AMA 176 powerpoint
... Located on either side of the thyroid in the neck (four small oval bodies). Parathyroid hormone (PTH) takes calcium from bones and puts it into the bloodstream to help with proper functioning of body tissues, especially the muscles. ...
... Located on either side of the thyroid in the neck (four small oval bodies). Parathyroid hormone (PTH) takes calcium from bones and puts it into the bloodstream to help with proper functioning of body tissues, especially the muscles. ...
A dvanced Hypothalamus-Pituitary
... pituitary glands. The interconnection and communication between all three glands is known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. The HPA axis is a major thoroughfare between the brain and endocrine system; it must be maintained and balanced to help the body cope with acute and chronic str ...
... pituitary glands. The interconnection and communication between all three glands is known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. The HPA axis is a major thoroughfare between the brain and endocrine system; it must be maintained and balanced to help the body cope with acute and chronic str ...
chapt14-endocrine system
... The anterior pituitary produces at least six types of hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid; ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex; the gonadotropic hormones FSH and LH stimulate the gonads; prolactin causes mammary glands to produce milk; and growth hormone promotes bone g ...
... The anterior pituitary produces at least six types of hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid; ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex; the gonadotropic hormones FSH and LH stimulate the gonads; prolactin causes mammary glands to produce milk; and growth hormone promotes bone g ...
Podcast summary chapter 15
... The endocrine system is composed of a series of glands, connected by the cardiovascular system. Endocrine glands secrete hormones onto their surface, rather than through ducts like exocrine glands. Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the glands of the endocrine system to communicate with oth ...
... The endocrine system is composed of a series of glands, connected by the cardiovascular system. Endocrine glands secrete hormones onto their surface, rather than through ducts like exocrine glands. Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the glands of the endocrine system to communicate with oth ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissue and its connection to the hypothalamus is neural. Posterior Pituitary produces 2 hormones: ADH and oxytocin. These are produced by the nerve cell bodies that are located in the hypothalamus, where they are packaged into secretor ...
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissue and its connection to the hypothalamus is neural. Posterior Pituitary produces 2 hormones: ADH and oxytocin. These are produced by the nerve cell bodies that are located in the hypothalamus, where they are packaged into secretor ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
Introduction to the endocrine system and hormones
... environment by producing chemical regulatory substances called hormones ...
... environment by producing chemical regulatory substances called hormones ...
bio 342 human physiology
... 2 Cells in the anterior pituitary gland that secrete TSH a) have receptors for TRH in their cell membranes b) can sense the levels of T3 and T4 in the plasma c) will release more TSH as levels of TRH rise d) Should release less TSH after a person has been treated with ...
... 2 Cells in the anterior pituitary gland that secrete TSH a) have receptors for TRH in their cell membranes b) can sense the levels of T3 and T4 in the plasma c) will release more TSH as levels of TRH rise d) Should release less TSH after a person has been treated with ...
growth hormone
... – the basal level of PRL returns to normal – Lactation is maintained by surge in Prolactin secretion • nursing baby causes a 10 to 20 fold secretion of PRL and lasts for 1 h ...
... – the basal level of PRL returns to normal – Lactation is maintained by surge in Prolactin secretion • nursing baby causes a 10 to 20 fold secretion of PRL and lasts for 1 h ...
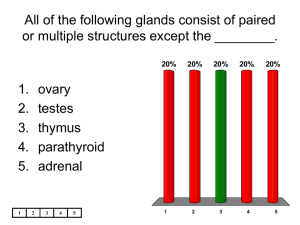
All of the following glands consist of paired or multiple structures
... The secretion of hormones by the anterior pituitary is often controlled by releasing hormones secreted by the ________. ...
... The secretion of hormones by the anterior pituitary is often controlled by releasing hormones secreted by the ________. ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... Control of trophic hormone secretion from the adenohypophysis by hypothalamic-releasing hormones (RH) and release-inhibiting hormones (RIH). The releasing and release-inhibiting hormones are synthesized by neurons in the hypothalamus, transported by axonal processes, and released into capillary plex ...
... Control of trophic hormone secretion from the adenohypophysis by hypothalamic-releasing hormones (RH) and release-inhibiting hormones (RIH). The releasing and release-inhibiting hormones are synthesized by neurons in the hypothalamus, transported by axonal processes, and released into capillary plex ...
Important Glands of the Endocrine System
... heart and posterior to the sternum. It is very important in the maturation of T cells (infection fighting cells) for the immune system. It is the link between the endocrine system and the immune system. ...
... heart and posterior to the sternum. It is very important in the maturation of T cells (infection fighting cells) for the immune system. It is the link between the endocrine system and the immune system. ...
Endocrine Systems - Science Geek.net
... (1) PIH inhibits prolactin release b. Low levels of estrogen after pregnancy inhibit release of PIH (2) Absence of PIH stimulates prolactin release B. Oxytocin 1. Produced in the hypothalamus 2. Released by the posterior pituitary a. Causes milk producing glands to contract and move milk into the ni ...
... (1) PIH inhibits prolactin release b. Low levels of estrogen after pregnancy inhibit release of PIH (2) Absence of PIH stimulates prolactin release B. Oxytocin 1. Produced in the hypothalamus 2. Released by the posterior pituitary a. Causes milk producing glands to contract and move milk into the ni ...
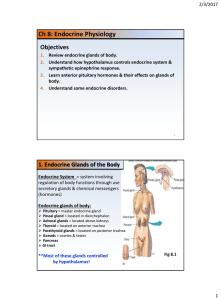
1. Endocrine Glands of the Body
... secretory glands & chemical messengers (hormones) Endocrine glands of body: Pituitary = master endocrine gland Pineal gland = located in dienchephalon Adrenal glands = located above kidneys Thyroid = located on anterior trachea Parathyroid glands = located on posterior trachea Gonads = o ...
... secretory glands & chemical messengers (hormones) Endocrine glands of body: Pituitary = master endocrine gland Pineal gland = located in dienchephalon Adrenal glands = located above kidneys Thyroid = located on anterior trachea Parathyroid glands = located on posterior trachea Gonads = o ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine System Hormone: a chemical signal that is secreted into the extra cellular fluid, carried by the circulatory system – communicates regulatory messages within the body Endocrine system: all of an animal’s hormone-secreting cells Coordinates slower, longer acting ...
... Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine System Hormone: a chemical signal that is secreted into the extra cellular fluid, carried by the circulatory system – communicates regulatory messages within the body Endocrine system: all of an animal’s hormone-secreting cells Coordinates slower, longer acting ...
guide2409.ppt [Compatibility Mode]
... nucleus, creating a complex that transduces the signal 3. Hormone-receptor complex attaches to specific site on cell's DNA 4. Binding to DNA stimulates transcription of genes into RNA, which is translated into proteins ...
... nucleus, creating a complex that transduces the signal 3. Hormone-receptor complex attaches to specific site on cell's DNA 4. Binding to DNA stimulates transcription of genes into RNA, which is translated into proteins ...
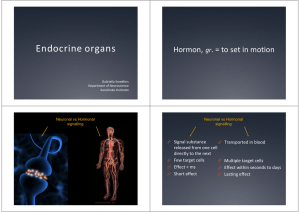
Endocrine organs - Ping Pong
... o Eg. Adrenalin, GH o Eg. steroid hormones o Free transport in blood o Transport in blood bound to plasma proteins o Extracellular receptors o Intracellular receptors ...
... o Eg. Adrenalin, GH o Eg. steroid hormones o Free transport in blood o Transport in blood bound to plasma proteins o Extracellular receptors o Intracellular receptors ...
endocrine
... 1. secretory products of endocrine glands, endocrine cells and some neurons that the delivers to nonadjacent target cells a. one type of signaling molecule (molecules that help integrate activities within and between cells) -some other signaling molecules are: -neurotransmitters – that we talked abo ...
... 1. secretory products of endocrine glands, endocrine cells and some neurons that the delivers to nonadjacent target cells a. one type of signaling molecule (molecules that help integrate activities within and between cells) -some other signaling molecules are: -neurotransmitters – that we talked abo ...
physio unit 14 Ch78 Ch79
... Macrosomia, but more importantly ARDS occurs in conditions of hyperinsulinemia i. Therefore, ARDS occurs only to children of type II diabetics 36. What can delay breathing of newborns? Prolonged hypoxia during delivery can cause depression of the respiratory center ...
... Macrosomia, but more importantly ARDS occurs in conditions of hyperinsulinemia i. Therefore, ARDS occurs only to children of type II diabetics 36. What can delay breathing of newborns? Prolonged hypoxia during delivery can cause depression of the respiratory center ...
Bio 100 Guide 24
... nucleus, creating a complex that transduces the signal 3. Hormone-receptor complex attaches to specific site on cell's DNA 4. Binding to DNA stimulates transcription of genes into RNA, which is translated into proteins ...
... nucleus, creating a complex that transduces the signal 3. Hormone-receptor complex attaches to specific site on cell's DNA 4. Binding to DNA stimulates transcription of genes into RNA, which is translated into proteins ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE PITUITARY GLAND
... the releasing organ (if applicable, specify if from the medulla or cortex), name of the hormone, and it’s general function. ...
... the releasing organ (if applicable, specify if from the medulla or cortex), name of the hormone, and it’s general function. ...
Lesson 2.3: Chemical Communication Essential Questions
... A protein hormone that is produced especially by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and that promotes an increase in the sugar content of the blood by increasing the rate of breakdown of glycogen in the liver. Any one of the many circulating chemical signals found in all multicellular organisms tha ...
... A protein hormone that is produced especially by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and that promotes an increase in the sugar content of the blood by increasing the rate of breakdown of glycogen in the liver. Any one of the many circulating chemical signals found in all multicellular organisms tha ...
4. Regulation- The Endocrine System
... • Master gland of body • When change in homeostasis is detected, the hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary gland. -- Pituitary gland is located beneath the hypothalamus; it releases its own chemicals or stimulate other glands to release them. -- Exs) – thyroid stimulating hormone – growth hormone (S ...
... • Master gland of body • When change in homeostasis is detected, the hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary gland. -- Pituitary gland is located beneath the hypothalamus; it releases its own chemicals or stimulate other glands to release them. -- Exs) – thyroid stimulating hormone – growth hormone (S ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.














![guide2409.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001502774_1-62a347145ddf836c3494bd6f5c6ae337-300x300.png)