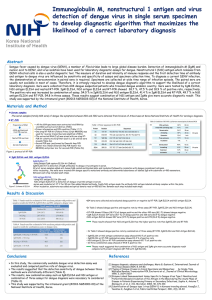
Microglia important in initiation of pain facilitation
... and changes in function (e.g., migration to sites of damage, phagocytosis, release of proinflammatory mediators) After resolution of a challenge – either return to basal state or remain primed (can be for prelonged period) ...
... and changes in function (e.g., migration to sites of damage, phagocytosis, release of proinflammatory mediators) After resolution of a challenge – either return to basal state or remain primed (can be for prelonged period) ...
- Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
... hygiene hypothesis is the skewing of the TH1/TH2 balance away from allergy-promoting TH2 cells toward TH1 cells.1 The link between the TH1/TH2 balance and allergic diseases is mediated in part by IgE: TH2 cells, by secreting IL-4 and IL-13, promote immunoglobulin class-switch recombination to IgE (f ...
... hygiene hypothesis is the skewing of the TH1/TH2 balance away from allergy-promoting TH2 cells toward TH1 cells.1 The link between the TH1/TH2 balance and allergic diseases is mediated in part by IgE: TH2 cells, by secreting IL-4 and IL-13, promote immunoglobulin class-switch recombination to IgE (f ...
In vitro blood mononuclear cells Jenny Clifford
... classified according to what cytokines they secrete (17). Th1 cells, which are mainly focussed on viral combat and the cellular branch of the adaptive immune system, secrete mainly Interferon (IFN) -γ and IL-2 (14-16, 18). This activates primarily macrophages, which in turn secrete TNF-α, IL-6 and ...
... classified according to what cytokines they secrete (17). Th1 cells, which are mainly focussed on viral combat and the cellular branch of the adaptive immune system, secrete mainly Interferon (IFN) -γ and IL-2 (14-16, 18). This activates primarily macrophages, which in turn secrete TNF-α, IL-6 and ...
Lactobacilli- and Staphylococcus aureus mediated
... conducting the appropriate response relies on the gut associated lymphoid tissues (GALT) (2). GALT is the largest immune organ, rich in both innate and adaptive immune cells. The innate cells consist of macrophages (MФ), mast cells, neutrophils, eosinophils and dendritic cells (DCs). They provide an ...
... conducting the appropriate response relies on the gut associated lymphoid tissues (GALT) (2). GALT is the largest immune organ, rich in both innate and adaptive immune cells. The innate cells consist of macrophages (MФ), mast cells, neutrophils, eosinophils and dendritic cells (DCs). They provide an ...
Long-term protection from syngeneic acute
... Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common form of cancer in children, accounting for one-third of all childhood malignancies and nearly 80% of all pediatric leukemias.1 Although current therapies have resulted in event-free survival approaching 75%,2 relapsed ALL comprises nearly 6% of a ...
... Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common form of cancer in children, accounting for one-third of all childhood malignancies and nearly 80% of all pediatric leukemias.1 Although current therapies have resulted in event-free survival approaching 75%,2 relapsed ALL comprises nearly 6% of a ...
PDF
... respective faculty remains preferable to provide an appropriate foundation in the period required for basic science. To the contrary, several medical schools have been able to integrate “some” or “a large portion” of medical microbiology and immunology into other coursework. The purpose of developin ...
... respective faculty remains preferable to provide an appropriate foundation in the period required for basic science. To the contrary, several medical schools have been able to integrate “some” or “a large portion” of medical microbiology and immunology into other coursework. The purpose of developin ...
Analysis of immune deviation elicited by antigens injected
... in 1991 that immune privilege is extended to allogeneic tumor cells injected into the vitreous cavity (VC).10 Because an important goal of our research is to transplant retinal tissues into the subretinal space, our interests were focused on immune reactions after inoculation of antigens into the su ...
... in 1991 that immune privilege is extended to allogeneic tumor cells injected into the vitreous cavity (VC).10 Because an important goal of our research is to transplant retinal tissues into the subretinal space, our interests were focused on immune reactions after inoculation of antigens into the su ...
R E V I E W S
... cells is now appreciated, both to contain the initial infection and to promote an appropriate adaptive response, which takes several days to mature9. Antigen-presenting dendritic cells (DCs) and subsets of T cells, such as CD1d-restricted NKT cells, regulate responses to peptide antigens that are pr ...
... cells is now appreciated, both to contain the initial infection and to promote an appropriate adaptive response, which takes several days to mature9. Antigen-presenting dendritic cells (DCs) and subsets of T cells, such as CD1d-restricted NKT cells, regulate responses to peptide antigens that are pr ...
Viral evasion of intracellular DNA and RNA sensing
... virus (EBOV) outbreak in West Africa in 2014. Therefore, an understanding of how viruses evade or antagonize the host antiviral response at the molecular level could guide the design of live attenuated vaccines and the development of new antiviral drugs. Furthermore, detailed insights into the molec ...
... virus (EBOV) outbreak in West Africa in 2014. Therefore, an understanding of how viruses evade or antagonize the host antiviral response at the molecular level could guide the design of live attenuated vaccines and the development of new antiviral drugs. Furthermore, detailed insights into the molec ...
Stem cells are influenced by microbial ligands
... cells are divided into two main categories; the embryonic stem cell and the adult stem cell. The focus of the report will be on adult stem cells, further referred to as stem cells. Adult stem cells are defined as undifferentiated cells found in specialized tissue that are able to self-renew and diff ...
... cells are divided into two main categories; the embryonic stem cell and the adult stem cell. The focus of the report will be on adult stem cells, further referred to as stem cells. Adult stem cells are defined as undifferentiated cells found in specialized tissue that are able to self-renew and diff ...
Drosophila melanogasteras a model for human intestinal infection
... (Qin et al., 2010). Host-microbe interactions occur primarily along skin and mucosal surfaces, and one of the largest interfaces in humans is the intestinal mucosa (Qin et al., 2010). Mucosal immune responses to microbes must distinguish commensal bacteria and mutualists from pathogenic bacteria. In ...
... (Qin et al., 2010). Host-microbe interactions occur primarily along skin and mucosal surfaces, and one of the largest interfaces in humans is the intestinal mucosa (Qin et al., 2010). Mucosal immune responses to microbes must distinguish commensal bacteria and mutualists from pathogenic bacteria. In ...
The Growth Factor and Amino Acid Requirements of
... the four named above and two additional ones for which the names L.paramesenteroides and L. oenos are proposed. Leuconostoc cremoris (group I) remains unaltered. Whittenbury ( I 966) found that some strains included in this species gave rise to ‘sucrose-fermenting mutants’, but these mutants were in ...
... the four named above and two additional ones for which the names L.paramesenteroides and L. oenos are proposed. Leuconostoc cremoris (group I) remains unaltered. Whittenbury ( I 966) found that some strains included in this species gave rise to ‘sucrose-fermenting mutants’, but these mutants were in ...
The Growth Factor and Amino Acid Requirements of
... the four named above and two additional ones for which the names L.paramesenteroides and L. oenos are proposed. Leuconostoc cremoris (group I) remains unaltered. Whittenbury ( I 966) found that some strains included in this species gave rise to ‘sucrose-fermenting mutants’, but these mutants were in ...
... the four named above and two additional ones for which the names L.paramesenteroides and L. oenos are proposed. Leuconostoc cremoris (group I) remains unaltered. Whittenbury ( I 966) found that some strains included in this species gave rise to ‘sucrose-fermenting mutants’, but these mutants were in ...
NS1 antigen ELISA
... Dengue fever caused by dengue virus (DENV), a member of Flaviviridae leads to large global disease burden. Detection of immunoglobulin M (IgM) and nucleic acid to DENV, and virus isolation have been used for laboratory diagnostic assays for dengue. Nonstructural 1 (NS1) antigen which releases from D ...
... Dengue fever caused by dengue virus (DENV), a member of Flaviviridae leads to large global disease burden. Detection of immunoglobulin M (IgM) and nucleic acid to DENV, and virus isolation have been used for laboratory diagnostic assays for dengue. Nonstructural 1 (NS1) antigen which releases from D ...
Immune System
... b. We have million of B-cells and each one produces a different antibody, which will bind to a different antigen (one B-cell, one antigen). c. B-cells display the antibody they make (~100,000 of them) on their surface as an antigen receptor and wait in the lymph system and spleen for an antigen that ...
... b. We have million of B-cells and each one produces a different antibody, which will bind to a different antigen (one B-cell, one antigen). c. B-cells display the antibody they make (~100,000 of them) on their surface as an antigen receptor and wait in the lymph system and spleen for an antigen that ...
Deciphering the STING Paradox
... direct administration of cGAMP. With several close structural examinations, another key discovery was made. Metazoan cGAMP is structurally distinct to the bacterial cGAMP5,6. Metazoan cGAMP contains [G(2′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p] phosphodiester linkages, whereas bacterial cGAMP contains [G(3′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p] l ...
... direct administration of cGAMP. With several close structural examinations, another key discovery was made. Metazoan cGAMP is structurally distinct to the bacterial cGAMP5,6. Metazoan cGAMP contains [G(2′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p] phosphodiester linkages, whereas bacterial cGAMP contains [G(3′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p] l ...
Consent Agenda - Geisel School of Medicine
... ribosomes necessary for the rapid protein synthesis required for rapid growth.) Some bacterial cells also have flagella. However, the structure of bacterial flagella is very different (a long, helical filament composed of repeating protein (flagellin) subunits with a hollow tube down the middle). Th ...
... ribosomes necessary for the rapid protein synthesis required for rapid growth.) Some bacterial cells also have flagella. However, the structure of bacterial flagella is very different (a long, helical filament composed of repeating protein (flagellin) subunits with a hollow tube down the middle). Th ...
Raulet, D.H. 2003. Roles of the NKG2D immunoreceptor and its ligands. Nat Rev Immunol 3:781-790.
... present, H60 is the only ligand that is known to be expressed at high levels by normal adult cells, in particular thymocytes in BALB/c (not C57BL/6) mice42. It is probable, however, that the thymus is inaccessible to most mature lymphocytes that are potentially responsive to H60, which might help to ...
... present, H60 is the only ligand that is known to be expressed at high levels by normal adult cells, in particular thymocytes in BALB/c (not C57BL/6) mice42. It is probable, however, that the thymus is inaccessible to most mature lymphocytes that are potentially responsive to H60, which might help to ...
The role of lymph node sinus macrophages in host defense
... example is that of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), an arthropod-borne rhabdovirus that causes fatal paralytic disease in mammals, including mice.65 Upon arrival in LNs, VSV readily replicates in SCS, but not medullary, macrophages.15,18,30,66 Several phenotypic and functional features of SCS and m ...
... example is that of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), an arthropod-borne rhabdovirus that causes fatal paralytic disease in mammals, including mice.65 Upon arrival in LNs, VSV readily replicates in SCS, but not medullary, macrophages.15,18,30,66 Several phenotypic and functional features of SCS and m ...
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis on the Vulva: A Case Report and
... showing mono- or multinucleated Langerhans cells, histiocytes, and eosinophils. For a definitive diagnosis of LCH, Birbeck’s granules must be detected by electronic microscopy, or else the S-100 protein must be found, or the histiocytic cells in lesions consistent with LCH must be found to be positi ...
... showing mono- or multinucleated Langerhans cells, histiocytes, and eosinophils. For a definitive diagnosis of LCH, Birbeck’s granules must be detected by electronic microscopy, or else the S-100 protein must be found, or the histiocytic cells in lesions consistent with LCH must be found to be positi ...
Immunology - Department of Pathology
... All those who undertake a Research Project will have the opportunity to present their work at a day of Project Presentations starting at 10:00 am on Thursday 4 May 2017 in the Seminar Room. Details will be emailed to students closer to the date. In preparation for the “practical exam” on data handli ...
... All those who undertake a Research Project will have the opportunity to present their work at a day of Project Presentations starting at 10:00 am on Thursday 4 May 2017 in the Seminar Room. Details will be emailed to students closer to the date. In preparation for the “practical exam” on data handli ...
Induced disruption of the transforming growth factor
... cells is sufficient to generate a fully developed and lethal inflammatory phenotype. For this purpose a conditional knockout model was developed, using the Cre/lox system,29-31 designed to disrupt the TRII in adult animals upon induction with interferon-␣/ or polyI:polyC, which releases interferon ...
... cells is sufficient to generate a fully developed and lethal inflammatory phenotype. For this purpose a conditional knockout model was developed, using the Cre/lox system,29-31 designed to disrupt the TRII in adult animals upon induction with interferon-␣/ or polyI:polyC, which releases interferon ...
Lymphocytic hypophysitis: a rare or underestimated disease?
... granulomatous hypophysitis (GRH), and xanthomatous hypophysitis (XH). It is unclear whether these are truly distinct entities or only different expressions of the same disease, since they share clinical and radiological features and can only be distinguished from each ...
... granulomatous hypophysitis (GRH), and xanthomatous hypophysitis (XH). It is unclear whether these are truly distinct entities or only different expressions of the same disease, since they share clinical and radiological features and can only be distinguished from each ...