Writing Chemical Equations
... 2Al(s) + 3Br2(l) → 2 AlBr3 • The physical state of each substance can be indicated by using (s) for solid, (l) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for an aqueous solution. ...
... 2Al(s) + 3Br2(l) → 2 AlBr3 • The physical state of each substance can be indicated by using (s) for solid, (l) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for an aqueous solution. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. • Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. • This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
... • Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. • Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. • This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
Year 8 Science Assessment Point 2
... all atoms in a compound 3. Limiting reactants: A reactant that is used up in a chemical reaction and stops it from continuing 4. Chromatography: A technique where a mixture is separated For example: • Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid. • When the reaction is over: Magnesium is the limiting rea ...
... all atoms in a compound 3. Limiting reactants: A reactant that is used up in a chemical reaction and stops it from continuing 4. Chromatography: A technique where a mixture is separated For example: • Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid. • When the reaction is over: Magnesium is the limiting rea ...
Study_guide_2010-01
... This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goa ...
... This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goa ...
Chemistry
... Colligative properties. Raoult’s law, relative lowering of vapour pressure, its relation to molecular weight of non-volatile solute. Elevation of boiling point and depression of freezing point. Derivation of relation between molecular weight and elevation in boiling point and depression in freezing ...
... Colligative properties. Raoult’s law, relative lowering of vapour pressure, its relation to molecular weight of non-volatile solute. Elevation of boiling point and depression of freezing point. Derivation of relation between molecular weight and elevation in boiling point and depression in freezing ...
green chemistry
... (petroleum, natural gas, or coal) or are mined. 11. Use catalysts, not stoichiometric reagents: Minimize waste by using catalytic reactions. Catalysts are used in small amounts and can carry out a single reaction many times. They are preferable to stoichiometric reagents, which are used in excess an ...
... (petroleum, natural gas, or coal) or are mined. 11. Use catalysts, not stoichiometric reagents: Minimize waste by using catalytic reactions. Catalysts are used in small amounts and can carry out a single reaction many times. They are preferable to stoichiometric reagents, which are used in excess an ...
Chemical Equations and Tests for anions
... Law of Conservation of Matter In any chemical reaction matter is neither created nor destroyed but merely changes from one form to another If there is a particular number of atoms at the start of a reaction then there must be the same number of atoms at the end of the reaction ...
... Law of Conservation of Matter In any chemical reaction matter is neither created nor destroyed but merely changes from one form to another If there is a particular number of atoms at the start of a reaction then there must be the same number of atoms at the end of the reaction ...
Key - Sardis Secondary
... 15. What is the relationship between the kinetic energy of molecules and their physical state? ...
... 15. What is the relationship between the kinetic energy of molecules and their physical state? ...
Alkenes - Calderglen High School
... 10. In industry, alcohols can be produced from alkenes as shown in the example below. ...
... 10. In industry, alcohols can be produced from alkenes as shown in the example below. ...
Nahla abd elmoaty mohamed
... Chemical and biological studies on some Heterocyclic nitrogen derivatives ...
... Chemical and biological studies on some Heterocyclic nitrogen derivatives ...
Chemistry Review
... Organic compounds: “chemicals of life”, contain a lot of Carbon ex. C6H12O6 (usually also hydrogen, but not always) Hydrocarbons: only contain C and H, ex. CH4 Inorganic compounds do not contain Carbon ex. HCl ...
... Organic compounds: “chemicals of life”, contain a lot of Carbon ex. C6H12O6 (usually also hydrogen, but not always) Hydrocarbons: only contain C and H, ex. CH4 Inorganic compounds do not contain Carbon ex. HCl ...
Macromolecule Wkst
... Below is an example of dehydration synthesis. In dehydration synthesis, a hydrogen atom from one molecule joins with a hydroxyl group (-OH) from another molecule to form water, leaving two molecules bonded to the same oxygen atom. For example, when glucose and glucose combine by dehydration synthesi ...
... Below is an example of dehydration synthesis. In dehydration synthesis, a hydrogen atom from one molecule joins with a hydroxyl group (-OH) from another molecule to form water, leaving two molecules bonded to the same oxygen atom. For example, when glucose and glucose combine by dehydration synthesi ...
National 5 Whole Course Revision Questions Unit 1 Chemical
... 1. Describe how temperature, concentration and particle size affect the rate of a chemical reaction- mention collision theory in your answer. 2. a) How do catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction? b) Name the types of catalysts and describe how they differ from each other? 3. What is an enzy ...
... 1. Describe how temperature, concentration and particle size affect the rate of a chemical reaction- mention collision theory in your answer. 2. a) How do catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction? b) Name the types of catalysts and describe how they differ from each other? 3. What is an enzy ...
Option D: Evolution
... inheritance possible The packaging of these molecules into membranes with an internal chemistry different from their surroundings. ...
... inheritance possible The packaging of these molecules into membranes with an internal chemistry different from their surroundings. ...
Unit 13 Worksheet Answers
... They each cause more collisions so the reaction can happen faster. The temperature also causes the collisions to happen with more energy so there are more effective collisions. 4) It has been found that rates are more rapid at the beginning of a reaction than toward the end, assuming the temperature ...
... They each cause more collisions so the reaction can happen faster. The temperature also causes the collisions to happen with more energy so there are more effective collisions. 4) It has been found that rates are more rapid at the beginning of a reaction than toward the end, assuming the temperature ...
Chemistry of Life - juan-roldan
... ◦Are two or more forms of atoms of the same element ◦Contain the same number of protons and electrons, but the number of neutrons ...
... ◦Are two or more forms of atoms of the same element ◦Contain the same number of protons and electrons, but the number of neutrons ...
04 Carbon
... – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. – This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
... – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. – This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
Matter, Mass and Weight
... Law of conservation of energy Energy of an isolated system always remains constant. Energy may be converted from one form to another, but cannot be created or destroyed. A system can exchange its energy with its surrounding in two forms: heat and work. When a gas is in contact with an object at high ...
... Law of conservation of energy Energy of an isolated system always remains constant. Energy may be converted from one form to another, but cannot be created or destroyed. A system can exchange its energy with its surrounding in two forms: heat and work. When a gas is in contact with an object at high ...
BiochemPPt
... hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals interactions among hydrophobic R groups. ...
... hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals interactions among hydrophobic R groups. ...
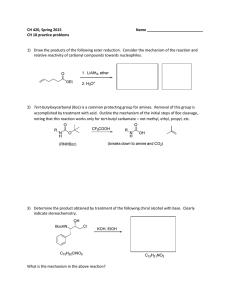
CH 420, Spring 2015 Name ___________________________ CH 18 practice problems
... noting that this reaction works only for tert-butyl carbamate – not methyl, ethyl, propyl, etc. ...
... noting that this reaction works only for tert-butyl carbamate – not methyl, ethyl, propyl, etc. ...