Lecture 5: Endocrine System
... A regulatory system that produces hormones. The endocrine system is not truly a distinct system (though it does have specific organs that are identified as “endocrine players”) because it plays a role in everything. 1. Hormone: a substance secreted by a gland (or single cell) into the blood that ac ...
... A regulatory system that produces hormones. The endocrine system is not truly a distinct system (though it does have specific organs that are identified as “endocrine players”) because it plays a role in everything. 1. Hormone: a substance secreted by a gland (or single cell) into the blood that ac ...
Nervous System P2
... into axon through a channel so the Na+ ions rush from the outside of the to the inside • This changes the across the neuron from (resting potential) to + ...
... into axon through a channel so the Na+ ions rush from the outside of the to the inside • This changes the across the neuron from (resting potential) to + ...
hormones
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
Slide 1
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
Pituitary hormones - Department of Molecular & Cell Biology
... responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics and cyclic changes in the viginal epithelium and endothelium of the uterus. ...
... responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics and cyclic changes in the viginal epithelium and endothelium of the uterus. ...
Chapter 10 - Hormonal and Reproductive Drugs
... messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
... messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
Hormones File
... Endocrine Glands and Hormones? • 41.4 How Do We Study Mechanisms of Hormone Action? ...
... Endocrine Glands and Hormones? • 41.4 How Do We Study Mechanisms of Hormone Action? ...
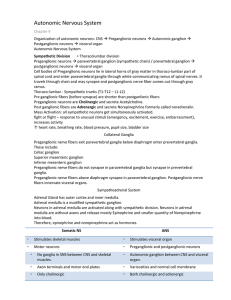
Autonomic Nervous System
... Post ganglionic fibers are Adrenergic and secrete Norepinephrine formerly called noradrenalin. Mass Activation: all sympathetic neurons get simultaneously activated. fight or flight – response to unusual stimuli (emergency, excitement, exercise, embarrassment), increases activity ↑ heart rate, breat ...
... Post ganglionic fibers are Adrenergic and secrete Norepinephrine formerly called noradrenalin. Mass Activation: all sympathetic neurons get simultaneously activated. fight or flight – response to unusual stimuli (emergency, excitement, exercise, embarrassment), increases activity ↑ heart rate, breat ...
2-3 endocrine sys Sp12
... cell surface Insulin binds to its receptor Insulin recruits glucose transporters from inside the cell to the cell surface Glucose is transported into cells ...
... cell surface Insulin binds to its receptor Insulin recruits glucose transporters from inside the cell to the cell surface Glucose is transported into cells ...
Background Information for the Teacher`s Guide
... dynamic equilibrium where feedback mechanisms are constantly being made so that levels are staying at or near the normal ranges. The endocrine glands are controlled by stimulation from the nervous system, by chemical receptors in the blood, and by hormones produced by other glands. ...
... dynamic equilibrium where feedback mechanisms are constantly being made so that levels are staying at or near the normal ranges. The endocrine glands are controlled by stimulation from the nervous system, by chemical receptors in the blood, and by hormones produced by other glands. ...
Hormone
... Acts with the nervous system to coordinate and integrate the activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities by means of hormones transported in the blood Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system ...
... Acts with the nervous system to coordinate and integrate the activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities by means of hormones transported in the blood Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system ...
Insulin
... Failure to produce adequate levels of glucocorticoid (cortisol) Cause: autoimmune / adrenal gland disorders immune system gradually destroys the adrenal ...
... Failure to produce adequate levels of glucocorticoid (cortisol) Cause: autoimmune / adrenal gland disorders immune system gradually destroys the adrenal ...
Hormones
... A. releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. B. releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs simultaneously. C. produces effects that can last for hours, days and even longer. D. Both A and B are correct. E. A, B and C ...
... A. releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. B. releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs simultaneously. C. produces effects that can last for hours, days and even longer. D. Both A and B are correct. E. A, B and C ...
CHAPTER 36
... markedly increased during the early period of sleep but is reduced during the later stages of sleep. In many cases, these cyclical variations in hormone secretion are due to ...
... markedly increased during the early period of sleep but is reduced during the later stages of sleep. In many cases, these cyclical variations in hormone secretion are due to ...
File - Mrs. Riggs Online
... synthesized and secreted by a group of specialized cells referred to as an endocrine gland; endocrine glands are ductless glands released by these cells directly into the circulatory system travels to another area of the body where it elicits specific biological responses from selected target ce ...
... synthesized and secreted by a group of specialized cells referred to as an endocrine gland; endocrine glands are ductless glands released by these cells directly into the circulatory system travels to another area of the body where it elicits specific biological responses from selected target ce ...
H UMAN BODY SYSTEMS
... that defend the body from viruses, bacteria, and even cancer cells. These invaders are neutralised when their antigens (proteins on their surfaces) are recognized by antibodies made by T-cells and B-cells (types of lymphocytes) . The inflammatory response: damaged cells release chemicals that signal ...
... that defend the body from viruses, bacteria, and even cancer cells. These invaders are neutralised when their antigens (proteins on their surfaces) are recognized by antibodies made by T-cells and B-cells (types of lymphocytes) . The inflammatory response: damaged cells release chemicals that signal ...
H UMAN BODY SYSTEMS
... that defend the body from viruses, bacteria, and even cancer cells. These invaders are neutralised when their antigens (proteins on their surfaces) are recognized by antibodies made by T-cells and B-cells (types of lymphocytes) . The inflammatory response: damaged cells release chemicals that signal ...
... that defend the body from viruses, bacteria, and even cancer cells. These invaders are neutralised when their antigens (proteins on their surfaces) are recognized by antibodies made by T-cells and B-cells (types of lymphocytes) . The inflammatory response: damaged cells release chemicals that signal ...
Hormones
... Adrenal Medulla • Secretes the catecholamines – Epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) – Bind to adrenergic receptors • Alpha () • Beta () ...
... Adrenal Medulla • Secretes the catecholamines – Epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) – Bind to adrenergic receptors • Alpha () • Beta () ...
Unit 22.2: The Endocrine System
... the blood. Insulin causes excess blood glucose to be taken up by the liver, which stores the glucose as glycogen. Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and release it back into the blood. The pancreas also secretes digestive enzymes into the digestive tract. • The two adr ...
... the blood. Insulin causes excess blood glucose to be taken up by the liver, which stores the glucose as glycogen. Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and release it back into the blood. The pancreas also secretes digestive enzymes into the digestive tract. • The two adr ...
2-Anterior pituitary hormones
... IV-The thyroid gland The thyroid gland is located in the lower pasrt of the neck wrapped around the front of the trachea.It composed of many spherical structures called follicles, each consisting of a single layer of epithelial cell surrounding an extracellular central space filled with a glycoprot ...
... IV-The thyroid gland The thyroid gland is located in the lower pasrt of the neck wrapped around the front of the trachea.It composed of many spherical structures called follicles, each consisting of a single layer of epithelial cell surrounding an extracellular central space filled with a glycoprot ...
PATHOLOGY OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Features common to all pituitary adenomas : • 10% of all intracranial neoplasms & 25% incidental 3% occur with MEN syndrome • 30-50 years of age • Primary pituitary adenomas usually benign • May or may not be functional • If functional, the clinical effects are secondary to the hormone produced. • ...
... Features common to all pituitary adenomas : • 10% of all intracranial neoplasms & 25% incidental 3% occur with MEN syndrome • 30-50 years of age • Primary pituitary adenomas usually benign • May or may not be functional • If functional, the clinical effects are secondary to the hormone produced. • ...
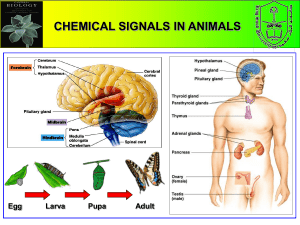
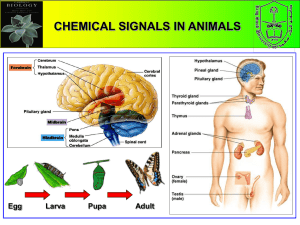
B. Chemical signal sent between individual are called C. Survival
... B. Name the disorder that is believed by some to be caused by an over activity of amygdale C. Glands that release their secretions into ducts leading to a body surface D. When a gland is stimulated to increase its secretion by the substance it produces e. group of lipids that have powerful, regulati ...
... B. Name the disorder that is believed by some to be caused by an over activity of amygdale C. Glands that release their secretions into ducts leading to a body surface D. When a gland is stimulated to increase its secretion by the substance it produces e. group of lipids that have powerful, regulati ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.