1 - The Pathology Guy
... List the three components of Whipple's triad. No partial credit here or anyplace else. [1. low blood glucose; 2. mental changes fasting/exercising; 3. relieved by giving glucose] ...
... List the three components of Whipple's triad. No partial credit here or anyplace else. [1. low blood glucose; 2. mental changes fasting/exercising; 3. relieved by giving glucose] ...
Keshara Senanayake Kraus notes Chapter 9 (what we used to
... inside. Enough Na+ diffuses into axon to reverse the balance of electrical charge and depolarize the membrane. Then K+ diffuses from inside to outside sufficiently to restore the positive charge outside the membrane. --> the Na+/K+ pump is restored and ion concentrations return to their original sta ...
... inside. Enough Na+ diffuses into axon to reverse the balance of electrical charge and depolarize the membrane. Then K+ diffuses from inside to outside sufficiently to restore the positive charge outside the membrane. --> the Na+/K+ pump is restored and ion concentrations return to their original sta ...
Endocrinology of reproduction I (Lecture 6 and 7 combined)
... Gonadal Polypeptide Hormones A. Relaxin 1. Made of 2 polypeptides that are connected with disulfide bonds. It is similar in size and structure to insulin. 2. Secreted by CL during pregnancy. 3. In some species it may be secreted by the uterus and/or placenta. 4. Generally requires tissue first be e ...
... Gonadal Polypeptide Hormones A. Relaxin 1. Made of 2 polypeptides that are connected with disulfide bonds. It is similar in size and structure to insulin. 2. Secreted by CL during pregnancy. 3. In some species it may be secreted by the uterus and/or placenta. 4. Generally requires tissue first be e ...
Endocrine functions of the pituitary and pineal glands 1/20
... no caloric intake for at least 8 hours • 2-hour plasma glucose of 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l) or more during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with load of 75 glucose in water • Classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, and random plasma glucose of 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l) or more • ...
... no caloric intake for at least 8 hours • 2-hour plasma glucose of 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l) or more during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with load of 75 glucose in water • Classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, and random plasma glucose of 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l) or more • ...
The Endocrine System • Endocrine and nervous systems work
... Controlling hormones enter blood Travel through portal veins Enter anterior pituitary at capillaries Growth Hormone Produced by somatotrophs Within target cells increases synthesis of insulinlike growth factors that act locally or enter bloodstream – common target cells are liver, skeletal muscle, c ...
... Controlling hormones enter blood Travel through portal veins Enter anterior pituitary at capillaries Growth Hormone Produced by somatotrophs Within target cells increases synthesis of insulinlike growth factors that act locally or enter bloodstream – common target cells are liver, skeletal muscle, c ...
Function Nervous System Endocrine System
... - Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH) (8 AA) - Oxytocin (8 AA) - Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) - Thyroid Releasing Hormone (TRH) ...
... - Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH) (8 AA) - Oxytocin (8 AA) - Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) - Thyroid Releasing Hormone (TRH) ...
Chapter 19 - endocrine - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Robert Pershing Wadlow Wadlow reached the height of 2.72 m (almost 9 ft) and a weight of 222 kg (488 lbs) before his death at the age of 22. His large size was attributed to a tumor in the pituitary. He was still in a growth phase when died of an infection. ...
... Robert Pershing Wadlow Wadlow reached the height of 2.72 m (almost 9 ft) and a weight of 222 kg (488 lbs) before his death at the age of 22. His large size was attributed to a tumor in the pituitary. He was still in a growth phase when died of an infection. ...
Hormone
... A. Ligand (hormone) attaching to the membrane receptor proteins causes a signal-transduction pathway to begin. 1. If the pathway ends in the cytoplasm – turned on/off an enzyme. 2. If the pathway ends in the nucleus – turned on/off transcription. B. Steroid hormones go through the phospholipid bilay ...
... A. Ligand (hormone) attaching to the membrane receptor proteins causes a signal-transduction pathway to begin. 1. If the pathway ends in the cytoplasm – turned on/off an enzyme. 2. If the pathway ends in the nucleus – turned on/off transcription. B. Steroid hormones go through the phospholipid bilay ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... • Each adrenal gland actually consists of two glands: the adrenal medulla (inner portion) and adrenal cortex (outer portion) ...
... • Each adrenal gland actually consists of two glands: the adrenal medulla (inner portion) and adrenal cortex (outer portion) ...
Endocrine System
... receptors on the target cell Neurohormones are a class of hormones that originate from neurons in the brain (i.e. hypothalamus) and diffuse through the bloodstream to act on target cells (possibly an endocrine gland to produce a 2nd hormone). ...
... receptors on the target cell Neurohormones are a class of hormones that originate from neurons in the brain (i.e. hypothalamus) and diffuse through the bloodstream to act on target cells (possibly an endocrine gland to produce a 2nd hormone). ...
hormone - Daniela Sartori
... All autocrines control gene expression in target cells Paracrine regulators are autocrines that are produced within one tissue and act on different tissue in same organ. Autocrines and paracrines include: Cytokines (lymphokines, interleukins) Growth factors (promote growth and cell division) N ...
... All autocrines control gene expression in target cells Paracrine regulators are autocrines that are produced within one tissue and act on different tissue in same organ. Autocrines and paracrines include: Cytokines (lymphokines, interleukins) Growth factors (promote growth and cell division) N ...
Endocrine System
... wide, 50 mm (2 inches) long, and 10 mm (0.4 inch) thick. Each gland consists of two parts: an inner medulla, which produces epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenaline and noradrenaline), and an outer cortex, which produces steroid hormones. The two parts differ in embryological origin, structure, an ...
... wide, 50 mm (2 inches) long, and 10 mm (0.4 inch) thick. Each gland consists of two parts: an inner medulla, which produces epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenaline and noradrenaline), and an outer cortex, which produces steroid hormones. The two parts differ in embryological origin, structure, an ...
The Endocrine System - Florida International University
... The adrenal cortex can be divided into three zones that produce different types of corticosteroid hormones. From superficial to deep: 1) Zona glomerulosa produces aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid ...
... The adrenal cortex can be divided into three zones that produce different types of corticosteroid hormones. From superficial to deep: 1) Zona glomerulosa produces aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid ...
Endocrine by IVS
... Stimulation tests—determine how an endocrine gland responds to stimulating hormone. If the hormone responds, then the problem lies w/hypothalmus or pituitary ...
... Stimulation tests—determine how an endocrine gland responds to stimulating hormone. If the hormone responds, then the problem lies w/hypothalmus or pituitary ...
Endocrine System
... Adrenal glands are located just above the kidneys – Have an outer layer—cortex – an inner layer--medulla • Adrenal cortex: – Secretion: mediated through hypothalamuspituitary secretions – Hormones: steroidal ...
... Adrenal glands are located just above the kidneys – Have an outer layer—cortex – an inner layer--medulla • Adrenal cortex: – Secretion: mediated through hypothalamuspituitary secretions – Hormones: steroidal ...
hormones
... pituitary to cut off any further supply of FSH and ICSH. As soon as the gonadal hormone level falls, FSH and ICSH output is automatically turned on again. The brain plays a key part in the feedback operation. It produces chemical compounds that signal the pituitary to secrete hormones. The gonadal h ...
... pituitary to cut off any further supply of FSH and ICSH. As soon as the gonadal hormone level falls, FSH and ICSH output is automatically turned on again. The brain plays a key part in the feedback operation. It produces chemical compounds that signal the pituitary to secrete hormones. The gonadal h ...
Chapter 18, Part 2
... ATP synthesis! 3. Increase glucose and glycogen synthesis (liver)! 4. Anti-inflammatory effects! • Decrease mast cell activity! • Increase sensitivity to vasoconstrictors! • Stabilize lysosome membranes! • Decrease capillary permeability! • Decrease phagocyte activity! ...
... ATP synthesis! 3. Increase glucose and glycogen synthesis (liver)! 4. Anti-inflammatory effects! • Decrease mast cell activity! • Increase sensitivity to vasoconstrictors! • Stabilize lysosome membranes! • Decrease capillary permeability! • Decrease phagocyte activity! ...
hormone
... because it releases calcium out of the bones (calcitonin causes bones to absorb calcium) this regulates calcium blood levels, which is necessary for muscle & heart contractions ...
... because it releases calcium out of the bones (calcitonin causes bones to absorb calcium) this regulates calcium blood levels, which is necessary for muscle & heart contractions ...
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
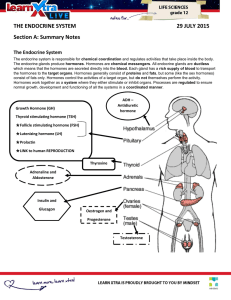
... The endocrine system is responsible for chemical coordination and regulates activities that take place inside the body. The endocrine glands produce hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers. All endocrine glands are ductless which means that the hormones are secreted directly into the blood. Each ...
... The endocrine system is responsible for chemical coordination and regulates activities that take place inside the body. The endocrine glands produce hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers. All endocrine glands are ductless which means that the hormones are secreted directly into the blood. Each ...
Lecture3
... medulla, ADRENAL STEROIDS from the adrenal cortex and THYROID HORMONES from thyroid glands. The adrenal hormone provides stress resistance. Epinephrine helps break down the glycogen that is stored in the liver and muscle as well as the fat that is stored in several locations in the body in order to ...
... medulla, ADRENAL STEROIDS from the adrenal cortex and THYROID HORMONES from thyroid glands. The adrenal hormone provides stress resistance. Epinephrine helps break down the glycogen that is stored in the liver and muscle as well as the fat that is stored in several locations in the body in order to ...
The Endocrine System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... regulate the levels of minerals such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Aldosterone is the most important hormone in this group, where it raises blood levels of sodium and water, and lowers blood potassium level. © 2016 Ebneshahidi ...
... regulate the levels of minerals such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Aldosterone is the most important hormone in this group, where it raises blood levels of sodium and water, and lowers blood potassium level. © 2016 Ebneshahidi ...
Unit One – Concept Two - Calgary Christian School
... Adrenaline – raises blood glucose Thyroxine – decreases blood glucose levels by increasing metabolism (more glucose used due to increased cellular ...
... Adrenaline – raises blood glucose Thyroxine – decreases blood glucose levels by increasing metabolism (more glucose used due to increased cellular ...
45_InstGuide_AR
... adeno- 5 gland; -hypo 5 below (adenohypophysis: also called the anterior pituitary, a gland positioned at the base of the hypothalamus) andro- 5 male; -gen 5 produce (androgens: the principal male steroid hormones, ...
... adeno- 5 gland; -hypo 5 below (adenohypophysis: also called the anterior pituitary, a gland positioned at the base of the hypothalamus) andro- 5 male; -gen 5 produce (androgens: the principal male steroid hormones, ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.