complex formation seemed to be obvious but no detailed analysis of the binding sites for either of the two Ni(II) complexes was presented [1]. In this work, a continuation of our ea ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...