C H A P T E R T W E N T Y
... from the hypothalamus directly to the anterior pituitary first, before the blood returns to the heart. Thus, it provides a pathway for hypothalamic hormones to immediately reach the anterior pituitary. In addition, the veins that drain this portal system provide a pathway by which the anterior pitui ...
... from the hypothalamus directly to the anterior pituitary first, before the blood returns to the heart. Thus, it provides a pathway for hypothalamic hormones to immediately reach the anterior pituitary. In addition, the veins that drain this portal system provide a pathway by which the anterior pitui ...
Endocrine problems after treatment for cancer
... vasopressin, a hormone for water balance, growth hormone, and several other signal hormones. ...
... vasopressin, a hormone for water balance, growth hormone, and several other signal hormones. ...
Chapter 46 - Workforce3One
... adenohypophysis and fibrous part called posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • Posterior pituitary releases two neurohormones – Antidiuretic hormone stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys and inhibits urine production. ii) Oxytocin stimulates milk ejection reflex and uterine contractions in wome ...
... adenohypophysis and fibrous part called posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • Posterior pituitary releases two neurohormones – Antidiuretic hormone stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys and inhibits urine production. ii) Oxytocin stimulates milk ejection reflex and uterine contractions in wome ...
Gn-RH-R - FertilityCenter
... Gn-RH is considered a neurohormone produced in a specific neural cell and released at its neural terminal. A key area for production of Gn-RH1 is the preoptic area of the hypothalamus, that contains most of the Gn-RH1-secreting neurons. Gn-RH1 is secreted in the hypophysial portal bloodstream at the ...
... Gn-RH is considered a neurohormone produced in a specific neural cell and released at its neural terminal. A key area for production of Gn-RH1 is the preoptic area of the hypothalamus, that contains most of the Gn-RH1-secreting neurons. Gn-RH1 is secreted in the hypophysial portal bloodstream at the ...
Endocrinology-general physiolofy of hormone, hormonal feed
... urine Osmotic regulation – osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus or somewhere near ...
... urine Osmotic regulation – osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus or somewhere near ...
Endocrine Control - Harford Community College
... c Cellular uptake of glucose from blood slows in many tissues, especially muscles (not the brain). ...
... c Cellular uptake of glucose from blood slows in many tissues, especially muscles (not the brain). ...
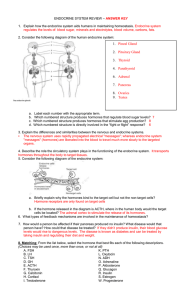
endocrine system review – answer key
... Which numbered structure produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels? 7 Which numbered structure produces hormones that stimulate egg production? 8 Which numbered structure is directly involved in the “fight or flight” response? 6 ...
... Which numbered structure produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels? 7 Which numbered structure produces hormones that stimulate egg production? 8 Which numbered structure is directly involved in the “fight or flight” response? 6 ...
1. Pineal Gland 2. Pituitary Gland 3. Thyroid 4. Parathyroid 6
... Which numbered structure produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels? 7 Which numbered structure produces hormones that stimulate egg production? 8 Which numbered structure is directly involved in the “fight or flight” response? 6 ...
... Which numbered structure produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels? 7 Which numbered structure produces hormones that stimulate egg production? 8 Which numbered structure is directly involved in the “fight or flight” response? 6 ...
Endocrine System - Dr. Diamond`s Website
... by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothalamus produces two hormones – These hormones are transported to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • Oxytocin • Antidiuretic hormone (also known as Vasopressin) ...
... by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothalamus produces two hormones – These hormones are transported to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • Oxytocin • Antidiuretic hormone (also known as Vasopressin) ...
Endocrine system
... C. Unlike exocrine glands that release their products at the body’s surface or into body cavities through ducts, the endocrine glands do not secrete substances into ducts instead their hormones are secreted directly into the surrounding extracellular space & then diffuse into nearby capillaries & a ...
... C. Unlike exocrine glands that release their products at the body’s surface or into body cavities through ducts, the endocrine glands do not secrete substances into ducts instead their hormones are secreted directly into the surrounding extracellular space & then diffuse into nearby capillaries & a ...
Name - PCC
... 22) Lipid-soluble hormones do NOT include a. steroid hormones b. thyroid hormones c. sex hormones d. protein hormones 23) Insulinlike growth factors are necessary for the full effect of a. insulin b. human growth hormone c. cortisol d. thyroxine 24) A hormone that opposes the action of another hormo ...
... 22) Lipid-soluble hormones do NOT include a. steroid hormones b. thyroid hormones c. sex hormones d. protein hormones 23) Insulinlike growth factors are necessary for the full effect of a. insulin b. human growth hormone c. cortisol d. thyroxine 24) A hormone that opposes the action of another hormo ...
The Endocrine Glands
... Only cells with receptors respond to hormones 2. Once bound to receptors, hormones produce response by inactivating or activating cellular processes 3. Hormones effective in very small concentrations 4. Response to a hormone differs among target organs and among species ...
... Only cells with receptors respond to hormones 2. Once bound to receptors, hormones produce response by inactivating or activating cellular processes 3. Hormones effective in very small concentrations 4. Response to a hormone differs among target organs and among species ...
Nervous System
... A hormone is released that will slow down a process Hormones can regulate enzyme production meaning it changes how fast processes are happening in your body. Examples: Blood glucose regulation ...
... A hormone is released that will slow down a process Hormones can regulate enzyme production meaning it changes how fast processes are happening in your body. Examples: Blood glucose regulation ...
Regulation and Control
... Mammary Production of glucocorticoids hormones; control gland growth; thyroid of menstrual cycle milk production hormones ...
... Mammary Production of glucocorticoids hormones; control gland growth; thyroid of menstrual cycle milk production hormones ...
The Endocrine System
... – Maintain homeostasis – Regulate growth and development – Respond to external factors (outside of the body) – Coordinate the production, use, and storage of energy ...
... – Maintain homeostasis – Regulate growth and development – Respond to external factors (outside of the body) – Coordinate the production, use, and storage of energy ...
My Endocrine System Notes - 2014 2015 - Key
... 1. Exocrine glands (not part of the endocrine system): secrete products into ducts which open into cavities in organs (ex: sweat and oil glands, digestive glands) 2. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Endocrine glands include the hypothalamus (in brain), pituitary (in brain), th ...
... 1. Exocrine glands (not part of the endocrine system): secrete products into ducts which open into cavities in organs (ex: sweat and oil glands, digestive glands) 2. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Endocrine glands include the hypothalamus (in brain), pituitary (in brain), th ...
PowerPoint - Pitt Honors Human Physiology
... POMC is cleaved within a vesicle to form ACTH, -Endorphin, LPH, and 16K fragment ...
... POMC is cleaved within a vesicle to form ACTH, -Endorphin, LPH, and 16K fragment ...
Anterior Pituitary: Growth Hormone (GH)
... In men, this gonadotropin stimulates growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm production ...
... In men, this gonadotropin stimulates growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm production ...
CHAPTER 18
... iv. Leutinizing Hormone (LH) males - maintains increased sperm production females - stimulates ovulation ...
... iv. Leutinizing Hormone (LH) males - maintains increased sperm production females - stimulates ovulation ...
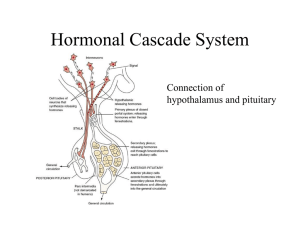
hypothalamo-Pituitary axis and regulatory mechanisms
... secretion of anterior pituitary Neurons send their nerve fibers to the median eminence (extension of hypothalamic tissue into the pituitary stalk) Hormones are secreted to the tissue fluids, absorbed into the hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system and transported to the sinuses of the anterior p ...
... secretion of anterior pituitary Neurons send their nerve fibers to the median eminence (extension of hypothalamic tissue into the pituitary stalk) Hormones are secreted to the tissue fluids, absorbed into the hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system and transported to the sinuses of the anterior p ...
Internal Regulation II
... the brain monitors the level of body fat and “defends” this source against perturbation Evidence suggests that fat cells release the hormone leptin to communicate the level of fat to the brain, thus regulating body mass. In particular, mice lacking both copies of the ob gene (which codes for leptin) ...
... the brain monitors the level of body fat and “defends” this source against perturbation Evidence suggests that fat cells release the hormone leptin to communicate the level of fat to the brain, thus regulating body mass. In particular, mice lacking both copies of the ob gene (which codes for leptin) ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.