The reticular activating system (RAS)
... secrete the hormone oxytocin, The main functions of oxytocin 1.it increase contractility of the myoepithelial cells surrounding the alveoli of the breasts, which then causes the alveoli to empty their milk through the nipples during baby suckling. 2. at time of labour, large quantities of oxytocin a ...
... secrete the hormone oxytocin, The main functions of oxytocin 1.it increase contractility of the myoepithelial cells surrounding the alveoli of the breasts, which then causes the alveoli to empty their milk through the nipples during baby suckling. 2. at time of labour, large quantities of oxytocin a ...
Endocrine System Bookwork KEY
... such as growth, development, metabolism and the functioning of the reproductive system. 3. Hormone—substances that arouse the body by altering cellular activity (such as raising or lowering normal metabolic processes). Steroids are lipid soluble, nonsteroid are water soluble. 5. Negative feedback, t ...
... such as growth, development, metabolism and the functioning of the reproductive system. 3. Hormone—substances that arouse the body by altering cellular activity (such as raising or lowering normal metabolic processes). Steroids are lipid soluble, nonsteroid are water soluble. 5. Negative feedback, t ...
Neurotransmitters v hormones
... Neurotransmitters: The body’s natural chemical messengers which transmit information from one neuron to another. The neurotransmitters are stored in the neurons terminal buttons. After crossing the synapse, the neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites on the post-synaptic membrane like a key in a l ...
... Neurotransmitters: The body’s natural chemical messengers which transmit information from one neuron to another. The neurotransmitters are stored in the neurons terminal buttons. After crossing the synapse, the neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites on the post-synaptic membrane like a key in a l ...
Photosynthesis Review Questions
... 12. What group of hormones released by the adrenal glands help to increase blood sugar levels? 13. What is Type 2 diabetes? How can it be managed/controlled? 14. What hormone causes an increase in blood calcium levels? a decrease in blood calcium levels? 15. Describe how a deficiency in iodine cause ...
... 12. What group of hormones released by the adrenal glands help to increase blood sugar levels? 13. What is Type 2 diabetes? How can it be managed/controlled? 14. What hormone causes an increase in blood calcium levels? a decrease in blood calcium levels? 15. Describe how a deficiency in iodine cause ...
Endocrine System
... The parathyroid glands control the level of calcium in the blood. The thymus gland is a gland that forms part of the immune system. Its function is to transform lymphocytes into T-cells that play an important part in fighting infections and disease. The adrenal glands release hormones which have imp ...
... The parathyroid glands control the level of calcium in the blood. The thymus gland is a gland that forms part of the immune system. Its function is to transform lymphocytes into T-cells that play an important part in fighting infections and disease. The adrenal glands release hormones which have imp ...
Endocrine System - KidsHealth in the Classroom
... Any five of the following: regulating mood, growth and development; tissue function; the fight or flight response; metabolism; blood glucose levels; sexual function and reproductive processes. ...
... Any five of the following: regulating mood, growth and development; tissue function; the fight or flight response; metabolism; blood glucose levels; sexual function and reproductive processes. ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
... Calcium binds to calmodulin (a protein), activating other enzymes. The steroid hormone diffuses across the plasma membrane into the cell and binds to a receptor. The steroid-receptor complex moves into the nucleus and binds to DNA. Specific genes are activated, and transcription and translation occu ...
... Calcium binds to calmodulin (a protein), activating other enzymes. The steroid hormone diffuses across the plasma membrane into the cell and binds to a receptor. The steroid-receptor complex moves into the nucleus and binds to DNA. Specific genes are activated, and transcription and translation occu ...
Hormones and puberty
... The pituitary gland is often called the ‘master gland’ because it controls the actions of other endocrine glands by stimulating them to release their hormones. The pituitary gland is in turn regulated by an area of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus detects messages from the nervous ...
... The pituitary gland is often called the ‘master gland’ because it controls the actions of other endocrine glands by stimulating them to release their hormones. The pituitary gland is in turn regulated by an area of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus detects messages from the nervous ...
Module 6
... Endocrine system communicates by using hormones that travel through the blood system ...
... Endocrine system communicates by using hormones that travel through the blood system ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system work to maintain homeostasis?
... Explain how impulses travel from nerve cell to nerve cell ...
... Explain how impulses travel from nerve cell to nerve cell ...
Endocrine System - Southwest High School
... inches) and his hands measured 12 3/4 inches from the wrist to the top of the middle finger. Wadlow was still growing when he died on July 15, 1940 and may have exceeded 9 feet in height. ...
... inches) and his hands measured 12 3/4 inches from the wrist to the top of the middle finger. Wadlow was still growing when he died on July 15, 1940 and may have exceeded 9 feet in height. ...
Adolescence and Puberty
... 3. Alterations/lesions/trauma of the hypothalamus and specific areas in the limbic system (amygdala, hippocampus) will prevent the prepubertal animal to develop a normal reproductive function ...
... 3. Alterations/lesions/trauma of the hypothalamus and specific areas in the limbic system (amygdala, hippocampus) will prevent the prepubertal animal to develop a normal reproductive function ...
endocrine_concept_map
... the area of the brain that coordinates the activities of the nervous and endocrine systems temperature, blood pressure, and emotions through signals sent from the nervous system as well as from blood concentrations of circulating hormones by producing hormones that provide response instructions to t ...
... the area of the brain that coordinates the activities of the nervous and endocrine systems temperature, blood pressure, and emotions through signals sent from the nervous system as well as from blood concentrations of circulating hormones by producing hormones that provide response instructions to t ...
Hypothalamus → Anterior Pituitary
... Negative feedback example The hypothalamus receives messages regarding the body’s temperature. This stimulates the anterior pituitary to release TSH. This in turn causes a release of hormones from the thyroid gland which will increase the metabolic rate. Generating heat. Warmer temperatures then inh ...
... Negative feedback example The hypothalamus receives messages regarding the body’s temperature. This stimulates the anterior pituitary to release TSH. This in turn causes a release of hormones from the thyroid gland which will increase the metabolic rate. Generating heat. Warmer temperatures then inh ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
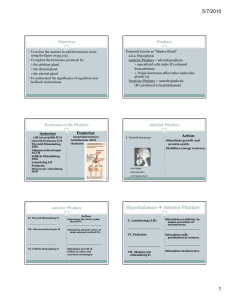
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Slide ()
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Endocrine System Notes
... WARM UP • List the 10 organs of the endocrine system, and one hormone produced by each. ...
... WARM UP • List the 10 organs of the endocrine system, and one hormone produced by each. ...
Chapter 11 Quiz
... 3. Responsiveness of cells to hormones is determined by the presence or absence of specific hormone receptor proteins. *A. True B. False 4. When two or more hormones work together to produce a particular result, their effects are A. permissive. B. antagonistic. *C. synergistic. D. inhibitory. 5. Ste ...
... 3. Responsiveness of cells to hormones is determined by the presence or absence of specific hormone receptor proteins. *A. True B. False 4. When two or more hormones work together to produce a particular result, their effects are A. permissive. B. antagonistic. *C. synergistic. D. inhibitory. 5. Ste ...
02 Endocrine and Cell Communication
... • EK 3.D.1 Cell communication processes share common features: – d. In multicellular organisms, signal transduction pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells. • EK 3D.2 Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signalin ...
... • EK 3.D.1 Cell communication processes share common features: – d. In multicellular organisms, signal transduction pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells. • EK 3D.2 Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signalin ...
Part B
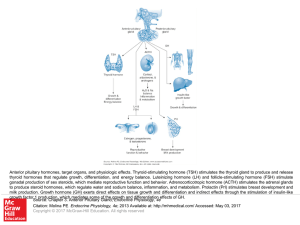
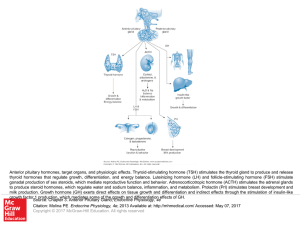
... – Some of these are tropic hormones that regulate the secretion of hormones from other glands – Gonadotropins – control the production of sex hormones as well as gametes • Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) • Regulation by gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) – Figure 1 ...
... – Some of these are tropic hormones that regulate the secretion of hormones from other glands – Gonadotropins – control the production of sex hormones as well as gametes • Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) • Regulation by gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) – Figure 1 ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.