Jon Storm-Mathisen - Universitetet i Oslo
... Theoretical questions – functional anatomy: emphasis on clinically relevant topics ...
... Theoretical questions – functional anatomy: emphasis on clinically relevant topics ...
Introduction to Human Anatomy
... فرح رزاق.م . Medial; nearer to the median plane . Lateral; away from the median plane These are terms used to describe the location of structures relative to the body as a whole or to other structures ...
... فرح رزاق.م . Medial; nearer to the median plane . Lateral; away from the median plane These are terms used to describe the location of structures relative to the body as a whole or to other structures ...
Part 8 - glenbrook s hs
... Its fluid cushions the suspended organs to prevent internal injury It enables internal organs to grow and move independently of the outer body wall; makes exercise not harmful to internal organs In soft-bodied animals (earthworms) it functions as a hydrostatic skeleton against which muscles can work ...
... Its fluid cushions the suspended organs to prevent internal injury It enables internal organs to grow and move independently of the outer body wall; makes exercise not harmful to internal organs In soft-bodied animals (earthworms) it functions as a hydrostatic skeleton against which muscles can work ...
Body System Organization Overview
... the human body? • Warm up: How many organ systems can you name in the human body? ...
... the human body? • Warm up: How many organ systems can you name in the human body? ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... Red blood cells: transport oxygen Nerve cell: have nerve fibers to transmit signals Root cell: found in plants that help absorb water from the soil Leaf guard cell: controls water loss ...
... Red blood cells: transport oxygen Nerve cell: have nerve fibers to transmit signals Root cell: found in plants that help absorb water from the soil Leaf guard cell: controls water loss ...
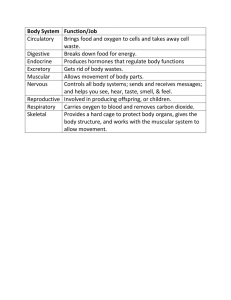
Body System chart - Issaquah Connect
... There are 600 muscles in our body The Gluteus Maximus is your largest muscle. ...
... There are 600 muscles in our body The Gluteus Maximus is your largest muscle. ...
Insecta
... structures that remove metabolic wastes from blood and return water to the cells • Exoskeleton—prevents water evaporation • Book Lungs—gas exchange without water loss (also used in respiration) ...
... structures that remove metabolic wastes from blood and return water to the cells • Exoskeleton—prevents water evaporation • Book Lungs—gas exchange without water loss (also used in respiration) ...
Common bile duct: On its way to 2nd part of duodenum. Therefore
... Despite its complexity, the human body is composed of only four basic types tissue. These tissues do not exist as isolated units, but rather in association one with Systematic Anatomy Gross another Regional and in variable proportions and combinations, Anatomy forming different organs and structure ...
... Despite its complexity, the human body is composed of only four basic types tissue. These tissues do not exist as isolated units, but rather in association one with Systematic Anatomy Gross another Regional and in variable proportions and combinations, Anatomy forming different organs and structure ...
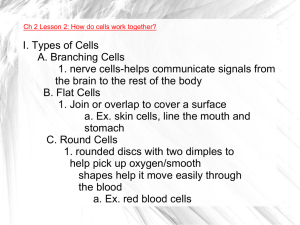
I. Types of Cells A. Branching Cells 1. nerve cells
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
the Animal kingdom
... part of its life There are only 2 groups of non- vertebrate chordates Lancelets Tunicates ...
... part of its life There are only 2 groups of non- vertebrate chordates Lancelets Tunicates ...
BODY SYSTEMS PP
... that work together. For example, the heart consists mainly of a specialized type of muscle tissue, which contracts rhythmically to provide the heart’s pumping action. But it also contains nervous tissue, which carries the electrical signals that bring about the contractions, and is lined with epithe ...
... that work together. For example, the heart consists mainly of a specialized type of muscle tissue, which contracts rhythmically to provide the heart’s pumping action. But it also contains nervous tissue, which carries the electrical signals that bring about the contractions, and is lined with epithe ...
Page 61
... Body Symmetry: bilateral with head end & tail end, left and right side Body Plan: long, narrow without legs – flat and soft as jelly Tissue/ organs/ organ systems: Respiratory & circulatory: not needed – body thin Nervous: interprets info and directs animals response Brain: knot of nerve tissue in h ...
... Body Symmetry: bilateral with head end & tail end, left and right side Body Plan: long, narrow without legs – flat and soft as jelly Tissue/ organs/ organ systems: Respiratory & circulatory: not needed – body thin Nervous: interprets info and directs animals response Brain: knot of nerve tissue in h ...
Intro to Zoology
... Not found in simple animals May aid in movement Fluid may act as a reservoir for nutrients and wastes, which diffuse into and out of the animal’s body ...
... Not found in simple animals May aid in movement Fluid may act as a reservoir for nutrients and wastes, which diffuse into and out of the animal’s body ...
The Human Body – Study Guide Part 1
... Explain the relationship between the 4 following things: Organs, cells, systems, tissue __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
... Explain the relationship between the 4 following things: Organs, cells, systems, tissue __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
BODY SYSTEMS - rivervaleschools.com
... Skeletal System Muscular System Digestive System Respiratory System Circulatory System Nervous System Urinary System ...
... Skeletal System Muscular System Digestive System Respiratory System Circulatory System Nervous System Urinary System ...
Science Chapter 5 Study Sheet
... When you hold your breath, hour brain sends a message to the diaphragm and rib muscles telling them to breathe. This message is sent to the brain when carbon dioxide builds up in the blood. ...
... When you hold your breath, hour brain sends a message to the diaphragm and rib muscles telling them to breathe. This message is sent to the brain when carbon dioxide builds up in the blood. ...
Chapter 29: Introduction to Invertebrates
... Parasitic flatworms are flukes (trematodes) and tapeworms (cestodes) Well-developed nerves and gastrovascular cavity are unnecessary ...
... Parasitic flatworms are flukes (trematodes) and tapeworms (cestodes) Well-developed nerves and gastrovascular cavity are unnecessary ...
Sponges & Cnidarians
... – Simplest animals, multicellular – No organs or body systems – Asymmetry – Cellular digestion – Feed by filtering water – Do not move – Reproduce sexually and asexually ...
... – Simplest animals, multicellular – No organs or body systems – Asymmetry – Cellular digestion – Feed by filtering water – Do not move – Reproduce sexually and asexually ...
Lecture Outline: ORGANISATION OF THE BODY
... and water) Anabolism: construction phase. Uses energy for producing chemical substances and parts for growth and repair. Homeostasis: The body's automatic tendency to maintain a relatively constant internal environment by regulating its temperature, blood pressure, ion concentrations in solution, pH ...
... and water) Anabolism: construction phase. Uses energy for producing chemical substances and parts for growth and repair. Homeostasis: The body's automatic tendency to maintain a relatively constant internal environment by regulating its temperature, blood pressure, ion concentrations in solution, pH ...
3 Phyla of Worms – Notes - Effingham County Schools
... B. Filarial worms cause__________________- fluid buildup that causes abnormally large limbs – transmitted through the bite of insects like mosquitos C. Ascarids cause __________________in humans, horses, cows, etc by filling the intestinal tract of its host and absorbing all nutrients D. Hookworms a ...
... B. Filarial worms cause__________________- fluid buildup that causes abnormally large limbs – transmitted through the bite of insects like mosquitos C. Ascarids cause __________________in humans, horses, cows, etc by filling the intestinal tract of its host and absorbing all nutrients D. Hookworms a ...
Kingdom Animalia Notes
... Has a top and bottom; no left or right Allows animals to detect and capture prey in any direction Developed from ectoderm and endoderm (2-layer body) Ex: jellyfish ...
... Has a top and bottom; no left or right Allows animals to detect and capture prey in any direction Developed from ectoderm and endoderm (2-layer body) Ex: jellyfish ...
INTRODUCTON
... In both ruminants and pigs, 2 digits normally support the weight of the body. In ruminants, the two non-weight supporting digits are vestigial and are called dewclaws. In horses, one digit supports the weight of the body. In dogs and cats, four digits support the weight of the body. The fifth digit ...
... In both ruminants and pigs, 2 digits normally support the weight of the body. In ruminants, the two non-weight supporting digits are vestigial and are called dewclaws. In horses, one digit supports the weight of the body. In dogs and cats, four digits support the weight of the body. The fifth digit ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.