physiology hormone-1
... heart rate and contractility, blood vessel diameters, and short-term energy usage ...
... heart rate and contractility, blood vessel diameters, and short-term energy usage ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... made within the islet tissue in the delta cells. nerve impulse transmission insulin and glucagon production ...
... made within the islet tissue in the delta cells. nerve impulse transmission insulin and glucagon production ...
1 Chapter 2: The Endocrine System Chemical Communication
... Steroid Receptors – located inside cells (in cytosol or nucleus), when receptors bind to hormone they move into nucleus to regulate gene transcription Protein and Peptide Hormone Receptors - embedded in the cell membrane containing 3 domains: o Extracellular domain which binds to ligand (hormone) o ...
... Steroid Receptors – located inside cells (in cytosol or nucleus), when receptors bind to hormone they move into nucleus to regulate gene transcription Protein and Peptide Hormone Receptors - embedded in the cell membrane containing 3 domains: o Extracellular domain which binds to ligand (hormone) o ...
Keshara Senanayake Audesirk Chapter 33
... >adrenal cortex also secretes the hormone aldosterone which regulates the sodium content of the blood. Sodium ions are most abundant positive ion in blood and extracellular fluid -> sodium ion gradient across plasma membranes is a factor in many cellular events, including the production of electrica ...
... >adrenal cortex also secretes the hormone aldosterone which regulates the sodium content of the blood. Sodium ions are most abundant positive ion in blood and extracellular fluid -> sodium ion gradient across plasma membranes is a factor in many cellular events, including the production of electrica ...
Chapter 10 - Delmar Cengage Learning
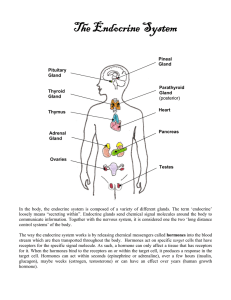
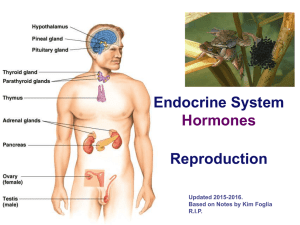
... glands that secrete chemical messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
... glands that secrete chemical messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
Chapter 23
... i. large, peripherally located adrenal cortex which is subdivided into three zones: a. outer zona glomerulosa that secretes mineralocorticoids which affect mineral (especially sodium and potassium) levels in the blood b. middle zona fasciculata that secretes glucocorticoids which affect glucose meta ...
... i. large, peripherally located adrenal cortex which is subdivided into three zones: a. outer zona glomerulosa that secretes mineralocorticoids which affect mineral (especially sodium and potassium) levels in the blood b. middle zona fasciculata that secretes glucocorticoids which affect glucose meta ...
193
... The pituitary gland or hypophysis is a small, bean-shaped gland located in the sella turcica. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior region (adenohypophysis) and a posterior region (neurohypophysis). The hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland, which in turn transmits its own hormones th ...
... The pituitary gland or hypophysis is a small, bean-shaped gland located in the sella turcica. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior region (adenohypophysis) and a posterior region (neurohypophysis). The hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland, which in turn transmits its own hormones th ...
16 - Brazosport College
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
Chp - HCC Learning Web
... Hyperthyroidism is the excessive secretion of thyroid hormones, leading to high body temperature, profuse sweating, weight loss, irritability, and high blood pressure. An insufficient amount of thyroid hormones is known as hypothyroidism. This condition can cause cretinism in infants. Adult ...
... Hyperthyroidism is the excessive secretion of thyroid hormones, leading to high body temperature, profuse sweating, weight loss, irritability, and high blood pressure. An insufficient amount of thyroid hormones is known as hypothyroidism. This condition can cause cretinism in infants. Adult ...
HORMON
... First, it must be able to distinguish the hormone from all the other chemicals present in the circulation and bind it. The hormone binding sites on receptors have evolved to have unique configurations that are complementary to the hormones they bind. Generally, hormone-receptor interactions are nonc ...
... First, it must be able to distinguish the hormone from all the other chemicals present in the circulation and bind it. The hormone binding sites on receptors have evolved to have unique configurations that are complementary to the hormones they bind. Generally, hormone-receptor interactions are nonc ...
S T U D Y G U I D E
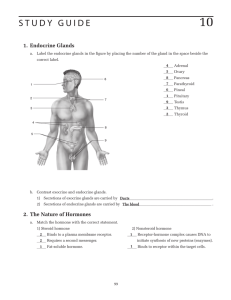
... b. Contrast exocrine and endocrine glands. 1) Secretions of exocrine glands are carried by __________________________________________________. ...
... b. Contrast exocrine and endocrine glands. 1) Secretions of exocrine glands are carried by __________________________________________________. ...
Lecture 9 th week
... – 1. The zona glomerulosa - these cells are the only ones in the adrenal gland capable of secreting significant amounts of aldosterone because they contain the enzyme aldosterone synthase – 2. The zona fasciculata- secretes the glucocorticoids cortisol and corticosterone, as well as small amounts of ...
... – 1. The zona glomerulosa - these cells are the only ones in the adrenal gland capable of secreting significant amounts of aldosterone because they contain the enzyme aldosterone synthase – 2. The zona fasciculata- secretes the glucocorticoids cortisol and corticosterone, as well as small amounts of ...
Lesson 1: Reproductive Systems
... gland can be defined as a tissue or an organ that produces a chemical substance. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream and influence many body processes. The effect of hormone secretion can be both general and specific. For example, the thyroid gland produces thyroxin, which affects ...
... gland can be defined as a tissue or an organ that produces a chemical substance. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream and influence many body processes. The effect of hormone secretion can be both general and specific. For example, the thyroid gland produces thyroxin, which affects ...
Chemical coordina Answer 1: (a) Exocrine gland
... Answer 5 (a) Parathyroid hormone (PTH): It is secreted by Parathyroid gland. It increases the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Thus, it plays an important role in calcium balance in the b ...
... Answer 5 (a) Parathyroid hormone (PTH): It is secreted by Parathyroid gland. It increases the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Thus, it plays an important role in calcium balance in the b ...
9 Endocrine Physiology
... cell. So, T3 gets used first by the body cells. T4 takes longer to be ready; one iodine has to drop off. As T3 is used up, T4 is being converted to more T3. • To make thyroid hormone, you need iodine in your body. Iodized salt has enough to meet this need. Iodine is brought into the follicular cells ...
... cell. So, T3 gets used first by the body cells. T4 takes longer to be ready; one iodine has to drop off. As T3 is used up, T4 is being converted to more T3. • To make thyroid hormone, you need iodine in your body. Iodized salt has enough to meet this need. Iodine is brought into the follicular cells ...
Chapter 46 - Workforce3One
... adenohypophysis and fibrous part called posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • Posterior pituitary releases two neurohormones – Antidiuretic hormone stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys and inhibits urine production. ii) Oxytocin stimulates milk ejection reflex and uterine contractions in wome ...
... adenohypophysis and fibrous part called posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • Posterior pituitary releases two neurohormones – Antidiuretic hormone stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys and inhibits urine production. ii) Oxytocin stimulates milk ejection reflex and uterine contractions in wome ...
ch18 outline
... 1. Clinical Connection: Synthetic hormones that block the receptors for particular naturally occurring hormones are available as drugs. B. Circulating and Local Hormones 1. Hormones that travel in blood and act on distant target cells are called circulating hormones or endocrines. 2. Hormones that a ...
... 1. Clinical Connection: Synthetic hormones that block the receptors for particular naturally occurring hormones are available as drugs. B. Circulating and Local Hormones 1. Hormones that travel in blood and act on distant target cells are called circulating hormones or endocrines. 2. Hormones that a ...
Document
... 1. Which of the following statements is not true of the endocrine system? (2.0 分)A.It is one of two major regulatory systems of the body. B.It is composed of glands that secrete chemical messengers into the blood. C.It is an important regulator of homeostatic mechanisms. D.It influences and is influ ...
... 1. Which of the following statements is not true of the endocrine system? (2.0 分)A.It is one of two major regulatory systems of the body. B.It is composed of glands that secrete chemical messengers into the blood. C.It is an important regulator of homeostatic mechanisms. D.It influences and is influ ...
Endocrine System Disorders
... The main groups of hormones Classic hormones (produced by specialised glands) are divided into three groups: 1. low molecular (amine) hormones (catecholamines, thyroid hormones, prostaglandins, leucotrienes, dopamine, serotonine, GABA, melatonin ...) 2. steroid hormones (e.g.gluco- and mineralocort ...
... The main groups of hormones Classic hormones (produced by specialised glands) are divided into three groups: 1. low molecular (amine) hormones (catecholamines, thyroid hormones, prostaglandins, leucotrienes, dopamine, serotonine, GABA, melatonin ...) 2. steroid hormones (e.g.gluco- and mineralocort ...
Endocrine
... a. produce somatostatin b. somatostatin release of somatotrophin by pituitary; inhibits release of insulin and glucagons 4. Other cells of the pancreatic islets a. pancreatic polypeptide cells (F cells) i. releases pancreatic polypeptide hormone which inhibits exocrine secretions of the pancreas b. ...
... a. produce somatostatin b. somatostatin release of somatotrophin by pituitary; inhibits release of insulin and glucagons 4. Other cells of the pancreatic islets a. pancreatic polypeptide cells (F cells) i. releases pancreatic polypeptide hormone which inhibits exocrine secretions of the pancreas b. ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.