University Studies Chem. 414 Math
... chemistry deals with the physical principles underlying chemistry and seeks to account for the properties of matter (such as atoms, electrons, and energy) in terms of fundamental concepts. It provides the basic framework for branches of chemistry such as inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry, bioch ...
... chemistry deals with the physical principles underlying chemistry and seeks to account for the properties of matter (such as atoms, electrons, and energy) in terms of fundamental concepts. It provides the basic framework for branches of chemistry such as inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry, bioch ...
CHE 297 Organic Workshop
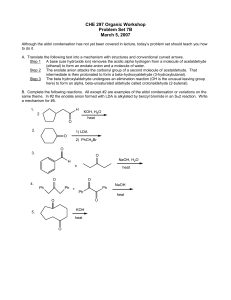
... Problem Set 7B March 5, 2007 Although the aldol condensation has not yet been covered in lecture, today’s problem set should teach you how to do it. A. Translate the following text into a mechanism with structures and conventional curved arrows. Step 1 A base (use hydroxide ion) removes the acidic a ...
... Problem Set 7B March 5, 2007 Although the aldol condensation has not yet been covered in lecture, today’s problem set should teach you how to do it. A. Translate the following text into a mechanism with structures and conventional curved arrows. Step 1 A base (use hydroxide ion) removes the acidic a ...
RXN-4-STUDENTS - Rothschild Science
... 4. What kind of quantitative observations would be helpful? ...
... 4. What kind of quantitative observations would be helpful? ...
Reaction rate and activation energy of the acidolysis
... energy activates the molecules (loosens bonds, polarisation etc.) so that they can react. The portion of molecules with this increased energy content increases with increasing temperature. The greater the portion of the molecules capable of reaction, the more molecules that will react, and so the hi ...
... energy activates the molecules (loosens bonds, polarisation etc.) so that they can react. The portion of molecules with this increased energy content increases with increasing temperature. The greater the portion of the molecules capable of reaction, the more molecules that will react, and so the hi ...
Lecture #
... This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goa ...
... This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document will be updated throughout the term. The goa ...
Properties of Hydrocarbons
... Where an atom or group of atoms is displaced by an atom or group of atoms CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr Non specific reaction. Can not control which hydrogen is substituted or how many are substituted CH3Br + Br2 → CH2Br2 + HBr ...
... Where an atom or group of atoms is displaced by an atom or group of atoms CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr Non specific reaction. Can not control which hydrogen is substituted or how many are substituted CH3Br + Br2 → CH2Br2 + HBr ...
Chapter 2
... electrons is shared Double covalent bond – 2 pairs of electrons shared Triple covalent bond – 3 pairs of electrons shared ...
... electrons is shared Double covalent bond – 2 pairs of electrons shared Triple covalent bond – 3 pairs of electrons shared ...
Test 4
... Au), calculate effective nuclear charge, identify number of valence electrons of any atom in s or p block, write electron configuration of ions. Chapter 9 1) Define, identify and/or give examples of: types of chemical bonds, ionic bond, covalent bond, metallic bonding, Lewis Dot Structure, Electron ...
... Au), calculate effective nuclear charge, identify number of valence electrons of any atom in s or p block, write electron configuration of ions. Chapter 9 1) Define, identify and/or give examples of: types of chemical bonds, ionic bond, covalent bond, metallic bonding, Lewis Dot Structure, Electron ...
F324 summary - Macmillan Academy
... • Benzene, C6H6, consists of a sigma-bonded framework of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Above and below the plane of atoms is a p-bond, which consists of a delocalised electron cloud. • The Kekule structure of benzene assumes that all the bonds are localised i.e. cannot move. However, evidence to supp ...
... • Benzene, C6H6, consists of a sigma-bonded framework of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Above and below the plane of atoms is a p-bond, which consists of a delocalised electron cloud. • The Kekule structure of benzene assumes that all the bonds are localised i.e. cannot move. However, evidence to supp ...
Day 8
... 12. Now, have each member of your group take a carbon atom and add 4 bonds. Add a hydrogen, chlorine (green), bromine (orange) and iodine (purple) to each stick. Compare your molecules by trying to superimpose them on each other (all atoms line up when one molecule is placed over the other). Did any ...
... 12. Now, have each member of your group take a carbon atom and add 4 bonds. Add a hydrogen, chlorine (green), bromine (orange) and iodine (purple) to each stick. Compare your molecules by trying to superimpose them on each other (all atoms line up when one molecule is placed over the other). Did any ...
Mass Spectroscopy
... Separation of Ions • Only the cations are deflected by the magnetic field. • Amount of deflection depends on m/z. • The detector signal is proportional to the number of ions hitting it. • By varying the magnetic field, ions of all masses are collected and counted. => ...
... Separation of Ions • Only the cations are deflected by the magnetic field. • Amount of deflection depends on m/z. • The detector signal is proportional to the number of ions hitting it. • By varying the magnetic field, ions of all masses are collected and counted. => ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section
... 2. Each carbon atom has ______________________ valence electrons. 3. Each carbon atom can make a total of ______________________ bonds. 4. Models of carbon backbones show how ______________________. 5. A covalently bonded compound that contains carbon is called a(n) ______________________. Match the ...
... 2. Each carbon atom has ______________________ valence electrons. 3. Each carbon atom can make a total of ______________________ bonds. 4. Models of carbon backbones show how ______________________. 5. A covalently bonded compound that contains carbon is called a(n) ______________________. Match the ...
Unit 4 test review Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration What is an
... 2. Name at least two organisms that obtain their energy through autotrophic nutrition. 3. What is a heterotroph? 4. Name at least two organisms that obtain their energy through heterotrophic nutrition. 5. Write the chemical equation for Photosynthesis: ...
... 2. Name at least two organisms that obtain their energy through autotrophic nutrition. 3. What is a heterotroph? 4. Name at least two organisms that obtain their energy through heterotrophic nutrition. 5. Write the chemical equation for Photosynthesis: ...
Chapter 1: Chemistry and You
... 3. Describe the basic structure of the atom in the modern atomic theory (be able to label protons, neutrons, electrons, and the nucleus) (Ch. 3): ...
... 3. Describe the basic structure of the atom in the modern atomic theory (be able to label protons, neutrons, electrons, and the nucleus) (Ch. 3): ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... C) Two molecules of HCl are formed in the reaction. D) One molecule of hydrogen contains 2 atoms. E) This reaction is an example of a decomposition reaction. 18) AB → A + B is to decomposition as A + B → AB is to A) synthesis. B) replacement. C) exchange. D) metabolism. E) combustion. ...
... C) Two molecules of HCl are formed in the reaction. D) One molecule of hydrogen contains 2 atoms. E) This reaction is an example of a decomposition reaction. 18) AB → A + B is to decomposition as A + B → AB is to A) synthesis. B) replacement. C) exchange. D) metabolism. E) combustion. ...
PowerPoint
... • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. – Mass is resistance to change in motion along a smooth and level surface. – Volume – measure of 3D space ...
... • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. – Mass is resistance to change in motion along a smooth and level surface. – Volume – measure of 3D space ...
the Organic Regents Review Worksheet with answers.
... D. fermentation 7. In which reaction is soap a product? A. addition C. saponification B. substitution D. polymerization 8. A double carbon-carbon bond is found in a molecule of A. pentane C. pentyne B. pentene D. pentanol 9. The compounds 2-butanol and 2-butene both contain A. double bonds, only C. ...
... D. fermentation 7. In which reaction is soap a product? A. addition C. saponification B. substitution D. polymerization 8. A double carbon-carbon bond is found in a molecule of A. pentane C. pentyne B. pentene D. pentanol 9. The compounds 2-butanol and 2-butene both contain A. double bonds, only C. ...
Just Enough Chemistry for Through Genetics
... – One atom holds e-’s closer (electronegativity) – H2O O ...
... – One atom holds e-’s closer (electronegativity) – H2O O ...
Ch. 4 notes
... Such spontaneous synthesis of organic compounds may have been an early stage in the origin of life. ...
... Such spontaneous synthesis of organic compounds may have been an early stage in the origin of life. ...