Biology 7 Study Guide – Exam #3
... posterior pituitary – stores, secretes ADH, oxytocin from hypothalamus o anterior pituitary – follicle stimulation hormone (FSH), leutinizing hormone (LH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), prolactin, growth hormone, melanocyte stimulating hormone o thyroid gla ...
... posterior pituitary – stores, secretes ADH, oxytocin from hypothalamus o anterior pituitary – follicle stimulation hormone (FSH), leutinizing hormone (LH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), prolactin, growth hormone, melanocyte stimulating hormone o thyroid gla ...
Endocrinology Regulation of Posterior pituitary hormones and
... The thyroid gland has 2 lobes of endocrine tissue joined in the middle by narrow portion of the gland called the isthmus. Looks similar to a bow tie. The gland is located immediately below the larynx on the ventral surface anterior to the trachea. If we took a cross section of each lobe, would find ...
... The thyroid gland has 2 lobes of endocrine tissue joined in the middle by narrow portion of the gland called the isthmus. Looks similar to a bow tie. The gland is located immediately below the larynx on the ventral surface anterior to the trachea. If we took a cross section of each lobe, would find ...
ANP 201 Dr Smith - University of Agriculture Abeokuta
... The thyroid gland produces two different kinds of hormones. The first group are thyroxine and triiodothyronine, the second is called calcitonin. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) released form the adenohypophysis maintains the volume, weight and secretory activity of the thyroid gland. As the name i ...
... The thyroid gland produces two different kinds of hormones. The first group are thyroxine and triiodothyronine, the second is called calcitonin. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) released form the adenohypophysis maintains the volume, weight and secretory activity of the thyroid gland. As the name i ...
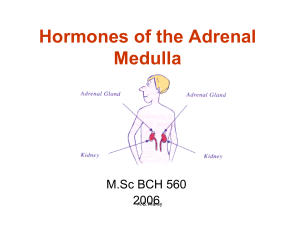
Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla
... In the United States alone this amounts to about 800,000 cases of newly diagnosed hypertension each year in which pheochromocytoma may represent a correctable cause of high blood pressure. It is not feasible or cost effective to screen for pheochromocytoma in every patient with hypertension, particu ...
... In the United States alone this amounts to about 800,000 cases of newly diagnosed hypertension each year in which pheochromocytoma may represent a correctable cause of high blood pressure. It is not feasible or cost effective to screen for pheochromocytoma in every patient with hypertension, particu ...
Powerpoint
... Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) Adrenal cortex secretes steroids (including mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens) ...
... Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) Adrenal cortex secretes steroids (including mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens) ...
Endocrine System Endocrine System: Overview Types of Hormones
... Preganglionic sympathetic nervous system (SNS) fibers stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete catecholamines ...
... Preganglionic sympathetic nervous system (SNS) fibers stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete catecholamines ...
Thyroid Gland
... 1. Paired glands: one located near upper portion of each kidney 2. Divided into 2 regions: a. Adrenal cortex: outer region b. Adrenal medulla: inner region ...
... 1. Paired glands: one located near upper portion of each kidney 2. Divided into 2 regions: a. Adrenal cortex: outer region b. Adrenal medulla: inner region ...
Hormones and regulation
... • Hormones from the adrenal glands help maintain homeostasis when the body is stressed • Adrenal medulla – Nervous signals from the hypothalamus stimulate secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine – These quickly trigger the fight or flight response ...
... • Hormones from the adrenal glands help maintain homeostasis when the body is stressed • Adrenal medulla – Nervous signals from the hypothalamus stimulate secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine – These quickly trigger the fight or flight response ...
BS1060
... • Hormones are information transferring molecules which move from one cell to another for the benefit of the organism as a whole Huxley) Endocrine Cell ...
... • Hormones are information transferring molecules which move from one cell to another for the benefit of the organism as a whole Huxley) Endocrine Cell ...
endocrine i laboratory
... Embryology - Arise from 2 separate primordia, one ectodermal (medulla) and one mesodermal (cortex). Cortex develops from mesenchymal cells on posterior body wall between gonad and mesentery (urogenital ridge). Medulla formed by ectodermal cells that migrate from neural crest of cortical region, via ...
... Embryology - Arise from 2 separate primordia, one ectodermal (medulla) and one mesodermal (cortex). Cortex develops from mesenchymal cells on posterior body wall between gonad and mesentery (urogenital ridge). Medulla formed by ectodermal cells that migrate from neural crest of cortical region, via ...
Lecture_36_2014_noquiz
... stimulates thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH): involved in production of sex hormones; regulate menstrual cycle in females Prolactin: stimulates mammary gland growth and milk production in females ...
... stimulates thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH): involved in production of sex hormones; regulate menstrual cycle in females Prolactin: stimulates mammary gland growth and milk production in females ...
Definitions
... The sympathetic division typically functions in actions requiring quick responses. ...
... The sympathetic division typically functions in actions requiring quick responses. ...
endocrine i laboratory
... Embryology - Arise from 2 separate primordia, one ectodermal (medulla) and one mesodermal (cortex). Cortex develops from mesenchymal cells on posterior body wall between gonad and mesentery (urogenital ridge). Medulla formed by ectodermal cells that migrate from neural crest of cortical region, via ...
... Embryology - Arise from 2 separate primordia, one ectodermal (medulla) and one mesodermal (cortex). Cortex develops from mesenchymal cells on posterior body wall between gonad and mesentery (urogenital ridge). Medulla formed by ectodermal cells that migrate from neural crest of cortical region, via ...
Endocrine System PPT
... the thyroid follicle. The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, which is made by the follicular cells. Since th ...
... the thyroid follicle. The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, which is made by the follicular cells. Since th ...
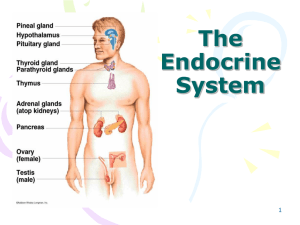
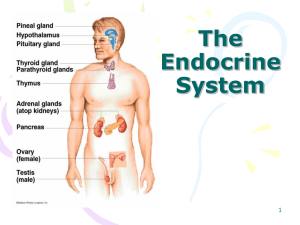
The Endocrine System
... the thyroid follicle. The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, which is made by the follicular cells. Since th ...
... the thyroid follicle. The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, which is made by the follicular cells. Since th ...
Endocrine I
... Embryology - Arise from 2 separate primordia, one ectodermal (medulla) and one mesodermal (cortex). Cortex develops from mesenchymal cells on posterior body wall between gonad and mesentery (urogenital ridge). Medulla formed by ectodermal cells that migrate from neural crest of cortical region, via ...
... Embryology - Arise from 2 separate primordia, one ectodermal (medulla) and one mesodermal (cortex). Cortex develops from mesenchymal cells on posterior body wall between gonad and mesentery (urogenital ridge). Medulla formed by ectodermal cells that migrate from neural crest of cortical region, via ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 22
... Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is secreted by the pars distalis region of the anterior pituitary. It regulates the development, growth, and reproductive processes of the human body. In the ovary, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicle. As the follicle grows and matures, it ...
... Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is secreted by the pars distalis region of the anterior pituitary. It regulates the development, growth, and reproductive processes of the human body. In the ovary, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicle. As the follicle grows and matures, it ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... • There are many glands located throughout the body. Hypothalamus: makes hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones Pituitary: controls growth and water in blood Thyroid: metabolism, energy levels, digestion Thymus: helps white blood cells fight off infection Adrenal Glands: breathe fa ...
... • There are many glands located throughout the body. Hypothalamus: makes hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones Pituitary: controls growth and water in blood Thyroid: metabolism, energy levels, digestion Thymus: helps white blood cells fight off infection Adrenal Glands: breathe fa ...
P2 – Brilliant Biopsych booklet
... Which two of the following statements about the fight or flight response are correct? Choose two responses only. During the fight or flight response: A there is a decrease in the release of adrenaline B the flow of blood is diverted from the surface of the skin C the process of digestion is inhibite ...
... Which two of the following statements about the fight or flight response are correct? Choose two responses only. During the fight or flight response: A there is a decrease in the release of adrenaline B the flow of blood is diverted from the surface of the skin C the process of digestion is inhibite ...
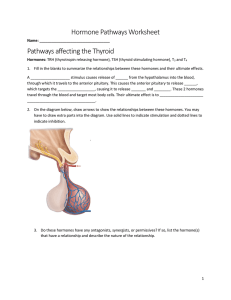
Hormone Pathways worksheet
... Pathways involving Blood Volume and Pressure Hormones: ADH (antidiuretic hormone), aldosterone, Renin Angiotensin II, ANP (atrial natriuretic hormone), erythropoietin 15. Fill in the blanks to summarize the relationships between these hormones and their ultimate effects. When blood is too concent ...
... Pathways involving Blood Volume and Pressure Hormones: ADH (antidiuretic hormone), aldosterone, Renin Angiotensin II, ANP (atrial natriuretic hormone), erythropoietin 15. Fill in the blanks to summarize the relationships between these hormones and their ultimate effects. When blood is too concent ...
Anat2_04_Endocrine
... (also slows wound healing). Depression of immune responses (utilized with organ transplant recipients). ...
... (also slows wound healing). Depression of immune responses (utilized with organ transplant recipients). ...
Endocrine System Powerpoint
... decreased digestive and kidney activity 6. Increased metabolic rate © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... decreased digestive and kidney activity 6. Increased metabolic rate © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Anatomy chapter 11 (Endocrine system)
... cells using chemicals called hormones. •Endocrine glands and their hormones regulate a number of metabolic processes within cells, and the whole body. •Their actions are precise, they only affect specific ...
... cells using chemicals called hormones. •Endocrine glands and their hormones regulate a number of metabolic processes within cells, and the whole body. •Their actions are precise, they only affect specific ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.