Organic Chemistry
... • The low density fractions are thin and light coloured, the high density fractions are ‘viscous’ and dark ...
... • The low density fractions are thin and light coloured, the high density fractions are ‘viscous’ and dark ...
organic chemistry i - cm2113
... The goal of the course is to have the student acquire a basic knowledge of organic chemistry beginning with bonding and molecular structure. This will be supplemented and emphasized using nomenclature of functional groups and organic compounds. Basic principles of organic reactions will be introduce ...
... The goal of the course is to have the student acquire a basic knowledge of organic chemistry beginning with bonding and molecular structure. This will be supplemented and emphasized using nomenclature of functional groups and organic compounds. Basic principles of organic reactions will be introduce ...
Unit 4 Evolution
... Let’s review yesterday’s activities and begin a couple of review activities over energy and properties of matter. ...
... Let’s review yesterday’s activities and begin a couple of review activities over energy and properties of matter. ...
2014MSC(ORGANIC(CHEMISTRY!
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
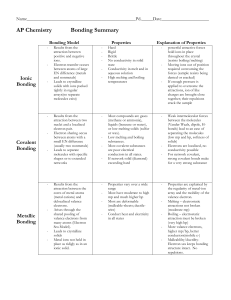
Types of Bonding Summary
... (malleable-sheets; ductilewire) Conduct heat and electricity in all states ...
... (malleable-sheets; ductilewire) Conduct heat and electricity in all states ...
Chapter 4
... which has an H and an X attached to it. The arrangement with both Xs on the same side of the double bond is called a cis isomer; the arrangement with the Xs on opposite sides is called a trans isomer. o The biochemistry of vision involves a light-induced change in the structure of rhodopsin in the r ...
... which has an H and an X attached to it. The arrangement with both Xs on the same side of the double bond is called a cis isomer; the arrangement with the Xs on opposite sides is called a trans isomer. o The biochemistry of vision involves a light-induced change in the structure of rhodopsin in the r ...
Chapter 3 Lecture
... only act as storage depots. • More recent data, however, support the idea that lipid droplets are highly dynamic organelles which participate in several cellular processes and interact with various other cellular compartments. ...
... only act as storage depots. • More recent data, however, support the idea that lipid droplets are highly dynamic organelles which participate in several cellular processes and interact with various other cellular compartments. ...
Unit 2 Biochemistry Chp 4 Organic Chemistry Notes
... These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o ...
... These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o ...
with answers
... Pauli Principle: No two electrons in an atom can have all four quantum numbers identical. Or an orbital can be occupied by at most two electrons, which must then have antiparallel spin. Hund’s Rule: Orbitals will be filled with electrons in order of increasing energy; orbitals of the same energy wil ...
... Pauli Principle: No two electrons in an atom can have all four quantum numbers identical. Or an orbital can be occupied by at most two electrons, which must then have antiparallel spin. Hund’s Rule: Orbitals will be filled with electrons in order of increasing energy; orbitals of the same energy wil ...
STRUCTURE, INTERMOLECULAR FORCES AND SOLUBILITY
... London Dispersion Forces (LDF) = weakest intermolecular force. ...
... London Dispersion Forces (LDF) = weakest intermolecular force. ...
ACA__Beat_sheet_bonding_2016
... thermal and electrical conductivity, malleability, and ductility ...
... thermal and electrical conductivity, malleability, and ductility ...
Document
... alkanes, alkenes, and aromatic compounds) have many highly useful properties and are found in many everyday products. Some, particularly halogenated aromatic compounds, are very persistent in the environment. ...
... alkanes, alkenes, and aromatic compounds) have many highly useful properties and are found in many everyday products. Some, particularly halogenated aromatic compounds, are very persistent in the environment. ...
doc - STAO
... produced by a chemical reaction by water displacement, using a known (e.g., the molar volume of hydrogen quantity of calcium carbide and the gas from the reaction of magnesium molar mass determined. with hydrochloric acid) [PR, AI] The purity of the calcium carbide can then be determined by comparin ...
... produced by a chemical reaction by water displacement, using a known (e.g., the molar volume of hydrogen quantity of calcium carbide and the gas from the reaction of magnesium molar mass determined. with hydrochloric acid) [PR, AI] The purity of the calcium carbide can then be determined by comparin ...
Chapter 22/23-Organic Chemistry
... 2. Draw the following organic compounds: a. 2,4,4-trimethyl-1-pentene b. 1,2,3-triphenylheptane c. 1,3-dibromo-2-chloro-5-methylcylcohexane d. 3,3-difluoro-1,4-pentadiene e. 4–ethyl–2,6–dimethyl–2–heptene. f. 1,1-dichlorobenzene 3. Based on what you know about the ability of a carbon-carbon double b ...
... 2. Draw the following organic compounds: a. 2,4,4-trimethyl-1-pentene b. 1,2,3-triphenylheptane c. 1,3-dibromo-2-chloro-5-methylcylcohexane d. 3,3-difluoro-1,4-pentadiene e. 4–ethyl–2,6–dimethyl–2–heptene. f. 1,1-dichlorobenzene 3. Based on what you know about the ability of a carbon-carbon double b ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 17. State the Variation Theorem and prove it with a suitable example. ...
... 17. State the Variation Theorem and prove it with a suitable example. ...
Energy Matters Flashcards
... For water it has a value of 4.18 kJ kg-1 ⁰C-1. In other words, when 1 kg of water absorbs 4.18 kJ of heat its temperature will rise by 1⁰C. These are the intermolecular forces of attraction which result from the electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles; they are caused ...
... For water it has a value of 4.18 kJ kg-1 ⁰C-1. In other words, when 1 kg of water absorbs 4.18 kJ of heat its temperature will rise by 1⁰C. These are the intermolecular forces of attraction which result from the electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles; they are caused ...
functional groups - U of L Class Index
... 2. Determine the total number of valence electrons. 3. Use one pair of electrons to make a single bond between each pair of bonded atoms. 4. Use any remaining electrons as lone pairs around each terminal atom (except H) so that each terminal atom has a complete octet, ...
... 2. Determine the total number of valence electrons. 3. Use one pair of electrons to make a single bond between each pair of bonded atoms. 4. Use any remaining electrons as lone pairs around each terminal atom (except H) so that each terminal atom has a complete octet, ...
CHEM 235 Syllabus
... √ Main reaction: write the main reaction involved in each experiment where appropriate √ Physical constants of main reagents: list all the key reagents in a table format; look up their molecular weight (MW), boiling point if any (b.p.), melting point (m.p.), and density. (These numbers will help you ...
... √ Main reaction: write the main reaction involved in each experiment where appropriate √ Physical constants of main reagents: list all the key reagents in a table format; look up their molecular weight (MW), boiling point if any (b.p.), melting point (m.p.), and density. (These numbers will help you ...
020H Product Info
... COOH-COOH crosslinking. GDH-H6/D6 is an isotopically-coded Glutaric acid 1,5-DiHydrazide which can form crosslinks between carboxy-groups when used together with carboxy-group activating reagents such as EDC or DMTMM [1,2]. Light (H6) and heavy (D6) forms of the reagent differ by 6 deuterium atoms i ...
... COOH-COOH crosslinking. GDH-H6/D6 is an isotopically-coded Glutaric acid 1,5-DiHydrazide which can form crosslinks between carboxy-groups when used together with carboxy-group activating reagents such as EDC or DMTMM [1,2]. Light (H6) and heavy (D6) forms of the reagent differ by 6 deuterium atoms i ...