ADENOHYPOPHYSIAL HORMONES
... (TSH) ===> thyroid gland ===> thyroxine ===> tissues - regulates development - regulates metabolic rate in adulthood Corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) ===> corticotrophin or adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) ===> cortisol, aldosterone - cortisol in inhibits protein synthesis, stimulates glucon ...
... (TSH) ===> thyroid gland ===> thyroxine ===> tissues - regulates development - regulates metabolic rate in adulthood Corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) ===> corticotrophin or adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) ===> cortisol, aldosterone - cortisol in inhibits protein synthesis, stimulates glucon ...
Chapter 17 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... – zona glomerulosa (outer) – zona fasciculata (middle) – zona reticularis (inner) ...
... – zona glomerulosa (outer) – zona fasciculata (middle) – zona reticularis (inner) ...
Endocrine System/Reproduction Notes File
... Endocrine System- regulates long-term changes in the body such as growth & development Endocrine gland- produces & releases chemical substances that signal changes in other parts of the body. Hormone- a chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland Endocrine glands include & regulate: *hypothala ...
... Endocrine System- regulates long-term changes in the body such as growth & development Endocrine gland- produces & releases chemical substances that signal changes in other parts of the body. Hormone- a chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland Endocrine glands include & regulate: *hypothala ...
Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... cause blood vessels to constrict in skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other viscera ...
... cause blood vessels to constrict in skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other viscera ...
CRYDERS-Endocrine System
... cause blood vessels to constrict in skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other viscera ...
... cause blood vessels to constrict in skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other viscera ...
endocrine system text
... excites stretch receptors in the vaginal wall. These cause action potentials to be sent to the CNS where the appropriate neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus receive nervous stimulation and release oxytocin in the pars nervosa. This hormone enters the circulatory system and is carried to the mus ...
... excites stretch receptors in the vaginal wall. These cause action potentials to be sent to the CNS where the appropriate neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus receive nervous stimulation and release oxytocin in the pars nervosa. This hormone enters the circulatory system and is carried to the mus ...
Chapter Summary- Notes
... actions of steroidal and nonsteroidal hormones. Next, the negative feedback mechanisms that control hormone release are presented. Hormonal, humoral, and neural stimuli are all explained through the use of selected examples. Endocrine glands are further described as ductless glands that release thei ...
... actions of steroidal and nonsteroidal hormones. Next, the negative feedback mechanisms that control hormone release are presented. Hormonal, humoral, and neural stimuli are all explained through the use of selected examples. Endocrine glands are further described as ductless glands that release thei ...
Hormones & the Endocrine System
... Depending on the species the pineal gland contains light sensitive cells or has nervous connections from the eyes that control its secretory activity Melatonin regulates functions related to light and seasons marked by changes in day length ...
... Depending on the species the pineal gland contains light sensitive cells or has nervous connections from the eyes that control its secretory activity Melatonin regulates functions related to light and seasons marked by changes in day length ...
Anterior Pituitary hormones
... 3. TSH causes TGB movement back into follicle where T3 and T4 are removed and then secreted ...
... 3. TSH causes TGB movement back into follicle where T3 and T4 are removed and then secreted ...
The Endocrine System
... A) Although hormones are carried to all parts of the body, they produce effects only in cells with proper receptors. B) Hormones are limited to steroid compounds C) Hormones are secreted by specialized exocrine glands. D) Most hormones are controlled by positive feedback mechanisms involving the pit ...
... A) Although hormones are carried to all parts of the body, they produce effects only in cells with proper receptors. B) Hormones are limited to steroid compounds C) Hormones are secreted by specialized exocrine glands. D) Most hormones are controlled by positive feedback mechanisms involving the pit ...
I- Match Table A with Table B
... ( )Androgens, estrogens, and progesterone are classified as what type of chemicals a.proteins ...
... ( )Androgens, estrogens, and progesterone are classified as what type of chemicals a.proteins ...
Endocrine System
... • Insulin increases amino acid uptake into cells and increases protein synthesis ...
... • Insulin increases amino acid uptake into cells and increases protein synthesis ...
Endocrine Ch 16-Fall 2016-PPT-Student
... (epinephrine and 1. Increased heart rate norepinephrine) 2. Increased blood pressure 3. Liver converts glycogen to glucose and releases glucose to blood 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive and kidney activity 6. Increas ...
... (epinephrine and 1. Increased heart rate norepinephrine) 2. Increased blood pressure 3. Liver converts glycogen to glucose and releases glucose to blood 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive and kidney activity 6. Increas ...
Marieb_ch9b - TCHS
... Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex Mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) Produced in outer adrenal cortex ...
... Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex Mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) Produced in outer adrenal cortex ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Exocrine gland = a gland that secretes substances into ducts which then leave the body (i.e. sweat/sebaceous glands) or into a internal space or lumen (i.e. digestive glands). Exocrine glands are not part of the endocrine system! ...
... Exocrine gland = a gland that secretes substances into ducts which then leave the body (i.e. sweat/sebaceous glands) or into a internal space or lumen (i.e. digestive glands). Exocrine glands are not part of the endocrine system! ...
7. Endocrine System
... glomerulosa The zona glomerulosa layer is regulated by pituitary adrenocorticotrophin hormone (ACTH). ...
... glomerulosa The zona glomerulosa layer is regulated by pituitary adrenocorticotrophin hormone (ACTH). ...
Hormones - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Gonad activity is controlled by tropic hormones called gonadotropins from the anterior pituitary: • Luteinizing hormone (LH) • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Gonadotropins are controlled by hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)—its release ...
... Gonad activity is controlled by tropic hormones called gonadotropins from the anterior pituitary: • Luteinizing hormone (LH) • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Gonadotropins are controlled by hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)—its release ...
Chapter 45 - HCC Learning Web
... Adrenal Medulla • Secretes epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) in response to stress ...
... Adrenal Medulla • Secretes epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) in response to stress ...
endocrine system
... Some important glands…. • Hypothalamus – secretes hormones which then influence the pituitary gland to secrete corresponding hormones (see stress response) • The pituitary gland ‘ the pea sized governor’ or ‘master gland’ secretes hormones into the body maintaining homeostasis – this steady state ...
... Some important glands…. • Hypothalamus – secretes hormones which then influence the pituitary gland to secrete corresponding hormones (see stress response) • The pituitary gland ‘ the pea sized governor’ or ‘master gland’ secretes hormones into the body maintaining homeostasis – this steady state ...
hormones. - Mrs. Brenner`s Biology
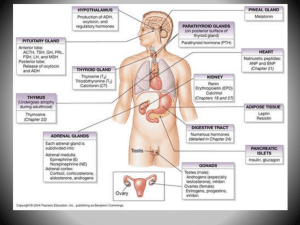
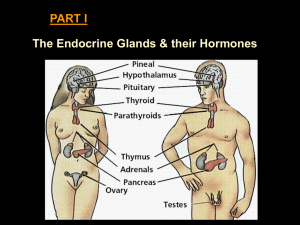
... Major Glands of The Human Endocrine System Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. HYPOTHALAMUS Releasing and inhibiting hormones: regulate the anterior pituitary ...
... Major Glands of The Human Endocrine System Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. HYPOTHALAMUS Releasing and inhibiting hormones: regulate the anterior pituitary ...
Chapter 37: The Endocrine System
... and translation. The corresponding protein product can then mediate changes in cell function. ...
... and translation. The corresponding protein product can then mediate changes in cell function. ...
The Endocrine System
... regulate the levels of minerals such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Aldosterone is the most important hormone in this group, where it raises blood levels of sodium and water, and lowers blood potassium level. © 2017 Ebneshahidi ...
... regulate the levels of minerals such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Aldosterone is the most important hormone in this group, where it raises blood levels of sodium and water, and lowers blood potassium level. © 2017 Ebneshahidi ...
Endokrin Sistem - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... So insulin LOWERS glucose levels by INCREASING glucose UPTAKE in cells where it is stored as glycogen. 2. Glucagon : Increases blood glucose levels by stimulating the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver. ...
... So insulin LOWERS glucose levels by INCREASING glucose UPTAKE in cells where it is stored as glycogen. 2. Glucagon : Increases blood glucose levels by stimulating the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver. ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.