BY 124 Worksheet #16 Answers Short Answer Questions What
... Means swift birth o Males do have oxytocinimportant in testes because it causes muscle contractionmove sperm through testes so it can be ejaculated ...
... Means swift birth o Males do have oxytocinimportant in testes because it causes muscle contractionmove sperm through testes so it can be ejaculated ...
01 - Fort Bend ISD
... _____________________. 13. The pituitary releases _____________________. 14. The thyroid releases _____________________, which increases cell activity. 15. _____________________ stimulate the hypothalamus to stop producing TRH. MAIN IDEA: Hormonal imbalances can cause serious illness. Fill in the bl ...
... _____________________. 13. The pituitary releases _____________________. 14. The thyroid releases _____________________, which increases cell activity. 15. _____________________ stimulate the hypothalamus to stop producing TRH. MAIN IDEA: Hormonal imbalances can cause serious illness. Fill in the bl ...
The anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
... • Hypothalamic neurons communicate with the anterior pituitary by chemical signals called releasing factors and release inhibiting factors. In almost all cases, these are small peptides. ...
... • Hypothalamic neurons communicate with the anterior pituitary by chemical signals called releasing factors and release inhibiting factors. In almost all cases, these are small peptides. ...
10/2 SI A ECL 365 Endocrine The endocrine system works with the
... i. Maturation of mammary glands, mild production, nest building, protection of young Name and describe the hormones stored in the posterior pituitary. a. Oxytocin i. Uterine contractions in mammals, milk release 1. can stimulate labor b. Vasopressin (also ADH) i. Regulates water loss by kidneys ...
... i. Maturation of mammary glands, mild production, nest building, protection of young Name and describe the hormones stored in the posterior pituitary. a. Oxytocin i. Uterine contractions in mammals, milk release 1. can stimulate labor b. Vasopressin (also ADH) i. Regulates water loss by kidneys ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Hypothalamopituitary portal vessel • Blood supply to the anterior pituitary is a portal circuit • Releasing hormones from hypothalamus into the first capillary bed (median eminence) • venous drainage transports these neurohormones to a second capillary bed supplying the anterior pituitar ...
... Hypothalamopituitary portal vessel • Blood supply to the anterior pituitary is a portal circuit • Releasing hormones from hypothalamus into the first capillary bed (median eminence) • venous drainage transports these neurohormones to a second capillary bed supplying the anterior pituitar ...
Oxytocin Pathway - Ms. Shunkwiler`s Wiki!
... Oxytocin is released to the target cells-myometrial (uterus contractions) & myoepithelial (milk release) It is a hormone that acts like a neurotransmitter because it is produced by nerve cells and electrical signals cause it’s release from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland fro secretion. ...
... Oxytocin is released to the target cells-myometrial (uterus contractions) & myoepithelial (milk release) It is a hormone that acts like a neurotransmitter because it is produced by nerve cells and electrical signals cause it’s release from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland fro secretion. ...
Lecture 1 - Principles of Endocrinology
... Flgure 9-5 Hormonal secretion Irom the primate pituitary gland (hypophysis) is controlled by the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe 01the pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) consists 01 the pars distal is, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis, (The pars tuberalis, not shown, consists 01 a thin layer 01 ce ...
... Flgure 9-5 Hormonal secretion Irom the primate pituitary gland (hypophysis) is controlled by the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe 01the pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) consists 01 the pars distal is, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis, (The pars tuberalis, not shown, consists 01 a thin layer 01 ce ...
FUNCTION OF KEY BRAIN STRUCTURES
... The Hypothalamus It is hypothesized that Nexalin stimulates the Hypothalamus, which is a collection of specialized cells located in the lower central part of the brain. This vital area is the control center of all autonomic regulatory activities of the body. body It has been said that the hypothalam ...
... The Hypothalamus It is hypothesized that Nexalin stimulates the Hypothalamus, which is a collection of specialized cells located in the lower central part of the brain. This vital area is the control center of all autonomic regulatory activities of the body. body It has been said that the hypothalam ...
Sensory –approx 15 to 16 questions
... Paracrine and Autocrine signaling Comparison b/w endocrine and nervous system responses Endocrine vs exocrine glands Major endocrine organs in the body Regulation and control of hormone secretion Structure/relationship b/w hypothalamus and anterior and posterior pituitary (i.e., capillary beds and v ...
... Paracrine and Autocrine signaling Comparison b/w endocrine and nervous system responses Endocrine vs exocrine glands Major endocrine organs in the body Regulation and control of hormone secretion Structure/relationship b/w hypothalamus and anterior and posterior pituitary (i.e., capillary beds and v ...
Endocrine System
... hormone circ. System (blood) • Ant. Pit. hormones in blood will target specific glands to release hormone circulatory system (blood) • To specific cells for desired response Hormones of Anterior Pituitary: thyroid–stimulating hormone (TSH): ** target tissue = thyroid – stimulates thyroid to prod ...
... hormone circ. System (blood) • Ant. Pit. hormones in blood will target specific glands to release hormone circulatory system (blood) • To specific cells for desired response Hormones of Anterior Pituitary: thyroid–stimulating hormone (TSH): ** target tissue = thyroid – stimulates thyroid to prod ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide File
... 19. Identify the following endocrine glands: Adrenals, Hypothalamus, Ovaries, Pancreas, Parathyroid, Pineal, Pituitary, Testis, Thymus, and Thyroid ...
... 19. Identify the following endocrine glands: Adrenals, Hypothalamus, Ovaries, Pancreas, Parathyroid, Pineal, Pituitary, Testis, Thymus, and Thyroid ...
Slide ()
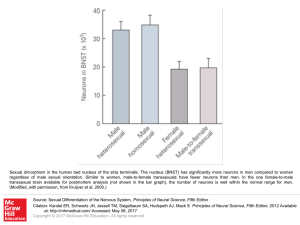
... Sexual dimorphism in the human bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. The nucleus (BNST) has significantly more neurons in men compared to women regardless of male sexual orientation. Similar to women, male-to-female transsexuals have fewer neurons than men. In the one female-to-male transsexual brain ...
... Sexual dimorphism in the human bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. The nucleus (BNST) has significantly more neurons in men compared to women regardless of male sexual orientation. Similar to women, male-to-female transsexuals have fewer neurons than men. In the one female-to-male transsexual brain ...
Endocrine System
... Other Endocrine Tissues and Their Secretions • Pineal gland: Melatonin – What is the significance of its location near the thalamus? – Why is it significant that this gland is innervated by sympathetic nerves? ...
... Other Endocrine Tissues and Their Secretions • Pineal gland: Melatonin – What is the significance of its location near the thalamus? – Why is it significant that this gland is innervated by sympathetic nerves? ...
File - Ms. G`s Classroom
... In females, stimulates the maturation of a follicle and egg inside the ovary. In males, stimulates sperm production. Stimulate ovulation in females and the formation of the corpus luteum from the empty follicle Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary. Acts on the kidneys to increa ...
... In females, stimulates the maturation of a follicle and egg inside the ovary. In males, stimulates sperm production. Stimulate ovulation in females and the formation of the corpus luteum from the empty follicle Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary. Acts on the kidneys to increa ...
Nervous co-ordination gives control. Endocrine co
... The two systems interact in a dynamic way in order to maintain the constancy of the animal's internal environment, while permitting changes in response to a varying external environment. Both systems secrete chemicals, the nervous system as a transmitter between neurones and the endocrine system as ...
... The two systems interact in a dynamic way in order to maintain the constancy of the animal's internal environment, while permitting changes in response to a varying external environment. Both systems secrete chemicals, the nervous system as a transmitter between neurones and the endocrine system as ...
Chapter 45 Essentials
... neurohormone, simple neuroendocrine, feedback loop, negative feedback Concept Check- 1,2,3 45.2 Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways the culminate in specific cell responses Intro- bloodstream, proteins, peptides, amines, steroids Cell Surface Re ...
... neurohormone, simple neuroendocrine, feedback loop, negative feedback Concept Check- 1,2,3 45.2 Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways the culminate in specific cell responses Intro- bloodstream, proteins, peptides, amines, steroids Cell Surface Re ...
Objectives for Chapter 9
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
Lecture 15
... - messengers transported via blood/lymph structures that produce/release hormones cause short to long lasting changes in target cells with receptors for them ...
... - messengers transported via blood/lymph structures that produce/release hormones cause short to long lasting changes in target cells with receptors for them ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.