chemical coordination and integration
... They are a pair of yellowish, flat, pyramid like glands which lie over the upper end of the kidneys. They look like a cap on the kidney. Each gland has an outer yellow adrenal cortex and inner reddish brown adrenal medulla. Adrenal Medulla : secretes 2 hormones called adrenaline or epinephrine and n ...
... They are a pair of yellowish, flat, pyramid like glands which lie over the upper end of the kidneys. They look like a cap on the kidney. Each gland has an outer yellow adrenal cortex and inner reddish brown adrenal medulla. Adrenal Medulla : secretes 2 hormones called adrenaline or epinephrine and n ...
hormones
... secrete materials they have produced directly into the bloodstream or surrounding tissue. ...
... secrete materials they have produced directly into the bloodstream or surrounding tissue. ...
Chapter 13 – The Endocrine System ()
... nucleus. The hormone - receptor structure then binds to DNA. This causes the activation of certain genes and protein synthesis. An example of a steroid hormone is cortisol. ...
... nucleus. The hormone - receptor structure then binds to DNA. This causes the activation of certain genes and protein synthesis. An example of a steroid hormone is cortisol. ...
Structure and Functions of Important Endocrine Glands
... pituitary, but located in the tail and associated with the spinal cord • The hormones of urophysis are called “urotensins” and four kinds of them are identified • These are urotensin I, II, III and IV • These are peptides and all the 4 may not be present in the same fish • However, urotensin I and I ...
... pituitary, but located in the tail and associated with the spinal cord • The hormones of urophysis are called “urotensins” and four kinds of them are identified • These are urotensin I, II, III and IV • These are peptides and all the 4 may not be present in the same fish • However, urotensin I and I ...
Follicular cells
... The juxtaglomerular cells release renin in response to a decrease in blood pressure or a low blood sodium level. renin catalyse the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which in turn is converted by angiotensinconverting enzyme(ACE) to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II stimulate the cells of ...
... The juxtaglomerular cells release renin in response to a decrease in blood pressure or a low blood sodium level. renin catalyse the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which in turn is converted by angiotensinconverting enzyme(ACE) to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II stimulate the cells of ...
Endocrine System Outline
... Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS Adrenal cortex – glandular tissue derived from embryonic mesoderm ...
... Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS Adrenal cortex – glandular tissue derived from embryonic mesoderm ...
21 Endocrine
... THYMUS GLAND • Hormones produced by this organ stimulate the production of T cells. ...
... THYMUS GLAND • Hormones produced by this organ stimulate the production of T cells. ...
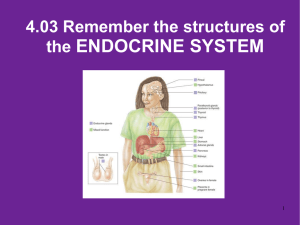
4.03 Remember Structures of the endocrine system What are the
... What is the chemical that is secreted by the endocrine glands? TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) is secreted by the pituitary and acts on what gland? Which gland is divided into anterior and posterior lobes? Which gland is butterfly shaped and is located in the neck? Which endocrine gland is located ...
... What is the chemical that is secreted by the endocrine glands? TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) is secreted by the pituitary and acts on what gland? Which gland is divided into anterior and posterior lobes? Which gland is butterfly shaped and is located in the neck? Which endocrine gland is located ...
Hormonal Control of Growth in Animals
... They are produced in one part of the body (in tiny quantities) and carried in the blood to another part of the body where they have their effect. ...
... They are produced in one part of the body (in tiny quantities) and carried in the blood to another part of the body where they have their effect. ...
Ch 45 Notes
... ◦ Hormones regulate activity of other cells and organs ◦ Hormones bind to cell surface receptors ...
... ◦ Hormones regulate activity of other cells and organs ◦ Hormones bind to cell surface receptors ...
HYPOPHYSIS (PITUITARY GLAND)
... 5. Nervous system is not affected by STH. Metabolism – a. on protein metabolism:- it increases the neuclic acid and protien synthesis, decreases nitrogen excrition in the urine and the nitrogen thus retained helps in the synthesis of tissue protein. STH is a protein anabolic hormone and prevents the ...
... 5. Nervous system is not affected by STH. Metabolism – a. on protein metabolism:- it increases the neuclic acid and protien synthesis, decreases nitrogen excrition in the urine and the nitrogen thus retained helps in the synthesis of tissue protein. STH is a protein anabolic hormone and prevents the ...
Endocrine System
... • Made up of endocrine glands that secrete hormones. • Uses the blood stream to get to the target cells • Is indirect control. And controls tissues regulatory actions and homeostasis. • It’s speed to get places is like mailing a letter • It has more sustained impulses • It is a “duct” less system. I ...
... • Made up of endocrine glands that secrete hormones. • Uses the blood stream to get to the target cells • Is indirect control. And controls tissues regulatory actions and homeostasis. • It’s speed to get places is like mailing a letter • It has more sustained impulses • It is a “duct” less system. I ...
Chemical Control of the Animal Body: The Endocrine System
... • The adrenal medulla: located at the center and secretes two amino acidderived hormones – Epinephrine and norepinephrine: released in response to emergency situations to prepare the body for action ...
... • The adrenal medulla: located at the center and secretes two amino acidderived hormones – Epinephrine and norepinephrine: released in response to emergency situations to prepare the body for action ...
chemical coordination and integration
... Over-secretion of GH stimulates abnormal growth of the body leading to gigantism and low secretion of GH results in stunted growth resulting in pituitary dwarfism. Prolactin regulates the growth of the mammary glands and formation of milk in them. TSH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of thyroi ...
... Over-secretion of GH stimulates abnormal growth of the body leading to gigantism and low secretion of GH results in stunted growth resulting in pituitary dwarfism. Prolactin regulates the growth of the mammary glands and formation of milk in them. TSH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of thyroi ...
test review key - Hartland High School
... - be able to label all endocrine glands on a human diagram - study & review your notes, homework, and the case study - understand and be able to explain the information covered in the following questions. 1. Describe the function of the Endocrine System. Along with the nervous system, it coordinates ...
... - be able to label all endocrine glands on a human diagram - study & review your notes, homework, and the case study - understand and be able to explain the information covered in the following questions. 1. Describe the function of the Endocrine System. Along with the nervous system, it coordinates ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... medulla are stimulated by sympathetic neurons that project from the spinal cord. Thus, the adrenal medulla is often described as a modified sympathetic ganglion. The outer portion, the adrenal cortex, is a true endocrine gland that secretes steroid hormones. Specifically, it secretes aldosterone (af ...
... medulla are stimulated by sympathetic neurons that project from the spinal cord. Thus, the adrenal medulla is often described as a modified sympathetic ganglion. The outer portion, the adrenal cortex, is a true endocrine gland that secretes steroid hormones. Specifically, it secretes aldosterone (af ...
HPAT AXIS - DaVinci Labs
... The hypothalamus’ relationship to thyroid hormones is incredibly relevant to the the body’s ability to maintain hormone balance. The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4, and responds by releasing thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The release of TRH tells the ...
... The hypothalamus’ relationship to thyroid hormones is incredibly relevant to the the body’s ability to maintain hormone balance. The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4, and responds by releasing thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The release of TRH tells the ...
The Endocrine System
... There are three different kinds of molecules that could be hormones: Protein/Peptide hormones Anime (derived from amino acids) ...
... There are three different kinds of molecules that could be hormones: Protein/Peptide hormones Anime (derived from amino acids) ...
Hypophyseal portal system
... They secret glucocorticoids regulating protein + CHO metabolism The most important glucocorticoids cortisol (catabolic effects) Also they depress immune (by AB formation + lymphocyte production) + anti-inflammatory retard tissue growth. Secret small amount of androgen. The cells of zona fasciculate ...
... They secret glucocorticoids regulating protein + CHO metabolism The most important glucocorticoids cortisol (catabolic effects) Also they depress immune (by AB formation + lymphocyte production) + anti-inflammatory retard tissue growth. Secret small amount of androgen. The cells of zona fasciculate ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.