Unit P: Endocrine System
... Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the sternum, above and in front of the heart Begins to disappear at puberty ...
... Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the sternum, above and in front of the heart Begins to disappear at puberty ...
Chapter 30
... the release of many hormones. Transporting the signal - most are transported throughout the body by the bloodstream. Hitting the target - the hormone binds to a receptor on the target cell. Having an effect - when the hormone binds to the receptor protein, the protein changes shape and triggers a ch ...
... the release of many hormones. Transporting the signal - most are transported throughout the body by the bloodstream. Hitting the target - the hormone binds to a receptor on the target cell. Having an effect - when the hormone binds to the receptor protein, the protein changes shape and triggers a ch ...
Student Academic Learning Services The Endocrine System Quiz
... Student Services Building (SSB), Room 204 ...
... Student Services Building (SSB), Room 204 ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 85,29 КБ
... Once hormones have been produced by glands, they are distributed through the body via the bloodstream. As hormones travel through the body, they pass through cells or along the plasma membranes of cells until they encounter a receptor for that particular hormone. Hormones can only affect target cell ...
... Once hormones have been produced by glands, they are distributed through the body via the bloodstream. As hormones travel through the body, they pass through cells or along the plasma membranes of cells until they encounter a receptor for that particular hormone. Hormones can only affect target cell ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... gonadotropins (FSH and LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce and secrete some corticosteroid hormones. FSH and LH influence reproductive system activities by regulating hor ...
... gonadotropins (FSH and LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce and secrete some corticosteroid hormones. FSH and LH influence reproductive system activities by regulating hor ...
Quiz #6
... are stuck very stressed in a traffic jam on a freeway. Which of the following ANS “stress responses” are most likely happening in your body? A) your heart rate and force is increased B) your blood pressure increases C) the breakdown of fatty acids and triglycerides (fats) in your adipose tissue is i ...
... are stuck very stressed in a traffic jam on a freeway. Which of the following ANS “stress responses” are most likely happening in your body? A) your heart rate and force is increased B) your blood pressure increases C) the breakdown of fatty acids and triglycerides (fats) in your adipose tissue is i ...
Endocrine System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... response (US Mail service) than the nervous system (email) but usually effects last longer Maintains homeostasis by releasing chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream from glands ...
... response (US Mail service) than the nervous system (email) but usually effects last longer Maintains homeostasis by releasing chemicals called hormones into the bloodstream from glands ...
No Slide Title
... Adrenal Disorders • Pheochromocytoma – tumor of adrenal medulla, with hypersecretion of (nor-)epinephrine – causes BP, metabolic rate, hyperglycemia, ...
... Adrenal Disorders • Pheochromocytoma – tumor of adrenal medulla, with hypersecretion of (nor-)epinephrine – causes BP, metabolic rate, hyperglycemia, ...
The Endocrine System
... potassium ions. • Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, act on many cells to conserve glucose by utilizing fatty acids and proteins as an energy source (glucose-sparing effect), and they function as anti-inflammatory agents by inhibiting ce\1ls in the immune system. • Androgens (gonadocorticoids) ar ...
... potassium ions. • Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, act on many cells to conserve glucose by utilizing fatty acids and proteins as an energy source (glucose-sparing effect), and they function as anti-inflammatory agents by inhibiting ce\1ls in the immune system. • Androgens (gonadocorticoids) ar ...
No Slide Title
... Adrenal Disorders • Pheochromocytoma – tumor of adrenal medulla, with hypersecretion of (nor-)epinephrine – causes BP, metabolic rate, hyperglycemia, ...
... Adrenal Disorders • Pheochromocytoma – tumor of adrenal medulla, with hypersecretion of (nor-)epinephrine – causes BP, metabolic rate, hyperglycemia, ...
Organs of the Endocrine System and Their Products
... (capillary networks and small veins) – carries regulatory hormones from hypothalamus to pituitary • releasing hormones stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones • inhibitory hormones inhibit secretion ...
... (capillary networks and small veins) – carries regulatory hormones from hypothalamus to pituitary • releasing hormones stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones • inhibitory hormones inhibit secretion ...
Title: The Endocrine System
... b-Only target cells have receptor sites (i.e., TSH only effects the thyroid gland because only the thyroid gland has receptor sites) c- Most target cells have between 200 -100,000 receptors for a particular hormone. When a hormone is present in excess, the target cell becomes less receptive to the h ...
... b-Only target cells have receptor sites (i.e., TSH only effects the thyroid gland because only the thyroid gland has receptor sites) c- Most target cells have between 200 -100,000 receptors for a particular hormone. When a hormone is present in excess, the target cell becomes less receptive to the h ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE PITUITARY GLAND
... • Draw a diagram of the pituitary gland to include the anterior pituitary, posterior pituitary, the capillary system, nerves from the hypothalamus, and the hypothalamus. PART II: TABLE OF HORMONES • Make a table of the hormones of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus (12) to include the releasing or ...
... • Draw a diagram of the pituitary gland to include the anterior pituitary, posterior pituitary, the capillary system, nerves from the hypothalamus, and the hypothalamus. PART II: TABLE OF HORMONES • Make a table of the hormones of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus (12) to include the releasing or ...
Biochemistry, Secretion, and Transport of Hormones
... hormones because they are derived from ___________. Stimulation of the chromaffin cells causes an influx of ________ ions, which causes the vesicles to merge with the plasma membrane and release the hormone by __________. Are catecholamines water soluble or lipid soluble? ...
... hormones because they are derived from ___________. Stimulation of the chromaffin cells causes an influx of ________ ions, which causes the vesicles to merge with the plasma membrane and release the hormone by __________. Are catecholamines water soluble or lipid soluble? ...
The Endocrine System - Highland 4U Biology with Mr. Byrnes
... • The class will be split into 2 groups. Each group will dramatically demonstrate the actions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, hormones and target cells/organs • Use cue cards and markers to illustrate which components of the system each person represents • Be sure to include details such as wh ...
... • The class will be split into 2 groups. Each group will dramatically demonstrate the actions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, hormones and target cells/organs • Use cue cards and markers to illustrate which components of the system each person represents • Be sure to include details such as wh ...
hormones and behavior
... to elevated blood glucose levels from increased gluconeogenesis, and increase blood amino acid levels from muscle and connective tissue protein breakdown (to combat starvation) ...
... to elevated blood glucose levels from increased gluconeogenesis, and increase blood amino acid levels from muscle and connective tissue protein breakdown (to combat starvation) ...
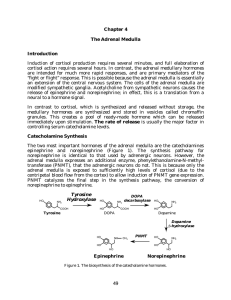
Chapter 4 The Adrenal Medulla Introduction - Rose
... output, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration (epinephrine is a powerful bronchodilator). They also increase blood flow to the muscles, while decreasing the splanchnic and renal blood flow. Finally, they increase alertness (chronic stimulation results in anxiety). The net effects are to rerout ...
... output, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration (epinephrine is a powerful bronchodilator). They also increase blood flow to the muscles, while decreasing the splanchnic and renal blood flow. Finally, they increase alertness (chronic stimulation results in anxiety). The net effects are to rerout ...
Ch13
... The nervous system uses bioelectrical signals that travel along the nerve cells while the endocrine system releases hormones into the bloodstream and these circulate throughout the body. The nervous system acts by using a rapid, short – lived response while the endocrine system produces a slow, ...
... The nervous system uses bioelectrical signals that travel along the nerve cells while the endocrine system releases hormones into the bloodstream and these circulate throughout the body. The nervous system acts by using a rapid, short – lived response while the endocrine system produces a slow, ...
Endocrinology Features of Endocrine system:
... Stimulate liver to build glucose from amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol ...
... Stimulate liver to build glucose from amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol ...
Hypothalamic Control of Pituitary Function
... innervate the posterior pituitary gland, which is responsible for ADH and oxytocin production. The arcuate nucleus is the chief hypothalamic structure which secretes releasing factors to the anterior pituitary. It does this by a unique blood supply called the hypophysial portal system which transpor ...
... innervate the posterior pituitary gland, which is responsible for ADH and oxytocin production. The arcuate nucleus is the chief hypothalamic structure which secretes releasing factors to the anterior pituitary. It does this by a unique blood supply called the hypophysial portal system which transpor ...
The Endocrine System
... The nervous system uses bioelectrical signals that travel along the nerve cells while the endocrine system releases hormones into the bloodstream and these circulate throughout the body. The nervous system acts by using a rapid, short – lived response while the endocrine system produces a slow, ...
... The nervous system uses bioelectrical signals that travel along the nerve cells while the endocrine system releases hormones into the bloodstream and these circulate throughout the body. The nervous system acts by using a rapid, short – lived response while the endocrine system produces a slow, ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... ENDOCRINE GLAND = a gland that secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream; a ductless gland. Exocrine gland = a gland that secretes substances into ducts which then leave the body (i.e. sweat/sebaceous glands) or into a internal space or lumen (i.e. digestive glands). Exocrine glands are not pa ...
... ENDOCRINE GLAND = a gland that secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream; a ductless gland. Exocrine gland = a gland that secretes substances into ducts which then leave the body (i.e. sweat/sebaceous glands) or into a internal space or lumen (i.e. digestive glands). Exocrine glands are not pa ...
Chapter 10 Endocrine System
... Integrative centers release regulatory hormones to control activity of the adenohypophysis (anterior lobe of the pituitary gland). Regulatory hormones reach their targets via the hypophyseal portal system, detailed below. ...
... Integrative centers release regulatory hormones to control activity of the adenohypophysis (anterior lobe of the pituitary gland). Regulatory hormones reach their targets via the hypophyseal portal system, detailed below. ...
PPT slides handout as PDF 08
... • Substance produced by endocrine gland • Acts on cells, tissues or organs at a place ...
... • Substance produced by endocrine gland • Acts on cells, tissues or organs at a place ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.