Endocrine Organs - V14-Study
... gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis in different organs (liver, adipose tissue) as well as suppress immune and inflammatory responses. ACTH controls the production and secretion of glucocorticoids. 3. Zona reticularis is a thinner zone that contains smaller cells that secret weak androgens (sex hormone ...
... gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis in different organs (liver, adipose tissue) as well as suppress immune and inflammatory responses. ACTH controls the production and secretion of glucocorticoids. 3. Zona reticularis is a thinner zone that contains smaller cells that secret weak androgens (sex hormone ...
Unit 12 Animal Anatomy and Physiology Part 2
... -These effects are reversed by PTH, which is secreted from the parathyroid glands when the concentration of blood Ca 2+ falls below the set point -Blood calcium levels begin to increase as target cells in the bones and kidneys respond to PTH -In addition to stimulating Ca2+ uptake in these organs di ...
... -These effects are reversed by PTH, which is secreted from the parathyroid glands when the concentration of blood Ca 2+ falls below the set point -Blood calcium levels begin to increase as target cells in the bones and kidneys respond to PTH -In addition to stimulating Ca2+ uptake in these organs di ...
Unit 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... Controls blood sugar by secreting insulin and glucagons ...
... Controls blood sugar by secreting insulin and glucagons ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 10 The Human Endocrine
... a. Control "Systems" of the Human Body. The structure and function of the human body is controlled and organized by several different "systems." (1) Heredity/environment. The interaction of heredity and environment is the fundamental control "system." Genes determine the range of potentiality and en ...
... a. Control "Systems" of the Human Body. The structure and function of the human body is controlled and organized by several different "systems." (1) Heredity/environment. The interaction of heredity and environment is the fundamental control "system." Genes determine the range of potentiality and en ...
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #1
... completely surrounds the inner medulla which forms about 10-20% of the organ. The cortex surrounds the deep medullary tissue and is divided into three layers. From superficial to dep these are the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis (figure 17.11b). You are not responsible for id ...
... completely surrounds the inner medulla which forms about 10-20% of the organ. The cortex surrounds the deep medullary tissue and is divided into three layers. From superficial to dep these are the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis (figure 17.11b). You are not responsible for id ...
Target cells
... The Adrenal Cortex • secretes mineralocorticoids, mostly aldosterone – Target – kidneys – Effect – increases blood sodium, decreases blood potassium • – secretes glucocorticoids (cortisol, corticosterone) – Target – most cells – Effect – conserve blood glucose, anti-inflammatory effects • – secrete ...
... The Adrenal Cortex • secretes mineralocorticoids, mostly aldosterone – Target – kidneys – Effect – increases blood sodium, decreases blood potassium • – secretes glucocorticoids (cortisol, corticosterone) – Target – most cells – Effect – conserve blood glucose, anti-inflammatory effects • – secrete ...
Adrenal Glands
... CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
01 - ALCA
... office find his house in a couple of days to deliver the message. Now…much like the postal office’s options of priority and express mail, the endocrine system can also speed up delivery of certain messages based on importance. Now we can see the mechanism of message delivery for the nervous vs. endo ...
... office find his house in a couple of days to deliver the message. Now…much like the postal office’s options of priority and express mail, the endocrine system can also speed up delivery of certain messages based on importance. Now we can see the mechanism of message delivery for the nervous vs. endo ...
Endocrinology
... TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH are called tropic hormones because they regulate secretory activity in other endocrine glands. In addition, all four hormones affect their target cells via a cAMP second-messenger system. The mechanisms for GH and PRL action are not fully understood. Growth hormone GH is respo ...
... TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH are called tropic hormones because they regulate secretory activity in other endocrine glands. In addition, all four hormones affect their target cells via a cAMP second-messenger system. The mechanisms for GH and PRL action are not fully understood. Growth hormone GH is respo ...
chapter 45 - Biology Junction
... stimulate the anterior pituitary to release its hormones. Others (inhibiting hormones) inhibit hormone secretion. Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are secreted into capillaries at the base of the hypothalamus. The capillaries drain into portal vessels that subdivide into a second c ...
... stimulate the anterior pituitary to release its hormones. Others (inhibiting hormones) inhibit hormone secretion. Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are secreted into capillaries at the base of the hypothalamus. The capillaries drain into portal vessels that subdivide into a second c ...
chapt17_student - Human Anatomy and Physiology
... • mobilize high energy fuels, lactate, fatty acids, and glucose • glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis boost glucose levels • glucose-sparing effect because inhibits insulin secretion – muscles use fatty acids saving glucose for brain ...
... • mobilize high energy fuels, lactate, fatty acids, and glucose • glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis boost glucose levels • glucose-sparing effect because inhibits insulin secretion – muscles use fatty acids saving glucose for brain ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 10e
... Melatonin: regulates biological rhythms Thyroid gland (see Figures 41.12 and 41.14) Thyroxine (T3 and T4 ): increases cell metabolism; essential for growth and neural development Calcitonin: stimulates incorporation of calcium into bone Parathyroid glands (on posterior surface of thyroid; see Figure ...
... Melatonin: regulates biological rhythms Thyroid gland (see Figures 41.12 and 41.14) Thyroxine (T3 and T4 ): increases cell metabolism; essential for growth and neural development Calcitonin: stimulates incorporation of calcium into bone Parathyroid glands (on posterior surface of thyroid; see Figure ...
Chapter 18
... produces pancreatic juice (enzymes) and a duct system. The endocrine part consists of pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) separated into: Alpha cells (glucagon production, protein) ...
... produces pancreatic juice (enzymes) and a duct system. The endocrine part consists of pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) separated into: Alpha cells (glucagon production, protein) ...
Pituitary Articles
... the pituitary to produce the necessary hormones. Some of these hormones are produced specifically for the “fight or flight” response, a part of the sympathetic nervous system. Hormones .The hormones released by the posterior pituitary gland are actually synthesized by the hypothalamus. They migrate ...
... the pituitary to produce the necessary hormones. Some of these hormones are produced specifically for the “fight or flight” response, a part of the sympathetic nervous system. Hormones .The hormones released by the posterior pituitary gland are actually synthesized by the hypothalamus. They migrate ...
The Endocrine System - Austin Community College
... Stimulation of calcitriol production at kidneys; enhanced Ca2+, PO4-3, absorption by digestive tract >> Calcium levels rise *Normal calcium levels: 8.5 – 11 mg/dL Adrenal (Suprarenal) Glands Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys Structurally and functionally, they are two g ...
... Stimulation of calcitriol production at kidneys; enhanced Ca2+, PO4-3, absorption by digestive tract >> Calcium levels rise *Normal calcium levels: 8.5 – 11 mg/dL Adrenal (Suprarenal) Glands Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys Structurally and functionally, they are two g ...
3 Endocrinology
... TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH are called tropic hormones because they regulate secretory activity in other endocrine glands. In addition, all four hormones affect their target cells via a cAMP second-messenger system. The mechanisms for GH and PRL action are not fully understood. Growth hormone GH is respo ...
... TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH are called tropic hormones because they regulate secretory activity in other endocrine glands. In addition, all four hormones affect their target cells via a cAMP second-messenger system. The mechanisms for GH and PRL action are not fully understood. Growth hormone GH is respo ...
endocr
... TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH are called tropic hormones because they regulate secretory activity in other endocrine glands. In addition, all four hormones affect their target cells via a cAMP second-messenger system. The mechanisms for GH and PRL action are not fully understood. Growth hormone GH is respo ...
... TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH are called tropic hormones because they regulate secretory activity in other endocrine glands. In addition, all four hormones affect their target cells via a cAMP second-messenger system. The mechanisms for GH and PRL action are not fully understood. Growth hormone GH is respo ...
The Endocrine System
... The Anterior Pituitary: The anterior pituitary secretes a number of different tropic hormones, including GH (Growth Hormone) which stimulates bone growth when we are young, Prolactin, which stimulates milk production in nursing females, FSH (FollicleStimulating Hormone) which stimulates sperm and ov ...
... The Anterior Pituitary: The anterior pituitary secretes a number of different tropic hormones, including GH (Growth Hormone) which stimulates bone growth when we are young, Prolactin, which stimulates milk production in nursing females, FSH (FollicleStimulating Hormone) which stimulates sperm and ov ...
Stress materials - Stephenson College
... that functions involuntarily, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and breathing. 3. Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands involved in the body’s response to stress, including the metabolism of fat, glucose, and protein. 4. Distress is stress caused by adverse events that ...
... that functions involuntarily, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and breathing. 3. Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands involved in the body’s response to stress, including the metabolism of fat, glucose, and protein. 4. Distress is stress caused by adverse events that ...
Growth and Development
... 2. Describe the influences of the endocrine system on growth and development. The endocrine system produces hormones that go directly into the bloodstream. The hormones are then carried to different parts of the body to control various functions, including growth and development. ...
... 2. Describe the influences of the endocrine system on growth and development. The endocrine system produces hormones that go directly into the bloodstream. The hormones are then carried to different parts of the body to control various functions, including growth and development. ...
Lesson Overview
... The activity of the thyroid gland is controlled by the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland. When the hypothalamus senses that thyroxine levels are low, it secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). ...
... The activity of the thyroid gland is controlled by the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland. When the hypothalamus senses that thyroxine levels are low, it secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). ...
Adrenal gland

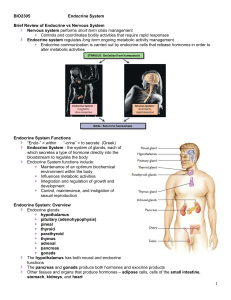
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.