Physiological changes during pregnancy
... the hypothalmus are transported by axonal transport and are released from the nerve terminals in the posterior pituitary into the ...
... the hypothalmus are transported by axonal transport and are released from the nerve terminals in the posterior pituitary into the ...
Brain Organization or, why everyone should have some
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
Title - Iowa State University
... a. Thymus, heart, liver, stomach, etc. 4.) What is the difference between endocrine glands and organs with endocrine cells? a. 5.) When specialized neurons typically found in the brain secrete molecules that diffuse from nerve cell endings into the bloodstream, this process is a part of what signali ...
... a. Thymus, heart, liver, stomach, etc. 4.) What is the difference between endocrine glands and organs with endocrine cells? a. 5.) When specialized neurons typically found in the brain secrete molecules that diffuse from nerve cell endings into the bloodstream, this process is a part of what signali ...
Sexual Differentiation in Mammals (Chap 11)
... • Masculinizing of the rat brain is not just due to testosterone • Testosterone entering rat brain is turned into estradiol! • Estradiol, in turn, triggers “masculinization” of the brain. • Brain areas like the hypothalamus which show sex differences have high levels of aromatase enzyme that convert ...
... • Masculinizing of the rat brain is not just due to testosterone • Testosterone entering rat brain is turned into estradiol! • Estradiol, in turn, triggers “masculinization” of the brain. • Brain areas like the hypothalamus which show sex differences have high levels of aromatase enzyme that convert ...
HERE
... Male disorders (too little or ineffective testosterone) – androgenic insensitivity 1. XY: X chromosome is responsible for the testosterone receptors i. These receptors become insensitive to testosterone ii. Child is born with appearance of female genitalia **Mullerian inhibiting system is okay; so ...
... Male disorders (too little or ineffective testosterone) – androgenic insensitivity 1. XY: X chromosome is responsible for the testosterone receptors i. These receptors become insensitive to testosterone ii. Child is born with appearance of female genitalia **Mullerian inhibiting system is okay; so ...
Hypothalamus - Assignment Point
... Compare the basic organization and function of the ES and the NS Describe the structural and functional organization of the hypothalamus and the pituitary and explain their relationship Discuss the locations and structures of the thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands as well as the thymus and the ...
... Compare the basic organization and function of the ES and the NS Describe the structural and functional organization of the hypothalamus and the pituitary and explain their relationship Discuss the locations and structures of the thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands as well as the thymus and the ...
Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]
... -Nervous system controls endocrine function; these ...
... -Nervous system controls endocrine function; these ...
Hypothalamus
... Compare the basic organization and function of the ES and the NS Describe the structural and functional organization of the hypothalamus and the pituitary and explain their relationship Discuss the locations and structures of the thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands as well as the thymus and the ...
... Compare the basic organization and function of the ES and the NS Describe the structural and functional organization of the hypothalamus and the pituitary and explain their relationship Discuss the locations and structures of the thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands as well as the thymus and the ...
nervous system - gloriousbiology
... PTH is produced by the parathyroid glands, embedded on the surface of the thyroid. The dual functioning pancreas functions in both the endocrine and digestive systems. Produces glucagon and insulin Produces bicarbonate and digestive enzymes Reactions to danger are part of the fight-or-flight res ...
... PTH is produced by the parathyroid glands, embedded on the surface of the thyroid. The dual functioning pancreas functions in both the endocrine and digestive systems. Produces glucagon and insulin Produces bicarbonate and digestive enzymes Reactions to danger are part of the fight-or-flight res ...
endocrine system
... hormones directly into the bloodstream • Target Cells – the cells that a hormone directly affects; if a cell does not have receptors or the receptors don’t respond, the hormone has no effect. ...
... hormones directly into the bloodstream • Target Cells – the cells that a hormone directly affects; if a cell does not have receptors or the receptors don’t respond, the hormone has no effect. ...
The Endocrine System
... helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
... helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
Endocrine system notes
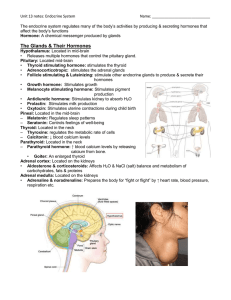
... The Glands & Their Hormones Hypothalamus: Located in mid-brain • Releases multiple hormones that control the pituitary gland. Pituitary: Located mid-brain • Thyroid stimulating hormone: stimulates the thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic: stimulates the adrenal glands • Follicle stimulating & Luteinizing: ...
... The Glands & Their Hormones Hypothalamus: Located in mid-brain • Releases multiple hormones that control the pituitary gland. Pituitary: Located mid-brain • Thyroid stimulating hormone: stimulates the thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic: stimulates the adrenal glands • Follicle stimulating & Luteinizing: ...
Essentials of Pathophysiology CHAPTER 31 ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... The endocrine system uses chemical substances called hormones as a means of regulating and integrating body functions. F All hormones can cross the cell membrane. T The hypothalamus controls the release of pituitary hormones. T The pituitary gland has been called the master gland because its h ...
... The endocrine system uses chemical substances called hormones as a means of regulating and integrating body functions. F All hormones can cross the cell membrane. T The hypothalamus controls the release of pituitary hormones. T The pituitary gland has been called the master gland because its h ...
File
... set of relay molecules, which activate a protein that carries out a response. Steroid hormones enter the target cell and bind to a receptor inside. The receptor-‐hormone complex turns genes on or off. ...
... set of relay molecules, which activate a protein that carries out a response. Steroid hormones enter the target cell and bind to a receptor inside. The receptor-‐hormone complex turns genes on or off. ...
File
... This network of neurons alerts the higher brain to incoming messages and thus controls levels of arousal; when asleep, it is subdued. ...
... This network of neurons alerts the higher brain to incoming messages and thus controls levels of arousal; when asleep, it is subdued. ...
Outline
... activities of individual cells in ways that benefit the whole body 2. Only the cells with receptors for specific hormones are its targets 3. Many types of hormones influence gene transcription and protein synthesis in target cells 4. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland interact in ways to coordinat ...
... activities of individual cells in ways that benefit the whole body 2. Only the cells with receptors for specific hormones are its targets 3. Many types of hormones influence gene transcription and protein synthesis in target cells 4. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland interact in ways to coordinat ...
Stress Psychophysiology Introduction The Brain
... • The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a system of nerves that control the involuntary functions of the body. • The two components of the ANS are the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. • Generally speaking, the sympathetic system is responsible for expending energy ( ...
... • The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a system of nerves that control the involuntary functions of the body. • The two components of the ANS are the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. • Generally speaking, the sympathetic system is responsible for expending energy ( ...
The Endocrine System
... known as corticotropin, is often produced in response to biological stress. Its principal effects are increased production and release of corticosteroids • ACTH is also related to the circadian rhythm in many organisms ...
... known as corticotropin, is often produced in response to biological stress. Its principal effects are increased production and release of corticosteroids • ACTH is also related to the circadian rhythm in many organisms ...
File
... __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
endocrinesystemshort
... Target cells are cells that recognize the hormone’s chemical structure. A hormone interacts only with specific target cells the way a key fits into a lock. Hormones travel through the bloodstream until they find their “lock” or particular cell type. ...
... Target cells are cells that recognize the hormone’s chemical structure. A hormone interacts only with specific target cells the way a key fits into a lock. Hormones travel through the bloodstream until they find their “lock” or particular cell type. ...
Chemical signals in animals
... Hormones are compounds produced in one part of the body and transported to another location to produce specific responses; small amount s can induce substantial responses. Chemical signals produced by the body are mostly produced by glands. Hormones either affect a target effector organ directly or ...
... Hormones are compounds produced in one part of the body and transported to another location to produce specific responses; small amount s can induce substantial responses. Chemical signals produced by the body are mostly produced by glands. Hormones either affect a target effector organ directly or ...
The Endocrine System
... Parathyroid hormone(PTH) is regulated by calcium in the blood Pineal gland- small mass of tissue located near the center of the brain • Secretes the hormone melatonin which is involved in biological rhythms and is regulated by light/dark cycles • Melatonin signals your body that it is nighttime and ...
... Parathyroid hormone(PTH) is regulated by calcium in the blood Pineal gland- small mass of tissue located near the center of the brain • Secretes the hormone melatonin which is involved in biological rhythms and is regulated by light/dark cycles • Melatonin signals your body that it is nighttime and ...
Lies outside the central nervous system
... smooth and coordinated movement (like playing the piano or swinging a baseball bat) ...
... smooth and coordinated movement (like playing the piano or swinging a baseball bat) ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.







![Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016605577_1-a7aad459db07937df65df4f3a411aef9-300x300.png)