INTERPLAY BETWEEN HELICOBACTER PYLORI AND THE
... immune response, whereas MHC class I restricted CD8 T cells are not essential. Further experiments showed the presence of IL-12 (36) and IL-18 (37) in the gastric mucosa. Both of these cytokines are responsible for directing gastric T lymphocytes to Th1 mediated response. Experimental data in animal ...
... immune response, whereas MHC class I restricted CD8 T cells are not essential. Further experiments showed the presence of IL-12 (36) and IL-18 (37) in the gastric mucosa. Both of these cytokines are responsible for directing gastric T lymphocytes to Th1 mediated response. Experimental data in animal ...
Dialogue between skin microbiota and immunity
... Although sebum generally serves as an antibacterial coating, Propionibacterium acnes hydrolyzes triglycerides present in sebum, releases free fatty acids that promote bacterial adherence, and then colonizes sebaceous units (10). Many Malassezia and Corynebacterium species do not produce their own l ...
... Although sebum generally serves as an antibacterial coating, Propionibacterium acnes hydrolyzes triglycerides present in sebum, releases free fatty acids that promote bacterial adherence, and then colonizes sebaceous units (10). Many Malassezia and Corynebacterium species do not produce their own l ...
Gram Reaction
... - a substance recognized by T and B cell receptors Immunogen - a substance capable of eliciting immune response Hapten - a substance of low molecular weight, that can bind antibodies but induce response only if covalently attached to large carrier ...
... - a substance recognized by T and B cell receptors Immunogen - a substance capable of eliciting immune response Hapten - a substance of low molecular weight, that can bind antibodies but induce response only if covalently attached to large carrier ...
lwwus_ijg_jog-d-14-00286 59..61 - MyWeb
... environment such as the retina without cytotoxic T cells, macrophages, or natural killer cells. However, one process that can quickly result in the degeneration of an antibodybound cell in the retina is the activation of the classic complement cascade. This process, which is frequently initialized b ...
... environment such as the retina without cytotoxic T cells, macrophages, or natural killer cells. However, one process that can quickly result in the degeneration of an antibodybound cell in the retina is the activation of the classic complement cascade. This process, which is frequently initialized b ...
The role of the thymus in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell
... Thymic export and its detection via TREC analysis under steady-state conditions, in aged individuals and during acute GVHD. The top panel displays a scheme for thymus function in young individuals. The HSC-derived lymphoid progenitors ( ) enter the thymic microenvironment where they are committed to ...
... Thymic export and its detection via TREC analysis under steady-state conditions, in aged individuals and during acute GVHD. The top panel displays a scheme for thymus function in young individuals. The HSC-derived lymphoid progenitors ( ) enter the thymic microenvironment where they are committed to ...
Skin Immunity to Candida albicans
... Compartmentalization of Immunity Against C. albicans Skin Infection C. albicans is the most common and well-studied of the disease-causing Candida spp., and naturally colonizes the skin, genital, and/or intestinal mucosa in up to 70% of healthy individuals [1]. Under normal circumstances, the fungus ...
... Compartmentalization of Immunity Against C. albicans Skin Infection C. albicans is the most common and well-studied of the disease-causing Candida spp., and naturally colonizes the skin, genital, and/or intestinal mucosa in up to 70% of healthy individuals [1]. Under normal circumstances, the fungus ...
Allergen induced Treg response in the peripheral blood
... believed to play important roles in maintaining immunological tolerance and in controlling immune responses.3,4 Treg cells are considered to be important for the regulation of allergen-specific responses.5 They can suppress allergen-induced specific T-cell activation and also suppress effector cell ...
... believed to play important roles in maintaining immunological tolerance and in controlling immune responses.3,4 Treg cells are considered to be important for the regulation of allergen-specific responses.5 They can suppress allergen-induced specific T-cell activation and also suppress effector cell ...
Humoral and cellular immune responses induced by the urease
... each); esculetin and baicalein (300 μM final concentration each). Since the inhibitors’ stock solutions were prepared in 95 % ethanol, controls were performed with equivalent volumes of this solvent. For the remaining experiments, controls without Jaburetox were performed with the addition of the sa ...
... each); esculetin and baicalein (300 μM final concentration each). Since the inhibitors’ stock solutions were prepared in 95 % ethanol, controls were performed with equivalent volumes of this solvent. For the remaining experiments, controls without Jaburetox were performed with the addition of the sa ...
LETTERS
... Florencia Pereyra1, Mary Carrington1,5, Bruce D. Walker1,7 & Arup K. Chakraborty1,3,4,8 ...
... Florencia Pereyra1, Mary Carrington1,5, Bruce D. Walker1,7 & Arup K. Chakraborty1,3,4,8 ...
High Temperature Affects Cytokine Release by Human Peripheral
... inflammation others than those caused by pathogens. Compared to controls, stimulated and non-stimulated PBMC from patients with familial Mediterranean fever showed increased secretion of IL-6 and TNFα during crisis, whereas that of IL-1β and IL-1α was increased only by LPS stimulated cells. Non-sti ...
... inflammation others than those caused by pathogens. Compared to controls, stimulated and non-stimulated PBMC from patients with familial Mediterranean fever showed increased secretion of IL-6 and TNFα during crisis, whereas that of IL-1β and IL-1α was increased only by LPS stimulated cells. Non-sti ...
Anabolic androgenic steroids effects on the immune system: a review
... Figure 2. Molecular mechanism of androgenic anabolic steroid [145]. no androgen receptors. However rationale for this outcome may be explained by the presence of inactive androgen receptors [38] on these lymphocytes and the effect of AAS on intracellular signaling pathways on immune cells. Benten et ...
... Figure 2. Molecular mechanism of androgenic anabolic steroid [145]. no androgen receptors. However rationale for this outcome may be explained by the presence of inactive androgen receptors [38] on these lymphocytes and the effect of AAS on intracellular signaling pathways on immune cells. Benten et ...
Instructions for Handling PDF Galley Proofs
... SMs and AGMs exhibit a modest but transient decline of peripheral CD4+ T cell counts and a more severe loss of mucosal CD4+ T cells in both the gastrointestinal tract and lung (15, 16). In contrast to pathogenic infections where mucosal CD4+ T cells become progressively depleted during chronic infec ...
... SMs and AGMs exhibit a modest but transient decline of peripheral CD4+ T cell counts and a more severe loss of mucosal CD4+ T cells in both the gastrointestinal tract and lung (15, 16). In contrast to pathogenic infections where mucosal CD4+ T cells become progressively depleted during chronic infec ...
Immunomodulatory Roles of Lymphatic Vessels
... stimulatory cytokines or danger signals, antigen uptake by these cells helps to maintain peripheral tolerance to selfantigens because they present antigen to cognate T cells with low levels of costimulatory molecules. Obviously, soluble pathogenic antigens flow to the lymph nodes upon infection or va ...
... stimulatory cytokines or danger signals, antigen uptake by these cells helps to maintain peripheral tolerance to selfantigens because they present antigen to cognate T cells with low levels of costimulatory molecules. Obviously, soluble pathogenic antigens flow to the lymph nodes upon infection or va ...
Activation of an inflammatory response is context
... Interestingly, despite the growing interest in understanding the costs of deploying or maintaining immune effectors in natural populations, rarely has ontogeny been taken into account in these studies. This is unfortunate, as there is evidence that not only does the immune system develop differently ...
... Interestingly, despite the growing interest in understanding the costs of deploying or maintaining immune effectors in natural populations, rarely has ontogeny been taken into account in these studies. This is unfortunate, as there is evidence that not only does the immune system develop differently ...
Mastitis, Mammary Gland Immunity, and Nutrition
... Intramammary infections (IMI) result in a typical inflammatory response characterized by an influx of somatic cells composed primarily of neutrophils accompanied by variable numbers of macrophages and lymphocytes (Rainard and Riollet, 2003). The response is driven by the action of a variety of infla ...
... Intramammary infections (IMI) result in a typical inflammatory response characterized by an influx of somatic cells composed primarily of neutrophils accompanied by variable numbers of macrophages and lymphocytes (Rainard and Riollet, 2003). The response is driven by the action of a variety of infla ...
Immune recognition and rejection of allogeneic skin grafts
... to as minor histocompatibility antigens [46] , can serve as a source of determinants for recognition by allospecific T cells following transplantation [47–49] . It is clear that these proteins may represent a source of antigens for exogenous processing by recipient APCs and subsequent presentation i ...
... to as minor histocompatibility antigens [46] , can serve as a source of determinants for recognition by allospecific T cells following transplantation [47–49] . It is clear that these proteins may represent a source of antigens for exogenous processing by recipient APCs and subsequent presentation i ...
Slide 1
... Hepatic damage predominantly immune mediated - cytotoxic T cells HBV specific peptides presented on the infected liver cell surface recognized by Ag specific CD8 T cells hepatocellular inflammation and necrosis. AWACC 2009 ...
... Hepatic damage predominantly immune mediated - cytotoxic T cells HBV specific peptides presented on the infected liver cell surface recognized by Ag specific CD8 T cells hepatocellular inflammation and necrosis. AWACC 2009 ...
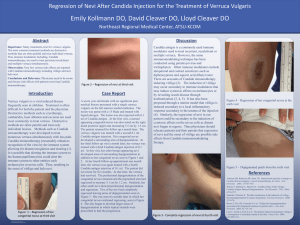
Regression of Nevi After Candida Injection for the Treatment of
... Thus immune modulators including, Candida immunotherapy, are used to treat persistent recalcitrant and multiple verruca simultaneously. Observation: Very few serious side effects are reported with Candida immunotherapy including vitiligo and now halo nevi. Conclusions and Relevance: Physicians need ...
... Thus immune modulators including, Candida immunotherapy, are used to treat persistent recalcitrant and multiple verruca simultaneously. Observation: Very few serious side effects are reported with Candida immunotherapy including vitiligo and now halo nevi. Conclusions and Relevance: Physicians need ...
Le Mercier I et al, 2013
... Despite active immunosurveillance, some tumors still progress and escape through immunosubversion processes (1, 2). The understanding of the paradoxical role of the immune system during cancer development is a major challenge for new immunotherapy strategies. Dendritic cells (DC), the most powerful ...
... Despite active immunosurveillance, some tumors still progress and escape through immunosubversion processes (1, 2). The understanding of the paradoxical role of the immune system during cancer development is a major challenge for new immunotherapy strategies. Dendritic cells (DC), the most powerful ...
NK cells in immunotolerant organs
... is also inducible to non-self-antigens.1,2 Therefore, immunotolerance is an important feature in protecting an organism from autoimmune damage and for the maintenance of the organism’s homeostasis. In the search for new therapeutics, researchers studying immunotolerance may be able to reprogram the ...
... is also inducible to non-self-antigens.1,2 Therefore, immunotolerance is an important feature in protecting an organism from autoimmune damage and for the maintenance of the organism’s homeostasis. In the search for new therapeutics, researchers studying immunotolerance may be able to reprogram the ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.