Endocrine System
... portal system • Primary capillary plexus • Hypophyseal portal veins • Secondary capillary plexus Anterior lobe of pituitary TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, GH, PRL, MSH ...
... portal system • Primary capillary plexus • Hypophyseal portal veins • Secondary capillary plexus Anterior lobe of pituitary TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, GH, PRL, MSH ...
glands of the human body
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
Objective: You will be able to identify all of the glands of the
... of the anterior and posterior pituitary hormones. Do Now: • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
... of the anterior and posterior pituitary hormones. Do Now: • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
Endocrine System
... • Regulates Na+ & K+ reabsorption in the kidneys this influences blood volume & blood pressure • Oxytocin, which, among other functions, helps deliver milk from the glands of the breast. ...
... • Regulates Na+ & K+ reabsorption in the kidneys this influences blood volume & blood pressure • Oxytocin, which, among other functions, helps deliver milk from the glands of the breast. ...
Hormone
... III. Local Hormones – These hormones travel in small localized areas. A. Growth Factors – These are hormones that cause cell replication. They are used for “normal” growing or repair. B. Nitric Oxide (NO) – If from neuron – Acts as neurotransmitter to inhibit a process. - If from WBC – Kills cell o ...
... III. Local Hormones – These hormones travel in small localized areas. A. Growth Factors – These are hormones that cause cell replication. They are used for “normal” growing or repair. B. Nitric Oxide (NO) – If from neuron – Acts as neurotransmitter to inhibit a process. - If from WBC – Kills cell o ...
Science Grade (Unit 6)
... 2. What hormone is responsible for causing the liver to break glycogen down into glucose? 3. What hormone is responsible for causing the liver to store glucose as glycogen? 4. What are the characteristics, symptoms, problems caused, age of onset, and treatments for type 1 and type 2 diabetes. 5. Whi ...
... 2. What hormone is responsible for causing the liver to break glycogen down into glucose? 3. What hormone is responsible for causing the liver to store glucose as glycogen? 4. What are the characteristics, symptoms, problems caused, age of onset, and treatments for type 1 and type 2 diabetes. 5. Whi ...
Chapter 36 Integration: Endocrine Control I. The Endocrine System
... receptors throughout the body; however, in testicular feminization syndrome, none of the target cells respond correctly, so the XY individual develops female characteristics. ...
... receptors throughout the body; however, in testicular feminization syndrome, none of the target cells respond correctly, so the XY individual develops female characteristics. ...
Pituitary gland
... 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, produces thyroid hormone that regulates metabolism 4. Ad ...
... 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, produces thyroid hormone that regulates metabolism 4. Ad ...
Hormones: definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids
... Endocrine glands - glands that secrete hormones. The human body has lots, only some of which will be covered here [Fig., not in text, but similar to 45.10, p. 981]. (Also, exocrine glands -> essentially hormones that are released outside body e.g., pheromones). See table on p. 987 for a list of horm ...
... Endocrine glands - glands that secrete hormones. The human body has lots, only some of which will be covered here [Fig., not in text, but similar to 45.10, p. 981]. (Also, exocrine glands -> essentially hormones that are released outside body e.g., pheromones). See table on p. 987 for a list of horm ...
Emotion and Motivation
... body weight is regulated around a set point body must provide feedback signals that control nutrient intake and metabolism ...
... body weight is regulated around a set point body must provide feedback signals that control nutrient intake and metabolism ...
Biology 30 Assignment 6 Endocrine System and Hormones
... assignments will not be accepted for full marks. Key Terms: 21 marks Pituitary Gland Posterior Pituitary Anterior Pituitary Human Growth Hormone (hGH) Thyroid Gland Thyroxine (T4) Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Goitre Adrenal Glands Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine Norep ...
... assignments will not be accepted for full marks. Key Terms: 21 marks Pituitary Gland Posterior Pituitary Anterior Pituitary Human Growth Hormone (hGH) Thyroid Gland Thyroxine (T4) Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Goitre Adrenal Glands Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine Norep ...
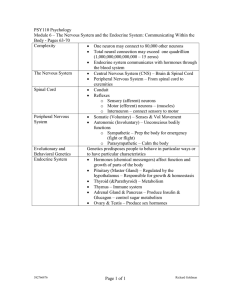
PSY110 Psychology
... o Motor (efferent) neurons – (muscles) o Interneuron – connect sensory to motor Peripheral Nervous Somatic (Voluntary) – Senses & Vol Movement System Autonomic (Involuntary) – Unconscious bodily functions o Sympathetic – Prep the body for emergency (fight or flight) o Parasympathetic – Calm the ...
... o Motor (efferent) neurons – (muscles) o Interneuron – connect sensory to motor Peripheral Nervous Somatic (Voluntary) – Senses & Vol Movement System Autonomic (Involuntary) – Unconscious bodily functions o Sympathetic – Prep the body for emergency (fight or flight) o Parasympathetic – Calm the ...
Endocrine Quiz Review
... -ANTERIOR PITUITARY: Releases GH (stimulate growth of skeletal muscle regulated by GHRH & GHIH), TSH (thyroid gland development, regulated by TRH and TSH), ACTH (stimulates Adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids), FSH (stimulates sex cell production, regulated by GnRH), LH (stimulates gonadal hor ...
... -ANTERIOR PITUITARY: Releases GH (stimulate growth of skeletal muscle regulated by GHRH & GHIH), TSH (thyroid gland development, regulated by TRH and TSH), ACTH (stimulates Adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids), FSH (stimulates sex cell production, regulated by GnRH), LH (stimulates gonadal hor ...
Endocrine System
... Thyroid gland secretes thyroxine which helps the body metabolize fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Thyroxine is controlled by negative feedback. The anterior pituitary released TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) which causes the thyroid gland to release thyroxine. As thyroxine levels in the blood inc ...
... Thyroid gland secretes thyroxine which helps the body metabolize fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Thyroxine is controlled by negative feedback. The anterior pituitary released TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) which causes the thyroid gland to release thyroxine. As thyroxine levels in the blood inc ...
Hormones: definition - a chemical signal released into body fluids
... - adrenal cortex responds to endocrine signals, not nervous system signals (more responsive to long term stress): - stress --> ACTH released by ant. pituitary --> causes adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids. (Note: ACTH = Adrenocorticotropic hormone). - the release of corticosteroids results in ...
... - adrenal cortex responds to endocrine signals, not nervous system signals (more responsive to long term stress): - stress --> ACTH released by ant. pituitary --> causes adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids. (Note: ACTH = Adrenocorticotropic hormone). - the release of corticosteroids results in ...
BIOS 1300 SI SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries (email:
... 1. The centers in the pons that modify the activity of the respiratory centers in the medulla oblongata are the: a. inferior and superior peduncles b. apneustic and pneumotaxic centers c. thalamus and hypothalamus d. cardiac and vasomotor centers 2. Even though almost completely separated, the two c ...
... 1. The centers in the pons that modify the activity of the respiratory centers in the medulla oblongata are the: a. inferior and superior peduncles b. apneustic and pneumotaxic centers c. thalamus and hypothalamus d. cardiac and vasomotor centers 2. Even though almost completely separated, the two c ...
Stress and Sex Objectives answers
... o ovaries are missing or incomplete, all other female organs are formed. Klinefelter’s Syndrome: (XXY) o overly feminine males (e.g., have both penis and breasts), always sterile 6. Understand the hormonal causes of body changes at puberty. Anterior pituitary Growth Hormone and Gonadotropins o ...
... o ovaries are missing or incomplete, all other female organs are formed. Klinefelter’s Syndrome: (XXY) o overly feminine males (e.g., have both penis and breasts), always sterile 6. Understand the hormonal causes of body changes at puberty. Anterior pituitary Growth Hormone and Gonadotropins o ...
File
... B) The physician is wrong – a hormone made in adenohypophysis could not influence fertility C) FSH stimulates sperm production in the testes. D) The man must be producing progesterone, which inhibits the synthesis of FSH. 17) Hormone(s) that would increase blood glucose concentrations? A) Insulin B) ...
... B) The physician is wrong – a hormone made in adenohypophysis could not influence fertility C) FSH stimulates sperm production in the testes. D) The man must be producing progesterone, which inhibits the synthesis of FSH. 17) Hormone(s) that would increase blood glucose concentrations? A) Insulin B) ...
Lecture 8 - Endocrine
... • Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and thyroxine Polypeptide Hormones • Hormones with a peptide structure • Insulin, prolactin, NGF, EGF, GH, PTH, TSH, enkephalin, TRH, ADH Steroids • Hormones derived from cholesterol • Testosterone, cortisol, aldosterone, progesterone, estradiol ...
... • Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and thyroxine Polypeptide Hormones • Hormones with a peptide structure • Insulin, prolactin, NGF, EGF, GH, PTH, TSH, enkephalin, TRH, ADH Steroids • Hormones derived from cholesterol • Testosterone, cortisol, aldosterone, progesterone, estradiol ...
Notes_Endocrine2013
... chemicals travel to target tissue, which has receptor proteins slow, long-lasting response ...
... chemicals travel to target tissue, which has receptor proteins slow, long-lasting response ...
Adrenal glands
... Pancreas Parathyroid gland Pineal gland (draw this in) Pituitary Testes Thymus gland (draw this in) Thyroid gland ...
... Pancreas Parathyroid gland Pineal gland (draw this in) Pituitary Testes Thymus gland (draw this in) Thyroid gland ...
Ch. 3 S. 3
... Hormones and Effect on the Body The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones stimulate reactions. Psychologists study hormones because they affect behavior and emotional reactions. Hormones are produced by several different glands. ...
... Hormones and Effect on the Body The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones stimulate reactions. Psychologists study hormones because they affect behavior and emotional reactions. Hormones are produced by several different glands. ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.