The Egyptian American International School
... Schrodinger’s wave mechanical model assumes the electron has both particle and wave properties and describes electrons as occupying orbitals. 1. The orbitals are different from the Bohr orbits. 2. Probability maps indicate the likelihood of finding the electron at a given point in space. 3. The si ...
... Schrodinger’s wave mechanical model assumes the electron has both particle and wave properties and describes electrons as occupying orbitals. 1. The orbitals are different from the Bohr orbits. 2. Probability maps indicate the likelihood of finding the electron at a given point in space. 3. The si ...
slides introducing IR/Raman of proteins
... • Long wavelength radiowaves are of low energy that is sufficient to ‘flip’ the spin of nuclei in a magnetic field (NMR). Nuclei interact weakly so spectral transitions between single, well defined energy levels are very sharp and well resolved. NMR is a vital technique for biological structure stud ...
... • Long wavelength radiowaves are of low energy that is sufficient to ‘flip’ the spin of nuclei in a magnetic field (NMR). Nuclei interact weakly so spectral transitions between single, well defined energy levels are very sharp and well resolved. NMR is a vital technique for biological structure stud ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 12 a. Mention in few lines, the best way of studying H2 molecule by spectroscopic technique? 12 b. Explain the theory of pure rotational Raman spectra of a linear molecule (2+ 5.5) 13 Write a note on Dissociation and energy and dissociation products. Show that γ max = (1/2xe )-1, where xe is anhormo ...
... 12 a. Mention in few lines, the best way of studying H2 molecule by spectroscopic technique? 12 b. Explain the theory of pure rotational Raman spectra of a linear molecule (2+ 5.5) 13 Write a note on Dissociation and energy and dissociation products. Show that γ max = (1/2xe )-1, where xe is anhormo ...
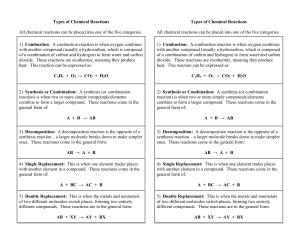
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
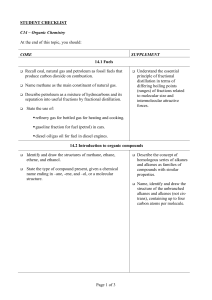
Unit 1 Test: Organic Chemistry Name
... d. Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) can also be used to test for unsaturated hydrocarbons. If KMnO4(aq) is added to ethane, the colour of the KMnO4 solution changes from purple to clear. What type of reaction has occurred? (1 mark) ...
... d. Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) can also be used to test for unsaturated hydrocarbons. If KMnO4(aq) is added to ethane, the colour of the KMnO4 solution changes from purple to clear. What type of reaction has occurred? (1 mark) ...
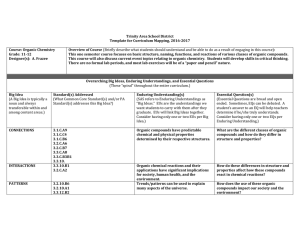
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Curriculum
... (SAS refers to Enduring Understandings as “Big Ideas.” EUs are the understandings we want students to carry with them after they graduate. EUs will link Big Ideas together. Consider having only one or two EUs per Big ...
... (SAS refers to Enduring Understandings as “Big Ideas.” EUs are the understandings we want students to carry with them after they graduate. EUs will link Big Ideas together. Consider having only one or two EUs per Big ...
Ch9
... 2. Draw all the possible resonance structures (indicated in parentheses) for each of these molecules. a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. Draw all the possible resonance structures (indicated in parentheses) for each of these molecules. a. b. c. d. ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture Outline
... Such spontaneous synthesis of organic compounds may have been an early stage in the origin of life. ...
... Such spontaneous synthesis of organic compounds may have been an early stage in the origin of life. ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture Outline
... Such spontaneous synthesis of organic compounds may have been an early stage in the origin of life. ...
... Such spontaneous synthesis of organic compounds may have been an early stage in the origin of life. ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Amino acids have the ability to link together and form proteins. Amino acids have carboxylic acid groups Amino acids have a base and an acid in the same molecule There are about 20 amino acids each of which has a different sidechain that yield different properties. All of the amino acids are nonpola ...
... Amino acids have the ability to link together and form proteins. Amino acids have carboxylic acid groups Amino acids have a base and an acid in the same molecule There are about 20 amino acids each of which has a different sidechain that yield different properties. All of the amino acids are nonpola ...
AP Ch. 25 Notes
... The Stabilities of Organic Molecules • Remember: - Bond strength increases from single to double to triple bond. - Bond length decreases in the same direction. - Strongest & shortest bond C ≡ C • Carbon and hydrogen have very similar electronegativities, so the C-H bond is essentially non-polar. ...
... The Stabilities of Organic Molecules • Remember: - Bond strength increases from single to double to triple bond. - Bond length decreases in the same direction. - Strongest & shortest bond C ≡ C • Carbon and hydrogen have very similar electronegativities, so the C-H bond is essentially non-polar. ...
H bonds - s3.amazonaws.com
... • new base added to sugar of previous base • polymer grows in one direction ...
... • new base added to sugar of previous base • polymer grows in one direction ...
organic chemistry i
... Write a neutral molecule CH2 assuming that the valence electrons of carbon are configured as follows: 2s2 2p2 Do you expect this molecule to be stable or not stable? Explain your answer. What model did you use to come up with your answer? ...
... Write a neutral molecule CH2 assuming that the valence electrons of carbon are configured as follows: 2s2 2p2 Do you expect this molecule to be stable or not stable? Explain your answer. What model did you use to come up with your answer? ...
C14_-_Organic_Chemistry
... State the type of compound present, given a chemical name ending in –ane, -ene, and –ol, or a molecular structure. ...
... State the type of compound present, given a chemical name ending in –ane, -ene, and –ol, or a molecular structure. ...
Topic Guide
... 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and β -Elimination 9.1 Nucleophilic Substitution in Haloalkanes 9.2 Mechanisms of Nucleophilic Aliphatic Substitution 9.3 Experimental Evidence for SN1 and SN2 Mechanisms 9.4 Analysis of Several Nucleophilic Sub Rxns ...
... 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and β -Elimination 9.1 Nucleophilic Substitution in Haloalkanes 9.2 Mechanisms of Nucleophilic Aliphatic Substitution 9.3 Experimental Evidence for SN1 and SN2 Mechanisms 9.4 Analysis of Several Nucleophilic Sub Rxns ...
Unit 01 Qual Chem
... Physical Change = a change that does not alter the identity of a substance (shape, size, state) Chemical Change = a change in which one or more substances are converted into substances with different chemical properties ...
... Physical Change = a change that does not alter the identity of a substance (shape, size, state) Chemical Change = a change in which one or more substances are converted into substances with different chemical properties ...
Chemistry 223 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Ala-Gly-Glu-Ala denotes the order in which the amino acids are connected. What is meant by secondary structure? Give an example. Secondary structure is the orientation the primary structure obtains (alpha helix or ...
... Ala-Gly-Glu-Ala denotes the order in which the amino acids are connected. What is meant by secondary structure? Give an example. Secondary structure is the orientation the primary structure obtains (alpha helix or ...
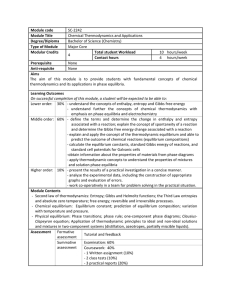
Module code SC-2242 Module Title Chemical Thermodynamics and
... On successful completion of this module, a student will be expected to be able to: Lower order: 30% - understand the concepts of enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy - understand further the concepts of chemical thermodynamics with emphasis on phase equilibria and electrochemistry M ...
... On successful completion of this module, a student will be expected to be able to: Lower order: 30% - understand the concepts of enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy - understand further the concepts of chemical thermodynamics with emphasis on phase equilibria and electrochemistry M ...
Calculating Percent Yield
... 3. Divide the number of grams of product obtained experimentally, by the number of grams obtained in the theoretical yield calculations and multiply by 100 to calculate the percent yield. Example: Assume 2.96g of salicylic acid was obtained experimentally. ...
... 3. Divide the number of grams of product obtained experimentally, by the number of grams obtained in the theoretical yield calculations and multiply by 100 to calculate the percent yield. Example: Assume 2.96g of salicylic acid was obtained experimentally. ...
Chapter 14 Chemical Reactions
... reacted in a closed container, you can show that the mass before and after the reaction is the same. ...
... reacted in a closed container, you can show that the mass before and after the reaction is the same. ...
3.6 Organic analysis
... 3) This molecule is cyclic and contains 6 carbon atoms. Use this information and the IR sepctra below to suggest a structure: ...
... 3) This molecule is cyclic and contains 6 carbon atoms. Use this information and the IR sepctra below to suggest a structure: ...